What is a 2N3904 Transistor & How Does it Work?
Introduction to the 2N3904 Transistor
The 2N3904 is a handy NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT), mainly employed as the low-power low-voltage electronics. Its versatility makes it an engineer's delight for employing in switching as well as amplification tasks. It can drive light current loads, typically no more than 200mA, with a steady-state voltage of about 40V.
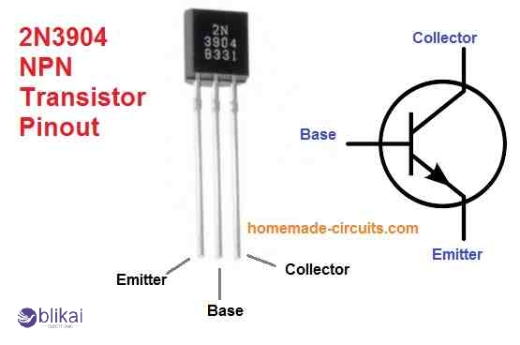
2N3904 Transistor Physical Characteristics
Package Types
The TO-92 package, which is a small three-pin plastic casing, is a standard casing for the 2N3904. Its small size makes it suitable for confined spaces and makes it easy to mount on crowded circuit boards. It is a compact car in the transistor world, efficient and as cramped as possible!
Pin Configuration
Pin configuration refers to the leads of the transistor-its emitter, base, and collector. When the transistor's flat surface is facing you, the configuration is the emitter, base, and collector from left to right. Just remember this order for the convenience of your circuit installation.
2N3904 Transistor Electrical Specifications
Maximum Ratings
Every superhero has its limit, and so does the 2N3904. It has a maximum collector-emitter voltage of 40V and a maximum collector current of 200mA. Remember these ratings so that you do not damage the transistor or mess up your circuits.
Key Parameters
Some critical parameters of the 2N3904 include current gain (hFE) from 100 to 300 and transition frequency, which is near 300 MHz. Such features enable growth in low-power applications.
How Does a 2N3904 Transistor Work?
Basic Principles of Transistor Operation
Now, into the core: how does this little gem work? A transistor is a small valve that controls the flow of electricity. It amplifies or switches electronic signals and electrical power.
NPN Configuration
The 2N3904 is a standard NPN transistor, meaning that, in its case, there are two N-type semiconductor regions separated by a P-type region. Imagine this as a sandwich; its "label" tells us that this transistor is of the NPN type in essence. It consists of two pieces of "negative" bread but has a "positive" filling in the middle.
Current Amplification
Here is where the magic happens. Placing a small current on the base of the transistor allows a much larger current to pass between the collector and emitter. Water can control a larger river-think of how neat it is.
Applications of the 2N3904 Transistor
Signal Amplification
The 2N3904 transistor usually finds application in low-power signal amplification circuits, which are to phase out weak electrical signals-like audio or radio frequency so that they become strong enough for further processing or transmission. The device is characterized by a high current gain, which makes it applicable in situations wherein a small input signal ought to be amplified for use in audio equipment or radio communications.
Switching Circuits
The reliable switch, i.e., 2N3904, permits higher-power components to be controlled in response to a small input current; that means motors relay other actuators-even controlling lights. So it can be an essential part of many control systems where it can turn on or off, say, large devices, yielding a practical low-power control circuit to interface with something high power.
Digital Logic Circuits
The 2N3904 is extensively used in the design of simple NOT, AND, and OR gates that form the basic building blocks of digital systems. For this reason, the 2N3904 transistor is part and parcel of a switching function permitting the processing of binary signals, importantly applied in designing combinational logic circuits as far apart as microcontrollers to highly sophisticated computational devices.
Oscillators
The 2N3904 can achieve the construction of low-frequency oscillators for generating periodic signals for any of its wide-ranging applications, such as clock generation in digital systems and tone generation in audio circuits. These oscillators create periodic waveforms that, by virtue of being stable, find use in timing and signal modulation in a wide variety of electronic devices.
Amplifiers in Audio Systems
When applied to audio amplifiers, this component is commonly located in the input or pre-amplifier stages, where it takes very weak audio signals from microphones or their sources and amplifies so that they are able to sufficiently drive other stages until they can deliver their full sound power into loudspeakers guaranteeing high sound quality, volume, and clarity without distortion.
Light Dimmer Circuits
As in this, the transistor controls how supply voltage, modulated with short pulses, reaches the electric motor while rapidly switching the current for the next period. In general, the amount of time that the voltage is on is the duty cycle, which primarily defines speed on this version of electric motors. Examples of operations include robotics, automation, and fan control systems.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) for Motor Control
In PWM circuits, which are very important for controlling the rotational speed of DC motors, the most commonly used transistor is the 2N3904. This transistor turns the current on and off, so by changing the duty cycle of the voltage fed to the motor, it modulates the average voltage supplied to the motor. This allows speed control of motors without generating too much heat and enables efficiency in Robotics, Automation, and Fan Control Systems.
Signal Conditioning in Sensors
In sensor applications, logging circuits implement the 2N3904 using signal conditioning to modify, amplify or invert sensor output signals. For instance, when dealing with sensors producing weak or noisy signals, the 2N3904 may be used to boost the signal to efficient levels or filter out unwanted noise to make the signal fit for subsequent processing within a microcontroller or other signal processing configuration.
Current Sensing and Feedback
The 2N3904 can also sense the current and provide feedback to an ongoing system state in current-sensing circuits. The feedback loop incorporating the transistor can be used to monitor and adjust the current in power supply circuits and prevent the overcurrent state of operation in battery chargers, power management systems, or motor drivers.
Switching Regulator Circuits
It is widely used in switching regulator circuits like buck or boost converters, where it has the main job of controlling the flow of current that drives the output voltage. Such circuits on-and-off the transistor at high frequencies to efficiently assess the control, sometimes increased, sometimes decreased, of the voltage levels with very little power loss, making 2N3904 a hugely suitable starting point in designs of power supplies for portable devices, communication other equipment and energy-efficient systems.
Advantages of Using 2N3904 Transistors
- Low Cost: 2N3904 is inexpensive. Hence, it has found its way into educational kits, DIY projects by hobbyists, and low-cost consumer electronics.
- Good Frequency Response: Its transition frequency is approximately 250 MHz, making it suitable for slight signal amplification, RF circuits, or audio applications.
- Compact Size: The most common transistors in use are compact ones, packaged within the TO-92 form factor, which makes them easy to implement in compact designs.
- Moderate Current Handling: The maximum collector current for a 2N3904 transistor is 200 milli amps and, therefore, can be readily employed in several general-purpose switching and amplification applications.
- High Gain: With an amplification factor (hFE) of producing gain from about 100 to 300, depending on the exact type of transistor, that can powerfully amplify weak signals.
- Low Power Consumption: It fits low-power applications, which are particularly suitable for portable devices or closed-circuit designs with tight power demands.
- Widely Available: The fact that it is such a common and used component should be enough to allow easy application, as it was designed for it, not to mention having widespread support in its design.
- Versatile Applications: These can go in switching circuits, amplifiers, signal processing, and digital logic circuits, among other applications.
Tips for Working with 2N3904 Transistors
1. Always check the datasheet for exact specifications.
2. Use heat sinks if you're pushing the transistor close to its limits.
3. Be careful with static electricity - these little guys are sensitive!
4. Practice proper soldering techniques to avoid damaging the transistor.
Related Articles
2N3904 vs 2N2222:What You Need to know










