What is the BC547 Transistor? Its Features & Applications
The BC547 NPN bipolar junction transistor( BJT) is largely recognized and considerably employed for its versatility in different electronic circuits. This article aims to give a comprehensive understanding of the BC547, covering its features, uses, and functional attributes.

Product Information
Blikai Part Number: 276-BC547
Manufacturer: Onsemi
Package: Bulk
Description: TRANS NPN 45V 0.1A TO92-3
Datasheet: PDF datasheet
Brief Description of BC547
The BC547 NPN transistor is highly versatile and reliable, offering an approximate maximum collector current of 100 mA and a collector-emitter voltage rating of around 45 volts. Its widespread application in electronic circuits includes signal processing, amplification, switching, and voltage regulation. Its moderate current and voltage attributes make it applicable for a range of low- to medium-power circuit applications.Enclosed in a compact TO-92 package, the BC547 is consistent with a different range of operational situations, which contributes to its popularity among both specialists and professionals.
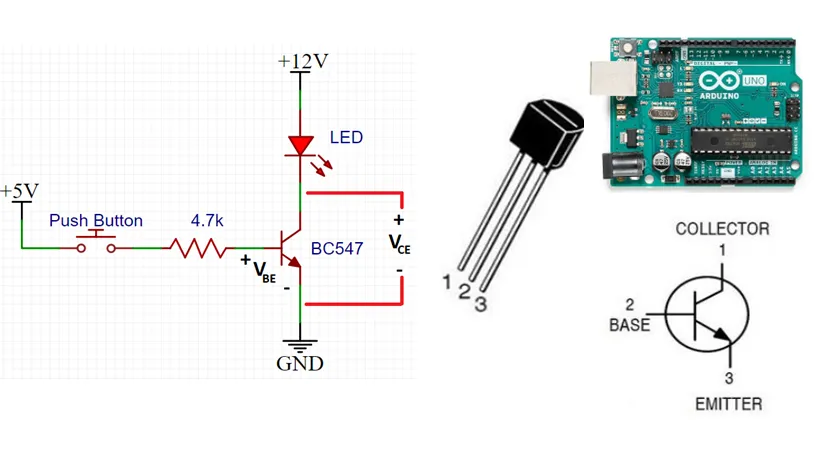
The Features of BC547
Switching and Amplifier
1. NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor: NPN Transistor with Three Semiconductor Layers.
2. Low Power: The maximum collector current( IC) is generally around 100 mA.
3. Low Voltage: Around 45V
4. Moderate Gain (hFE): Ranging from 110 to 800
5. TO-92 Package: Three-Lead Through-Hole Design for PCB Mounting.
6. Versatile: used in amplification, switching, voltage regulation, and signal processing.
7. Cost-effective: Readily Available and Cost-Effective
8. Temperature Range: A Range of -55°C to 150°C
The Specifications of BC547 Transistor
|
Type |
Parameter |
|
Mounting Type |
Through Hole |
|
Package / Case |
TO-226-3, TO-92-3 (TO-226AA) |
|
Weight |
200mg |
|
Voltage - Collector Emitter Breakdown (Max) |
45V |
|
Current - Collector Cutoff (Max) |
15nA(ICBO) |
|
Frequency Transition |
300 MHz |
|
Current - Collector (Ic) (Max) |
100mA |
|
Power Max |
500 mW |
About the BC547's Functional Transition
The BC547 transistor operates using its NPN configuration to enable various electronic functions, transitioning between different states based on the applied signal. This semiconductor device regulates the current across its three layers (negatively doped emitter, positively doped base, and collector) to facilitate amplification, switching, and signal processing. When active, a small base current controls a larger collector-to-emitter current, amplifying the signal. Conversely, without or with minimal base current, the transistor functions in a non-conductive state, serving as a switch or cutoff. This functional versatility supports its wide range of applications in electronic circuits.
BC547 Transistor Applications
1. Amplification: Used in audio amplifiers to boost weak audio signals to a higher level to drive speakers.
2. Switches: Used for electronic switches, controlling current in devices such as relays, LEDs, and motors.
3. Signal Processing: Integrated into signal processing circuits for filtering, modulation, and frequency manipulation in communication systems.
4. Voltage Regulation: Used in voltage regulator circuits to stabilize and regulate the voltage that powers electronic devices.
5. Oscillation: Incorporated into oscillator circuits and used to create periodic waveforms used in clock circuits, signal generators, and timekeepers.
6. Logic-Level Shifting: Used in level translation circuits to make connections between components operating at different voltage levels in digital systems.
7. Pulse circuits: Pulse circuits used to generate or shape pulse waveforms, which are critical for applications such as pulse-width modulation (PWM) and digital signal processing.
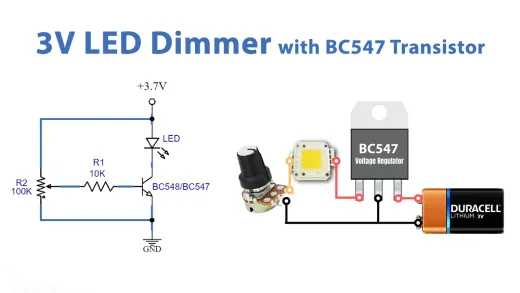
Applications of BC547 in Electrical Circuits
Circuits for alarms
Circuit with flashing LED
Indicator for water levels
Sensor-based circuitry
Circuitry for audio preamplifiers
RF circuits
Touch-sensitive switch circuitry
Thermal sensor circuitry
Moisture-sensitive alarm
Latching circuitry
Street light circuits
Single-channel-based relay driver
Volume indication
Circuits for RF
How Do Use BC547?
