Top Embedded Computer Solutions: Components, Advantages & Applications
Introduction
The central component of the contemporary electronic system lies in embedded computer solutions that drive all industrial automation as well as intelligent consumer devices. Embedded computers, unlike their traditional counterparts, are created to suit a particular purpose and execute it efficiently, usually with a very tight power and space budget. As IoT, robotics, automotive technology, and industrial control systems continue to grow at an impressive rate, the need to have quality embedded computing solutions has never been higher. Knowing the elements, benefits and uses of embedded computers can assist companies and developers in selecting the ideal solutions to their projects.
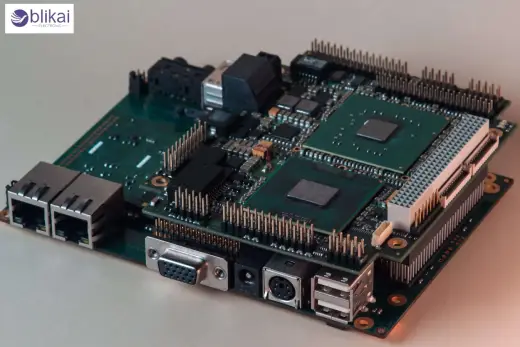
What is an Embedded Computer?
An embedded computer is a specific computer system that is designed to execute specific tasks within a larger machine or system. In contrast to general-purpose computers, which are designed to do many things, embedded systems are designed to be efficient, reliable, and real-time. Typical examples are systems based on microcontrollers, such as Arduino boards, single-board computers, such as Raspberry Pi, and factory industrial controllers.
Embedded computers are also often found in devices that require a computer to process sensor information, activate a motor, or communicate over a network. They are generally low-power consumption, small-scale, and software-hardware integrated, and are well adapted to IoT devices, car electronics, and medical devices.
Key Components of Embedded Computers
Microprocessors and Microcontrollers
The brain of the embedded system is the microprocessor or microcontroller. Microprocessors are generally applied in high-performance applications that require more complex computations, whereas microcontrollers are applied to simple, task-specific operations with memory and I/O peripherals built into them. These elements define the processing speed, processing efficiency and processing capabilities of the embedded computer.
Memory Units
Embedded computers have memory with RAM as temporary storage of data, ROM or flash memory as permanent storage of programs, and occasionally EEPROM as user-configurable storage. The type and size of memory used to support the data will serve as a guarantee of fast data access, consistent performance and enough storage capacity to support firmware and applications.
Input/Output Interfaces
Embedded computers can communicate with the external world via I/O interfaces. These are sensors, actuators, communication ports such as UART, SPI, I2C, USB and Ethernet. I/O interfaces should be designed properly to achieve the necessary data collection, device control and linkage to other systems.
Power Supply and Circuit Boards
Embedded systems require the use of a steady power source and a good PCB design to achieve reliable system performance. Designed low power consumption, voltage regulation and thermal control systems provide both durability and stability of operation, particularly in industrial or portable use.
Specialized Components
Certain embedded computers incorporate specialised hardware like GPUs to do graphics processing, FPGAs to provide hardware customisation, or AI accelerators to do edge computing. The components are optimized to deliver performance on complex tasks such as machine vision, AI inference, or real-time signal processing.
Advantages of Embedded Computer Solutions
Compact and Efficient Design
Embedded computers are designed to be small and energy efficient. They can fit in small machines, such as drones, wearable electronics, or small machines used in industries, due to their small sizes.
Real-Time Performance
The majority of embedded systems will have to be real-time. They can be predicted to be processed and responded to in real time, a property that is vital in robotics, automotive safety systems and industrial automation.
Reliability and Stability
Embedded systems are also created in a way that allows them to have a long, useful life. They can even operate 24 hours a day, which general-purpose computers cannot, and can be used in very hot, high-vibration, or coarse factory environments.
Cost-Effectiveness
Task-specific applications may require general-purpose computing solutions, but then tend to be more expensive compared to embedded computers. They are low-maintenance and very efficient in their operation over the long run, making them an economically smart business choice.
Scalability and Customization
Task-specific computing applications often use embedded computers that are cheaper than general-purpose computing solutions. They represent an economically intelligent option to businesses because of their long-term cost efficiency in operations and low maintenance.
Applications Across Industries
Industrial Automation
Embedded computers are widely used in PLCs, robotic arms, factory monitoring systems, and industrial controllers. They provide real-time data processing, control precision, and reliability required for automated manufacturing processes.
IoT Devices
Embedded systems are one of the cornerstones of IoT applications. Embedded computers are used to efficiently collect, process and transmit data in smart home appliances, wearable devices, environmental sensors, and connected industrial equipment.
Automotive Industry
Contemporary cars include built in infotainment, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems, engine control unit, and self driving capabilities in the form of embedded systems. The in-board solutions are safe, more connected and more performance.
Healthcare
Medical implantations like patient monitors, imaging, diagnostic equipment and portable health devices heavily rely on embedded computers. They are accurate, reliable and real-time processors of data in medical settings.
Consumer Electronics
Consumer electronics such as smart televisions, game consoles, home automation stations and portable media players also contain embedded systems. They are intelligent, user-friendly and responsive through their integration.
Future Trends in Embedded Computing
AI and Edge Computing Integration
Embedded systems are also beginning to add AI accelerators to execute complex functions at the edge to minimise bandwidth and latency. This trend is smart cameras, autonomous robots, and predictive maintenance systems.
Energy-Efficient Embedded Systems
As the world seeks to move towards sustainability, energy-efficient embedded systems are becoming significant. Energy harvesting, low-power processors and design of optimized firmware can all contribute to making electronics greener.
IoT and 5 G-Enabled Solutions
The 5G technology has enabled embedded systems to exchange messages with each other in a more reliable and faster way. Another important factor in real time IoT, smart cities, and connected cars is high-speed data communications and low latency.
Miniaturization and Wearable Technology
Embedded computers are getting smaller, lighter and more powerful. Small-scale solutions can now support complicated applications in wearable computers, unmanned aerial vehicles, and other compact medical devices.
Conclusion
Embedded computer solutions are the foundation of modern electronic systems and are highly efficient, reliable and versatile. Their understanding of their components, advantages and applications will allow businesses and developers to select the most suitable systems that can meet their needs. Embedded systems continue to transform the world by influencing every industry within any sector, including industrial automation, the Internet of Things, automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics. The embedded computer solution is chosen accordingly to attain high functionality, low costs and sustainable and innovative integration of technology.
FAQ
What is an embedded computer?
A dedicated computer hardware installed within a high-level device, such as IoT devices, industrial controllers and medical devices.
How does an embedded computer differ from a regular computer?
Embedded computers, as opposed to general-purpose computers, are designed to be efficient, work in real-time, and reliable, and may be very small and low-power.
What are the main components of an embedded computer?
Microprocessors or microcontrollers, memory (RAM, ROM, Flash), I/O interface (sensors, actuators, communication ports), power supply, and, in some cases, special-purpose units such as GPUs or FPGAs are all vital parts.
What are the advantages of using embedded computer solutions?
Embedded computers are small, real time, very reliable, cost effective, and scaled to industry applications.
Where are embedded computers commonly used?
They could be applied in industrial automation, Internet of Things, auto systems, medical devices, consumer electronics and wearable devices.
How is AI integrated into embedded systems?
Embedded systems can also process data locally on AI accelerators and edge computing to make real-time decisions in real-world scenarios, such as smart cameras, robotics, predictive maintenance, and more.
What are future trends in embedded computing?
Such trends are energy-efficient design, IoT and 5G connection, artificial intelligence, minimization, and the use of wearables.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.










