Flexible Flat Cable(FFC) Connector Guide: Types, Specs & Applications
Introduction
Flexible Flat Cable connectors are critical elements in the new world of electronics, allowing the ability to compress with small size and reliability in ferrying signals amongst circuit boards and devices. Their thinness and the ability to flex easily make them suited to applications where they have to conform to space limitations such as laptops, smartphones, cameras and automotive displays. This primer brings you up to date on everything there is to know about FFC connectors, including types and FFC connector key specifications, advantages and practical uses. This book on selecting and using FFC connectors contains all the information you would ever need, regardless of your profession.
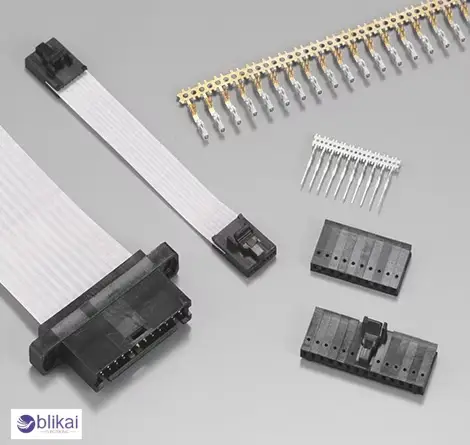
What is an FFC Connector?
An FFC connector is a connector that was specifically designed to connect with a flat flexible cable (FFC) and printed circuit board (PCB) or other device. As opposed to conventional ribbon cables, the FFCs have a thinner and judgmental nature that enables them to fit into narrow gaps. The FC connectors effectively and easily insert into pre-designed receptacles, maintaining a secure connection, and signal loss is reduced.
FFC vs FPC Connector
Even though FFC (Flexible Flat Cable) and FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) connectors are frequently mixed up, they do not really differ in their connector construction per se, only in cable structure. FCs are flat with ribbon-like wiring, whereas FPCs have etched copper strips that are flexible. The appropriate type is selected in order to provide the necessary electrical characteristics and mechanical stability.
Types of FFC Connectors
1. Based on Mounting Style
Surface Mount (SMT): Connectors constructed by being soldered directly to the surface of the PCB. SMT may be used in automation applications and is well-suited where size is a priority.
Through-Hole (THT): Connectors made by inserting through holes and soldering to PCBs, and more space consumption with better mechanical stability.
2. Based on Cable Orientation
ZIF (Zero Insertion Force): Lets the cable slide in without force a locking mechanism holds it in place. Suitable when one does frequent assembly and disassembly.
Non-ZIF: Requires slight pressure to insert the cable, often cheaper but less convenient.
Orientation: Vertical (straight) vs Right-Angle, depending on board layout and cable routing.
3. Based on Pitch
Common pitches include 0.5mm, 1.0mm, 1.25mm, and others. Pitch refers to the distance between contacts and is critical for signal integrity.
Comparison Table: FFC Connector Types
|
Type |
Mounting |
Orientation |
Pitch (mm) |
Typical Use |
|
SMT ZIF |
Surface Mount |
Vertical |
0.5, 1.0, 1.25 |
Smartphones, cameras |
|
SMT Non-ZIF |
Surface Mount |
Right-Angle |
1.0, 1.25 |
Laptops, tablets |
|
THT ZIF |
Through-Hole |
Vertical |
1.0 |
Industrial equipment |
|
THT Non-ZIF |
Through-Hole |
Right-Angle |
1.25 |
Automotive dashboards |
Key Specifications of FFC Connectors
Pitch
- Determines the spacing between each contact.
- Standard sizes: 0.5mm, 1.0mm, 1.25mm.
- Smaller pitches allow more compact connections but require precision handling.
Current and Voltage Rating
Common FFC connectors can have a supply current rating of 0.5-1.0A and a maximum of 50V regardless of design and use.
Temperature Range
Their current operating ranges go to -40 o C and up to 105 o C, which makes them applicable to consumer electronics and automobiles.
Number of Contacts / Pin Count
May have between 2 pins and up to 80 pins or more, depending on the signal requirements.
Durability / Insertion Cycles
ZIF connectors will perform 100- 500 insertion-removal cycles reliably, which makes the connectors ideal when used on a maintenance or high-use basis.
Advantages of Using FFC Connectors
Compact and Lightweight Design
FC connectors are both small and lightweight, making them perfectly suited to high-density modern electronics applications. They are small, making the systems designed by engineers have a thinner dimension. This can be especially useful in laptops and smartphones, cameras and other wearable devices where space is at a premium.
