2N3904 vs 2N2222:What You Need to know
Transistors are common electronic components that play an important role in our daily lives. For example, they can be used in televisions, stereos, computers, mobile phones, and other devices. In these devices, transistors can be used as amplifiers, switches, and other circuits. 2n3904 vs 2n2222 are two common transistors with some differences between them. In this article, we will compare these two transistors and discuss how they differ.
Ⅰ. Introduction to 2n3904 vs 2n2222 transistors
1.1What is the 2N3904?
2N3904:Affordable and adaptable NPN bipolar transistor. It has a maximum collector current (Ic) of 200mA and a maximum collector-emitter voltage (VCEO) of 40V. This transistor consists of two layers of N-type material sandwiched between a layer of P-type material and is controlled by current. In a circuit, their voltage and current are biased in the same way, and both must receive a positive voltage to operate. This product can provide 30 hours of continuous power before needing to be recharged.
the imagine of 2N3904
1.2What is the 2N2222?
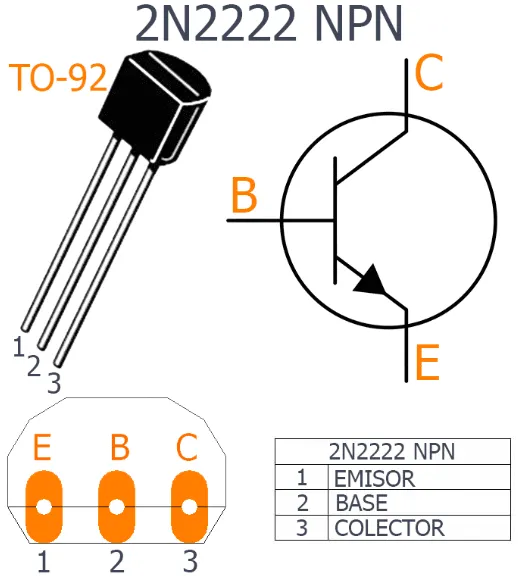
the imagine of 2N2222
2N2222:Also an NPN type bipolar transistor, but it can handle larger operating collector currents. It has a maximum collector current of 1A and a maximum collector-emitter voltage of 40V. Such products are often used in devices that require large amounts of power, such as digital cameras and high-tech LED flashlights. Just because it can handle more current than the 2N3904 doesn't necessarily mean it's the transistor you should use.
Ⅱ.Construction of 2n3904 vs 2n2222
The structures of 2n3904 vs 2n2222 both include three areas: emission area, base area and collector area. In an NPN transistor, the emitter region and collector region are both made of n-type semiconductor material, while the base region is made of p-type semiconductor material. When a forward bias voltage is applied to the emitter junction, electrons are injected from the emitter region into the base region, and then from the base region into the collector region. This forms a current amplifier.
3.1.Parameter differences between 2n3904 vs 2n2222
| parameter | 2N3904 | 2N2222 |
| Encapsulation | TO-92 | TO-92 |
| transistor type | NPN | PNP |
| Maximum collector current(IC) | 200mA | 800mA |
| Maximum collector-emitter voltage(VCE) | 40V | 40V |
| Maximum collector-base voltage(VCB) | 60V | 75V |
| Maximum emitter-base voltage(VBE) | 6V | 6V |
| Maximum collector dissipation(Pc) | 625mw | 625mw |
| maximum transition frequency(fT) | 300 MHz | 250MHz |
| Minimum and maximum DC current gain(hFE) | 100-300 | 35-300 |
Maximum storage, operating and junction temperature range Maximum storage temperature is -65°C to 150°C, maximum operating temperature is 150°C, maximum junction temperature is 150°C -55 to 150 degrees Celsius
3.1.Similarities between 2n3904 vs 2n2222
2n3904 vs 2n2222 are ordinary NPN transistors. Their working principle is to control the collector current by controlling the base current.
Ⅳ.2n3904 vs 2n2222:How to choose the right transistor
As mentioned above, the 2N3904 and 2N2222 are both Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs). This means that they are both controlled by the current applied to the base and provide current amplification at the collector-emitter end.
Since they are both NPN type BJTs, they consist of 2 layers of N material sandwiched by one layer of P material. This means that in a circuit, voltage and current bias them in exactly the same way - they both must receive a positive voltage to the base and collector terminals in order to operate.
