SMD Capacitor: Types, Characteristics & Applications
What Is an SMD Capacitor?
An SMD capacitor (Surface Mount Device capacitor) is a compact electronic component that stores and releases electrical energy, designed for direct mounting on PCB surfaces without through-hole leads. It supports automated assembly, saves board space, and offers excellent performance in filtering, coupling, and voltage stabilization. Due to its small size and reliability, the SMD capacitor is widely used in smartphones, IoT devices, automotive electronics, and communication systems, forming a vital part of modern electronic design.
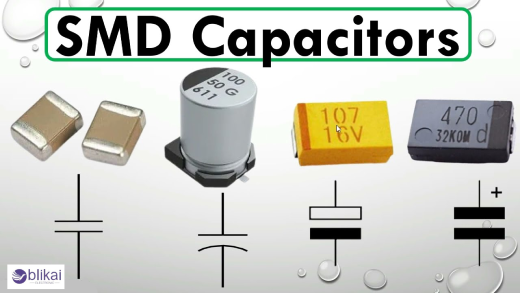
How Does an SMD Capacitor Work?
At its core, an SMD capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material (such as ceramic, tantalum oxide, or aluminum oxide). Upon applying a voltage, electrons pile up on the plate and are repelled off the other plate to form an electric field across the dielectric. This will enable the capacitor to store the electrical energy temporarily.
When the voltage supply goes down or the circuit needs power smoothing, the stored energy is returned to the circuit. This charge and discharge process is almost instantaneous, and capacitors are therefore useful in filtering, decoupling and timing.
SMD Capacitor Types
|
Type |
Full Name |
Polarity |
Key Features |
Common Applications |
|
MLCC |
Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor |
No |
Compact size, low ESR, high reliability, inexpensive |
Signal filtering, decoupling, timing circuits |
|
Tantalum |
Tantalum Electrolytic Capacitor |
Yes |
High capacitance per volume, stable over time, low leakage |
Smartphones, automotive ECUs, power circuits |
|
Aluminum |
Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor |
Yes |
Large capacitance, cost-effective, moderate ESR |
Power supplies, DC filtering, amplifiers |
|
Film |
Film Capacitor |
No |
High insulation resistance, excellent linearity |
Audio systems, timing and precision filters |
Additional Insight:
- MLCCs are the most common, used in over 70% of SMD capacitor applications. They are ideal for high-frequency and digital circuits.
- Tantalum capacitors are chosen when space is limited and high capacitance is needed.
- Film capacitors are less common in SMD form but are still used in specialized analog or high-precision circuits.
Key Characteristics and Specifications
SMD capacitors possess some of the most important features that determine their performance and their use in various applications. These can be summarised into major points as follows:
Capacitance and Voltage Rating
SMD capacitors range from fractions of a picofarad (pF) to hundreds of microfarads (μF). Voltage ratings typically span 4V to 100V, with specialized capacitors exceeding this for industrial and automotive applications. The voltage rating should be at least 1.5 times the circuit voltage to ensure reliability.
Tolerance
Tolerance indicates how close the actual capacitance is to the rated value, commonly ±1%, ±5%, ±10%, or ±20%. High-precision circuits, such as oscillators or timing networks, require tighter tolerances, while general decoupling circuits can use wider ranges.
Temperature Coefficient
Such classifications of EIA are NP0 (C0G), X7R, and Y5V, which describe the change in capacitance with temperature.
- NP0: Minimal change, ideal for precise timing and high-frequency applications.
- X7R: Moderate stability, suitable for decoupling and general-purpose use.
- Y5V: High capacitance density, but poor stability over temperature.
Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR)
ESR affects energy loss, heat generation, and filtering efficiency. Lower ESR capacitors are preferred in power supply filtering and high-speed circuits, while higher ESR may be acceptable in non-critical applications.
Frequency Response and Leakage Current
The performance of SMD capacitors in filtering, decoupling and signal integrity is determined by their performance at various frequencies and leakage current. Precision analog circuits are highly sensitive to leakage.
Common SMD Capacitor Package Sizes
SMD capacitors are available in standardized package codes. The length and width of the component are translated into code in the number of inches.
|
Package Code |
Dimensions (mm) |
Typical Capacitance Range |
Notes |
|
0402 |
1.0 × 0.5 |
Up to 0.1 μF |
Used in high-density mobile circuits |
|
0603 |
1.6 × 0.8 |
Up to 1 μF |
Common in consumer devices |
|
0805 |
2.0 × 1.25 |
Up to 10 μF |
General-purpose electronics |
|
1206 |
3.2 × 1.6 |
Up to 47 μF |
Power regulation circuits |
|
1210 / 1812 |
3.2 × 2.5 / 4.5 × 3.2 |
Up to 100 μF |
High-voltage or filtering applications |
A smaller package means that it has fewer capacitors to conduct, thus a smaller capacitance and lower voltage rating. Engineers often select the smallest size that still meets circuit requirements to save PCB space.
Applications of SMD Capacitors
SMD capacitors play multiple roles across electronic systems. They are so versatile that they cannot be done away with in almost any contemporary design.