High Flexibility
The plasticity of FFCconnectors enables them to be bent and folded without breaking the conducting members inside them. This has the benefit of making them a good candidate to be used where routing or frequent movement are requisite, e.g., robotic arms, foldable displays, and automobile control systems.
Easy Assembly and Maintenance
Zero Insertion Force (ZIF) FFC connectors include a cable insertion process that is quick enough and effortless to reduce the assembly time and risk of contact destruction. Although Non-ZIF connectors need a little pressure to put in, they are also easy to install. Both of them make it easier to maintain and replace components, as well as save time in both manufacturing and repair.
Reliable Signal Transmission
Thipwun FC connectors achieve a good electrical connection between the cable and the PCB, and stable and accurate transmission of signals. This minimizes cross-talk, signal losses and interference and thus, they are perfect in high-speed data and sensitive analog applications like cameras, displays and medical devices.
Cost-Effective Solution
FC connectors are made of the least material and are much easier to assemble by use of a simple system than traditional wiring. The combination of this cost-effectiveness, with their reliability and smallness, therefore makes them a common feature in consumer electronics, automotive, industrial, and medical devices.
Versatility Across Applications
FC connectors find use in many areas and can be applied to a broad range of devices in the areas of consumer electronics, automotive, industrial, medical, and telecommunications systems. They are flexible and thus make a long-term investment in small and large-scale electronic designs.
Common Applications of FFC Connectors
Consumer Electronics
FC connectors can be found across many consumer electronics applications, including laptops, smartphones, tablets, cameras, and wearable devices. They interconnect the displays, keyboards, touch screens, and internal modules. Their working in a thin, flexible form also allows it to form low detail profiles without affecting the quality of signal relay needed by high-resolution displays and miniaturized gadgets.
Automotive Electronics
The use of FFC connectors can be found within automotive systems where they are responsible for dashboard displays, infotainment, navigation systems and sensor modules. They are so flexible that they can fit into all other tight spaces behind a panel and can resist vibration, changes in temperature, and long-term mechanical stress, another reason why they are perfectly suited to vehicle electronics.
Industrial Equipment
The industrial fields of application are robotics, automated systems, and control panels. FC connectors enable a smaller wiring design, and flexible cables can be easily routed over moving parts in the machine. They are reliable to provide continuous operation and lessen maintenance time, which is important in high-performance industrial environments.
Medical Devices
The FFC connectors are common in portable diagnostic equipment, diagnostic imaging systems and in monitoring device applications. These connectors make it possible to transmit signals accurately and have small form factors required in portable and wearable medical equipment. They also add to the reliability and accuracy of sensitive measurements in health service applications.
Telecommunications and Networking
They are connectors in the form of FC in networking equipment like a router, switch and a communication module. They allow a secure connection to internal components, enabling a fast information transfer with little signal loss. They are flexible so that they can be arranged into compact network devices efficiently.
Other Emerging Applications
The number of FC connectors used in aircraft, smart home and IoT products, drones, and other newer technologies is also growing. These are portable and less cumbersome architectures, thus making them adaptable to gadgets where space saving and stable connection are significant.
How to Choose the Right FFC Connector
Match Pitch and Pin Count: Ensure compatibility with the FFC cable.
Select Orientation and Mounting Style: Based on PCB layout and mechanical requirements.
Check Electrical Ratings: Voltage, current, and temperature specifications.
Consider Durability: For devices requiring frequent maintenance or replacement.
Installation Tips and Best Practices
1. Take great care at connecting to handle connectors so that contacts are not forced.
2. Stack and align cables, particularly in ZIF cables.
3. Do not layer the cable in a position much below the minimum bend radius
4. Work around sensitive electronics with anti-static precautions.
Conclusion
FC connectors are compact, versatile and dependable connectivity tools in contemporary electronic designs. Knowledge of types, specifications, and applications allows engineers and designers to make the most suitable connector choice in their applications. Serving the consumer electronics industry as well as the automotive industry, FFC connectors are high-performance connectors that provide efficient signal transmission and space-saving system connectivity. Selecting an appropriate FFC connector and installing the connector properly is the best way to ensure optimum device performance and long life.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.
Types of Computer Cables: Everything You Need to Know
Monitor Cable Types: A Complete Guide (2025)
Monitor Cables: Types, Applications & Advantages
RJ45 Cables: A Guide to Ethernet Connectivity
Network Cable Connectors: Types, and Applications
D-Sub Cables: Types, Applications & Advantages
Modular Cables: Types, Advantages & Applications
What is Firewire Cables? All Explained
The Power of RG11 Coaxial Cable: Advantages and Applications
Varieties of Monitor Cables: A Beginner's Guide