In these respects, the 2N3904 and 2N2222 are identical. They can also handle the same amount of voltage from the collector to emitter terminals - both can handle voltages up to 40V.
The difference between them is that the 2N2222 can handle larger operating collector current. Collector current is the amplified current that flows from the emitter terminal to the collector terminal to supply power on the load that can be connected to the transistor. The 2N3904 can handle up to 200mA (milliamps) from the transmitter to the collector terminals. The 2N2222 can handle up to 5 times more as it can handle up to 1A (ampere) of current flowing from the emitter to the collector to power the load.
So, in this way, the 2N2222 does have an advantage as it can handle larger currents. However, it doesn't necessarily mean it's the transistor you should use. 200mA is still a lot of current and enough to power most electronic components. Typical components of transistors may be needed to drive motors, buzzers, solenoids, and high-power LEDs. These typically require much less than 200mA of current when powered. For example, motors typically require around 75mA to power up. This means that the 2N3904 is sufficient for these applications. However, if you want to power several of them, for example, you may need more current, i.e. from the 2N2222, up to 1A.
Therefore, the choice ultimately depends on how much current is required. If you need less than 200mA, a 2N3904 or 2N2222 will work. If you need more than 200mA but less than 1A, then the 2N2222 would be the one to use. If you need to output more than 1A, then Darlington transistors such as the TIP122 transistor can be used, which can handle up to 5A of amplified current. If you need more current, the TIP3055 can handle up to 15A.
But when you're dealing with electronics, unless you're into power electronics, you're pretty much stuck with things that never require such high amperage. These are indeed extreme conditions. Additionally, such high currents need to be used with caution as they are easily lethal and may result in death.
Usually a 2N3904 is sufficient for most circuits, but if you need more than 200mA then you should use a 2N2222 instead.
Ⅴ.Applications of 2n3904 vs 2n2222 transistors
The 2N2222A/PN2222 transistor is versatile and can be used in switching, amplification, RF applications, sensor and detector circuits, etc. The steps to use the 2N2222A/PN2222 transistor are the same as we would use any other BJT transistor. Some of the more common applications include:
1)Audio amplification
2)Audio preamplification
3) Switch applications
4)RF applications
5) Sensor circuit
6) Signal amplification
7) Darlington pair
The applications of 2N3904 NPN transistor mainly include the following aspects:
1) Used for driver modules such as LED drivers and relay drivers.
2) Used in amplifier modules such as signal amplifiers and audio amplifiers.
3) Voltages such as VBE and VCB are very high, so they can be used to control voltage loads up to 40V.
4) Can be used on TVs and other home appliances.
5) When it is used as a switch, it controls heavy loads due to high gain and low saturation voltage.
6) Due to its fast switching speed, this transistor can also be used in fast switching applications such as PWM (Pulse Width Modulation).
Ⅵ.FAQ
01 Can these transistors be recycled?
Transistors can be recycled, but recycling methods can vary depending on the type and material of the transistor. For example, the recycling of semiconductor materials requires complex, expensive, and polluting processes that often support exploitative and hazardous labor practices in developing countries. However, significant efforts have now been made to develop sustainable and efficient processes that can be used for various semiconductor devices. For example, silicon transistors used in solar panels can be recycled using physical recycling methods such as immersion in liquid nitrogen followed by pyrolysis and mechanical screening. In addition, recycling LEDs has become increasingly popular due to the critical raw materials they contain, such as gallium, indium and rare earth elements.
02 Are 2n3904 vs 2n2222 transistors interchangeable in circuits?
While both 2n3904 vs 2n2222 are NPN bipolar junction transistors, they have different characteristics and are not completely interchangeable in circuits.
03 What are the voltage ratings for 2n3904 vs 2n2222 transistors?
The voltage ratings for 2n3904 vs 2n2222 transistors depend on the manufacturer and specific model of the transistor. However, as a general rule, the maximum collector-emitter voltage (VCEO) for 2N3904 is around 40V, while for 2N2222 it is around 30V. It is important to note that these voltage ratings are not the only factors to consider when selecting a transistor for a particular application. Other factors such as maximum current rating, gain, and frequency response should also be taken into account.
04 What are the typical applications of 2N3904 transistor?
The 2N3904 transistor is a commonly used NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) in electronic circuits. It is a small signal transistor with a maximum current rating of 200 mA and a maximum voltage rating of 40 V.