The BC547 is an NPN transistor, so the collector and emitter will remain open (reverse biased) while the base pin is in position and closed (forward biased) when a signal is supplied to the base pin. The BC547 transistor exhibits a gain range of 110 to 800, which denotes its amplification capability. It is crucial to note that the maximum current passing through the collector pin should not exceed 100 mA, limiting the use of this transistor for loads exceeding this demand. Proper biasing of the transistor involves supplying a current to the base pin, which needs to be capped at 5 mA.
Once the transistor is adequately biased, it can support a current of up to 100 mA flowing through the collector and emitter, inducing saturation. During this stage, the recommended voltage levels across the collector-emitter (VCE) and base-emitter (VBE) junctions regularly range from 200 mV to 900 mV, respectively. Upon removal of the base current, the transistor becomes completely deactivated, transitioning into the cutoff region and eventually stabilizing with the base-emitter voltage at around 660 mV.
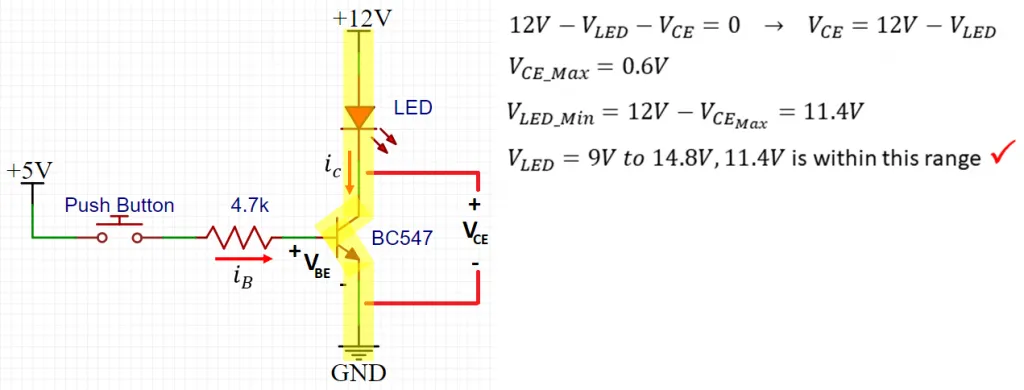
Circuit Applications for the BC547 Transistor
Using the BC547 transistor in conjunction with a touch-grounded ON/OFF switch offers a straightforward and effective system for managing electronic devices through touch perceptivity. In this setup, the BC547 transistor acts as a switch to turn the connected load on and off grounded on touch input.
This circuit typically comprises the following elements:
BC547 Transistor: Serves as the switching component. When a small current is presented to the base terminal through touch input, it enables a larger current to pass from the collector to the emitter, hence activating the transistor and enacting the load.
Resistor: Placed in arrangement with the transistor's base terminal to regulate the current and protect the transistor from potential damage.
Detection of a touch signal by the touch sensor leads to biasing of the base of the BC547 transistor. This in turn permits current to flow from the collector to the emitter, activating the load connected to the collector terminal and powering it up. When the touch input is removed, the transistor deactivates, turning the load off.
Summary of BC547 Transistor
The BC547 serves as a versatile NPN bipolar junction transistor frequently employed in electrical circuits to manage signals, regulate processes, and amplify output. Its low power consumption, high amplification capabilities, and voltage robustness make it well-suited for a range of circuit applications requiring low to moderate power. Frequently accessible in a streamlined TO-92 package, these transistors simplify installation on printed circuit boards. Their dependability, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with diverse operating conditions have rendered them popular among both professionals and hobbyists for a variety of electronic ventures and purposes.
FAQ of BC547 Transistor
1. What's the BC547 transistor?
Extensively employed in electrical circuits, the NPN bipolar junction transistor known as BC547 serves multiple functions such as switching, amplification, and signal processing. Its application extends beyond these functions and is also utilized in commercial circuits. Housed in a TO-92 format, it can handle a maximum output current of 100 mA.
2. What are the crucial features of the BC547 transistor?
The BC547 transistor's notable features include its compact TO-92 packaging, low collector-emitter voltage (VCEO), moderate gain (hFE), and low power consumption.
3. What's the typical operation of the BC547 transistor?
The versatile and reliable BC547 transistor finds extensive utilization in various low- and medium-power electronic applications. It is commonly employed in amplification, switching, and signal processing circuits. Its typical operations encompass audio amplifiers, electronic switches, voltage regulators, and oscillator circuits. Furthermore, it is applicable in logic level-shifting circuits and pulse circuits.
4. How do I safely long-run BC547 in a circuit?
When using the BC547 transistor in a circuit for extended periods of time, it's pivotal to make sure that the biasing is correct in order to prevent inordinate current. You should also limit voltage and current situations to the transistor's specified conditions and, if demanded, use a suitable heat Gomorrah to manage heat dispersion. Eventually, you should periodically check for signs of damage or overheating and make sure that there's enough ventilation for heat dispersion.
Related Articles
PN2222 Transistor: Equivalents, Applications and Features
2N3904 Transistor: Features, Applications and Datasheet
2N5088 Transistor : Pinout, Equivalent, Datasheet
MLX91221KDF-ABF-075-RE Melexis Technologies NV[All Explained]
2N5551 Transistor:Features,Applications and Pinout
Phototransistor : Circuit Pinout & Principle
What is Thin-Film Transistor(tft) monitors? All explained
Transistor Series Voltage Regulator:All You Need to Know
Junction Field-Effect Transistors: Principles, Applications, and Advantages
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor:Features and Pinout










