1N4005 vs 1N4007 DIODE:What are the Differences?
If you're deliberating between 1N4005 and 1N4007 for your upcoming electronics endeavor, you're not alone. Both of these diodes come with their own set of advantages and drawbacks, making the decision-making process a bit challening. By comparing these two diodes, you can determine which one best suits your project's requirements. To obtain a thorough understanding of each diode, it's recommended to peruse our article comparing the 1N4005 and 1N4007 diodes. So, without further delay, let's dive in!
Overview of 1N4005
The 1N4005, belonging to the 1N400x series, is a versatile diode widely employed across various electronic devices for rectification tasks and additional functions like voltage blocking and boosting.
With the ability to withstand a reverse voltage of up to 600V and a continuous current of up to 1A, along with a surge peak of 30A, the 1N4005 demonstrates impressive performance characteristics. Its reverse current measures at 5µA.
1N4005 Pinout

1N4005 Typical Application
- 50/60 Hz Mains Rectification,
- Power Supplies,Polarity Protection Commercial / industrial grade Special grade available, see1N400xGP/-Q/-AQ1) Features
- VRRM Up to 2000V
- Compliant to RoHS (exemp.7a), REACH,Conflict Minerals ) Mechanical Data') Taped in ammo pack Weight approx. Case material
- Solder & assembly conditions
Typische Anwendung
50/60 Hz Netzgleichrichtung, Stromversorgungen,Verpolschutz
Standardausführung
Hohere Qualifizierung erhältlich,
siehe 1N400xGP/-Q/-AQ1)
Besonderheit
VRRM bis zu 2000V
Konform zu RoHS (Ausn.7a), REACH, Konfliktmineralien1)
Mechanische Daten') Gegurtet in Ammo-Pack
Gewicht ca. GehÃusematerial
Löt- und Einbaubedingungen
Overview of 1N4007
The 1N4007 functions as a PN junction rectifier diode, exclusively permitting the flow of electric current in a single direction. This attribute makes it well-suited for converting alternating current into direct current. Electrically compatible with other rectifier diodes, the 1N4007 serves as a versatile replacement within the 1N400X series.
With its wide range of applications in practical scenarios, the 1N4007 is utilized in various contexts, including freewheeling diode applications, general rectification in power supplies, inverters, converters, and beyond.
1N4007 Features
- Low forward voltage drop Low leakage current
- High forward surge capability Solder dip 260C,40 s
- Component compliant with RoHS 2002/95/EC and WEEE 2002/96/EC regulations.
- This is a Halogen Free Device
- All SMC parts are traceable to the wafer lot
- Additional testing can be offered upon request
1N4007 Mechanical Data
- Case:SOD-123FL molded plastic
- Terminals: Plated leads solderable per MIL-STD-750,Method 2026
- Polarity: Color band denotes cathode end Mounting Position:Any
- Weight:0.0007 ounce,0.02 grams
| Characteristic | Symbol | 1N 4001FL | 1N 4002FL | 1N 4003FL | 1N 4004FL | 1N 4005FL | 1N 4006FL | 1N 4007FL | Units |
| Marking code | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 | A7 | ||
| Maximum repetitive peak reverse voltage Maximum DC blocking voltage | VRRM VDC | 50 | 100 | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 | V |
| Maximum RMS voltage | VRRM | 35 | 70 | 140 | 280 | 420 | 560 | 700 | V |
| Maximum average forward rectified current@TA=75°℃ | 1(AV) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | A |
| Peak forward surge current 8.3ms single half sine- wave superimposed on rated load (JEDEC Method) | IFSM | 30.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | A |
| Maximum instantaneous forward voltage at 1.0A | VF | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | V |
| Maximum DC reverse current@TA=25C at rated DC blocking voltage @TA=100℃ | IR | 5.050.0 | 5.050.0 | 5.050.0 | 5.050.0 | 5.050.0 | 5.050.0 | 5.050.0 | μA |
| Typical Junction Capacitance (Note 1) | Cj | 15.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | pf |
| Typical Thermal Resistance (Note 2) | ReJA | 75.0 | 75.0 | 75.0 | 75.0 | 75.0 | 75.0 | 75.0 | C/W |
| Operating and Storage Temperature Range | TJ.TsTG | -65 to +150 | -65 to +150 | -65 to +150 | -65 to +150 | -65 to +150 | -65 to +150 | -65 to +150 | ℃ |
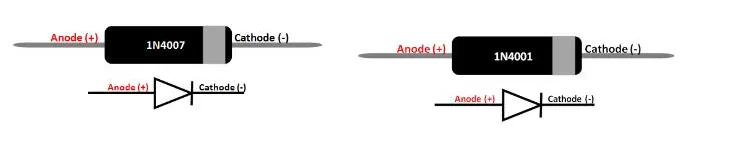
1N4001 VS 1N4007: Pin Configuration
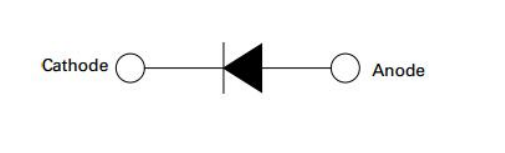
As depicted below, both the 1N4007 and 1N4001 diodes are equipped with two terminals: the anode and cathode, respectively. These terminals possess opposite electrical charges. The table below presents the names and charges associated with each terminal.
The 1N4007 and 1N4001 diodes are characterized by a cathode (-) and anode (+). In the schematic symbol, the cathode is denoted by the tip of the triangle with a line above it.
1N4005 CAD Model
Advantages of 1N4005:
- Economical design
- Minimal reverse leakage
- Reduced forward voltage drop
- Impressive current-handling capacity
- Exceptional surge current tolerance
Manufacturer of 1N4005
ON Semiconductor (Nasdaq: ON) is at the forefront of energy-efficient advancements, enabling customers to mitigate global energy consumption. The company provides an extensive range of energy-efficient power and signal management solutions, logic components, discrete devices, and tailored offerings to assist design engineers in overcoming their distinctive design obstacles across various sectors, including automotive, communications, computing, consumer electronics, industrial applications, LED lighting, medical technology, military/aerospace, and power supply sectors. ON Semiconductor manages a highly responsive and dependable supply chain, coupled with a top-notch quality assurance program, complemented by a network of manufacturing facilities, sales offices, and design centers strategically positioned across key markets in North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific regions.
FAQ
What is the 1N4005 diode?
The 1N4005 is part of the 1N400x series and is categorized as a general-purpose diode. It finds extensive application in electronic devices for rectification tasks and serves other functions such as voltage blocking and boosting.
How does the 1N4005 differ from the 1N4007?
The primary distinction lies in their reverse voltage capabilities: the 1N4005 can withstand up to 600 V, whereas the 1N4007 boasts a higher threshold of 1000 V.










