How do A4988 and DRV8825 vary from one another?
Compared to the A4988, the DRV8825 has a larger outside force voltage( 45V as opposed to 35V), which enables safe operation at advanced voltages while lowering the threat of damage from LC voltage harpoons. The features, operations, and distinctions between A4988 and DRV8825 will be covered in this composition.

Description of the DRV8825
The DRV8825 offers integrated motor driver solutions for printers, scanners, and other automation equipment applications. The device features two H-bridge drivers and a micro-stepping indexer designed to drive bipolar stepper motors. The output driver module utilizes an N-channel power MOSFET arranged in an all-H-bridge configuration to control the motor windings. The DRV8825 is capable of driving up to 2.5 A of current from each output with proper heat dissipation, at 24 V and 25°C.
The simple STEP/DIR interface makes it easy to connect to the controller circuits. The mode pin allows the motor to be configured for full stepping to 1/32 step mode. The decay mode is configurable, so you can use slow, fast, or mixed decay. The device offers a low-power sleep mode that shuts down internal circuitry
Achieve very low quiescent current consumption. The sleep mode can be configured by utilizing a specific nSLEEP pin.
Internal shutdown function is provided for overcurrent, short-circuit, under-voltage lockout, and over-temperature. Fault conditions are indicated via the nFAULT pin.
Short Overview of the A4988
The A4988 is a complete micro-speed motor drive with a built-in translator for easy operation. It is designed to operate all-polar, half-step, quarter, one-eight, and bipolar step engines in sixteen-step mode with an output drive capacity of up to 35 V and ± 2 A. The A4988 includes a fixed shutdown time current that can operate in a slow or mixed state. The A4988 converter simplifies the implementation of the A4988 by making it easy to input pulse motor signals through the STEP input. It does not require timing tables, high-frequency control lines, or complex programming interfaces, making it ideal for applications without access to or overwhelmed by complex microprocessors. The A4988 interface automatically selects the current decay mode - slow or mixed - during step-by-step operation through its built-in cut wave control.In hybrid decay mode, the device is initially set to rapidly decay a portion of the fixed off time, and then slowly decay the remaining off-time. The outcome is a hybrid attenuation current control that diminishes motor noise that is audible, enhances step accuracy, and lowers power consumption.
Comparison between A4988 and DRV8825 characteristics
Features of the A4988