Power Supply Filtering
In DC circuits, SMD capacitors serve as energy buffers that smooth voltage oscillations and sludge noise generated by switching controllers, ensuring stable power delivery. By storing and releasing charge fleetly, they suppress ripple and flash harpoons, perfecting circuit trustability and noise impunity. These capacitors are generally placed close to IC power pins or voltage controllers to minimize electromagnetic interference( EMI) and maintain harmonious voltage situations across sensitive electronic components.
Signal Coupling and Decoupling
SMD capacitors are demanded in electronic circuits to couple and uncouple signals and to insulate the AC and DC factors without loss of signal between circuit stages. When used as coupling capacitors, they block DC voltage and allow AC signals to pass through, precluding bias interference between amplifier stages. As capacitors, they stabilize power lines by absorbing flash harpoons and furnishing an original energy force near ICs, which helps reduce noise, voltage drops, and electromagnetic interference( EMI) in high-speed digital systems.
Timing and Oscillator Circuits
In timing and oscillator circuits, SMD capacitors work with resistors or chargers to determine time constants and oscillation frequentness. Their capability to charge and discharge at predictable rates allows them to define precise detainments and waveform characteristics. For stable timing performance, contrivers frequently elect NP0( C0G) ceramic capacitors, which offer minimum capacitance variation over temperature and voltage. Similar perfection makes SMD capacitors critical in timepieces, palpitation creators, microcontroller oscillators, and frequency pollutants, where thickness and low drift are essential.
Automotive and Industrial Electronics
In automotive and artificial systems, SMD capacitors are extensively used due to their high reliability, vibration resistance, and wide temperature range. They give noise repression, power stabilization, and flash voltage filtering in harsh surroundings similar to engine control units( ECUs), LED motorists, motor regulators, and communication modules. Automotive-grade MLCCs and tantalum capacitors are specifically designed to withstand temperature ranges up to 150 °C and mechanical stress, ensuring stable electrical performance under demanding operating conditions.
How to Identify and Read SMD Capacitor Markings
Most SMD capacitors do not carry printed values due to their tiny size. Identification is typically done through:
- PCB silkscreen labels (e.g., “C1”, “C45”)
- Manufacturer datasheets or BOM references
- Capacitance measurement tools like LCR meters
When in doubt, measuring directly is the most accurate method.
How to Select the Right SMD Capacitor
Step-by-Step Selection Process
Determine Required Capacitance and Voltage
Select the capacitance as per the circuit. The voltage rating should be at least 1.5 times the operating voltage, and tolerance and conditions should be taken into account to maintain stable operation.
Select the Dielectric Type
Choose the dielectric type based on circuit needs: NP0 (C0G) for high precision, X7R for general decoupling, or Y5V for high capacitance density, ensuring it fits performance and size requirements.
Match Package Size
Pick an SMD capacitor package that fits the PCB layout, balancing size, voltage rating, and capacitance, as smaller packages save space but may limit performance.
Consider ESR and Ripple Current
Check the ESR and ripple current rating, since low ESR reduces heat and improves efficiency in power and high-frequency circuits, while higher ESR may be acceptable for non-critical uses.
Evaluate Environmental Conditions
Account for temperature range, vibration, and mechanical stress to ensure reliable performance in automotive, industrial, or outdoor applications under harsh conditions.
Advantages of SMD Capacitors
- Compact and lightweight, perfect for high-density designs
- Automated assembly compatibility, saving labor and time
- Low ESR enhances efficiency in high-speed circuits
- Excellent vibration resistance for automotive and aerospace use
- Stable and reliable over long-term operation
Disadvantages of SMD Capacitors
- Difficult to handle manually during prototyping
- Limited capacitance range compared to large electrolytics
- Susceptible to mechanical cracking if PCBs are flexed
- Sensitive to soldering temperature, requiring precise reflow control
FAQ About SMD Capacitors
Why do MLCCs fail or crack?
Too much bending of PCB, vibration, or improper reflow profiles have the potential to crack ceramic layers and result in open circuits or short failures.
Are SMD capacitors suitable for RF or high-frequency circuits?
Absolutely. Low ESR and ESL (Equivalent Series Inductance) ceramic MLCCs have very impressive applications in RF, microwave and high-speed data.
Can I test SMD capacitors in-circuit?
Not accurately. It’s recommended to desolder at least one terminal to avoid interference from surrounding components.
What happens if you choose the wrong capacitor type?
Selecting an incorrect capacitor may cause noise instability, degraded signal integrity, or premature failure under voltage or temperature stress. Always review datasheets carefully.
Conclusion
SMD capacitors occupy a vital place in the contemporary electronic systems; their small size, high reliability and compatibility with automated assembly make this a standard component to the PCBs, which undertakes important roles such as filtering power circuits and stabilization of high frequency signals across a wide range of applications in communications, computers, automobile and industrial electronics and as technology advances to smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient designs the need to have high-capacity MLCCs and high-temperature automotive-grade capacitors will only increase.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.
What are Tantalum Capacitors?[All Explained]
What Does a Tantalum Capacitor Do
How to Calculate Coupling Capacitor Value
Different Capacitor Types: A Guide
What is a Bypass Capacitor & Why Do You Need One?
How to Test a Motor Capacitor
Installing a Dual Run Capacitor: What You Need to Know
What is a Ceramic Capacitor and How Does it Work?
What is an Audio Capacitor and Why Does it Matter?
What is a C65R Capacitor? A Beginner's Guide