▪ Low Rds(on) output
▪ Automatic current decay mode detection/selection
▪ Mixed and slow current decay modes
▪ Synchronous rectification for low power consumption
▪ Internal UVLO
▪ Cross-current protection
▪ 3.3 and 5 V compatible logic supplies
▪ Thermal shutdown circuitry
▪ Ground short circuit protection
▪ Load short-circuit protection
▪ Five selectable stepping modes: full step, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, and 1/16
Features of the DRV8825
• PWM Microstepping Motor Driver
– Built-in micro stepping indexer
– Up to 1/32 micro-stepping
• Multiple attenuation modes
– Mixed decay
– Slow decay
– Fast decay
• 8.2V to 45V operating supply voltage range
• Maximum drive current of 2.5A at 24V and T A = 25°C
• Simple STEP/DIR interface
• Low current sleep mode
• Built-in 3.3V reference output
• Small package and footprint
• Protection Characteristics
– Overcurrent Protection (OCP)
– Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
– Virtual Machine Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
– Fault Status Indication Pin (nFAULT)
Block Diagram of A4988 VS DRV8825
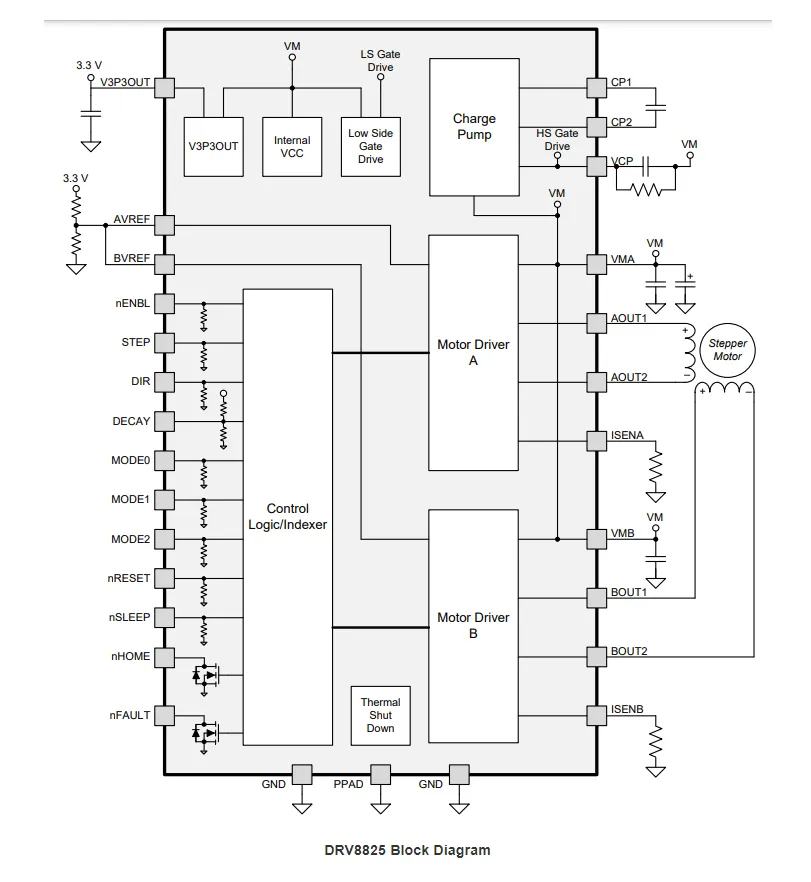
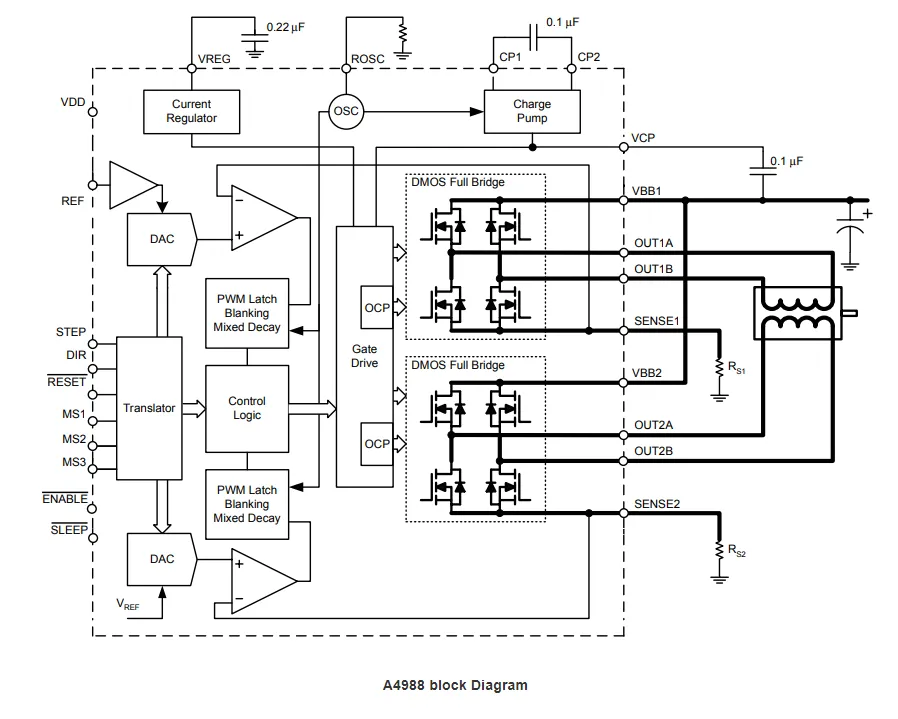
Applications of A4988 VS DRV8825
A4988 Applications
• Robotics
• 3D Printing
• CNC Machining
• Textile Machinery
• Medical Equipment
• Educational and Hobbyist Projects
• Security Camera and Gimbal Mechanism
DRV8825 applications
• Robotics
• Printers
• Scanners
• Gaming Machines
• Factory Automation
• Currency Processors
• Automatic Teller Machine
• Video Surveillance Cameras
• Office Automation Machines
Comparison Table of A4988 with DRV8825
|
Features |
DRV8825 |
A4988 |
|
Microstepping Levels |
1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32 |
1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16 |
|
Maximum Current |
Up to 2.5A |
Up to 2A |
|
Voltage Range |
8.2V to 45V |
8V to 35V |
|
Typical Rs value |
0.1 Ohm |
0.05 Ohm or 0.1 Ohm or 0.2 Ohm |
|
Step Pulse Timing |
Adjustable |
Fixed |
|
Applications |
Robotics, Printers, Scanners, Factory Automation, ect. |
Robotics,3D Printing,CNC Machining,Textile Machinery,etc. |
|
Cost |
Generally higher |
Generally lower |
|
IC packaging |
9.7x6.4mm 28HTSSOP |
5x5mm 28-lead QFN |
FAQ
What is the main Difference Between A4988 and DRV8825?
DRV8825 offers advanced step resolution(1/32 steps vs 1/16th step of the A4988) and has a lower RDS(on-resistance) for advanced effectiveness and lower heat generation. In addition, the working voltage range of the DRV8825 is lesser(8.2 V to 45V vs. 8V to 35V for the A4988). The A4988 is espoused in a QFN package, while the DRV8825 is espoused in an HTSSOP package. The QFN package is smaller than the HTSSOP package, but it's also more difficult to sell.
DRV8825 vs A4988: Which One Should I Choose?
Generally speaking, DRV8825 is more precious than A4988. This is a result of the DRV8825's better features and performance. However, the A4988 might be a name option. If you're someone who appreciates trustability and affordability together. On the other hand, individuals who need sophisticated features, meticulous accuracy, and the subtly peaceful characteristics of StealthChop would consider the DRV8825 to be an absolute model.
FAQs about DRV8825 vs A4988
1.What are the DRV8825 and A4988?
DRV8825 and A4988 are commonly used stepper motor driver ICs in robotics, CNC machines, 3D printers, and motion control applications, regulating the current and direction of the motor.
2. Which driver should I choose for my operation?
DRV8825 Opt for DRV8825 if you need advanced micro stepping resolution, need to drive stepper motors with advanced current conditions, or prioritize overcurrent protection and thermal effectiveness. A4988 Choose A4988 if you are looking for a cost-effective result with standard micro-stepping capabilities and moderate current conditions. It's suitable for numerous common stepper motor operations and offers a good balance between performance and affordability.
3. Where can I find more information about DRV8825 and A4988?
Relate to the datasheets handed out by the manufacturers(analogous to Texas Instruments for DRV8825 and Allegro Microsystems for A4988) for detailed technical specifications, operation notes, and operation guidelines. Also, online forums, community coffers, and manufacturer websites can offer precious perceptivity and support for using these stepper motor motorists effectively in your systems.
Final Verdict
Several crucial factors must be taken into consideration when comparing the stepper motor motorist modules of the DRV8825 and A4988. In comparison to the A4988, the DRV8825 has advanced current capabilities, fine micro-stepping options, and better thermal operation. This makes it suitable for operations that bear further necklace and smoother stir control, albeit at a slightly advanced cost. On the other hand, the A4988 is a more affordable option that still performs well enough for numerous operations, especially those with lower current conditions. In the end, the choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the operation, balancing factors similar to necklace conditions, delicacy, cost, and thermal considerations. Both drives have their strengths and are used in a wide variety of systems, furnishing masterminds and suckers with a variety of options for effectively driving stepper motors.










