Electrical Oscillator Circuit: Types, Components & Applications
What Is an Electrical Oscillator Circuit?
An electrical oscillator circuit is an electrical circuit that is designed to produce periodic and constant output signals by the application of positive feedback and frequency-selective components. When the circuit is energized, the circuit automatically oscillates, the oscillation frequency being determined by the internal component values and configuration. Oscillator circuits do not require an external source of the AC signal, and therefore, they are very efficient and commonly used in embedded systems and in electronic gadgets.
Basic Definition and Function
The core function of an electrical oscillator circuit is to generate a continuous periodic signal with a defined frequency and amplitude. Applications of this signal include: a timing signal, carrier wave or control signal, so that predictable and reliable operation of circuits can be achieved.
Importance of Oscillator Circuits in Electronics
Oscillator circuits are fundamental in the synchronization of the system, the generation of clocks and the modulation of signals. In the absence of the oscillators, digital processors would not have been able to execute in sequence, communication systems would not have been able to transmit a constant carrier frequency, and test equipment would not have a reliable source of signals.
Working Principle of Electrical Oscillator Circuits
The concept of electrical oscillator circuits is regenerative or positive feedback, i.e., a part of the output signal is fed back into the input in phase. This secondary response to the signal cancels losses, and in an ideal situation, the oscillations can persist indefinitely.
Feedback and Loop Gain
To be able to oscillate, the loop gain of the circuit has to be no less than and a little more than one. This ensures that an amplified feedback signal does not diminish the amplitude of oscillation and ensures the signal does not decline with time.
Barkhausen Criteria for Oscillation
The Barkhausen criterion defines the theoretical conditions for sustained oscillation: the total phase shift around the feedback loop must be 0° or 360°, and the loop gain must be unity. The criteria are used by engineers to make stable and reliable oscillator circuits.
Types of Electrical Oscillator Circuits
Electrical oscillator circuits are categorized based on the components used to determine frequency and the waveform produced.
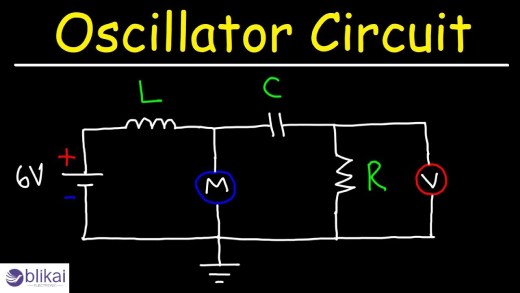
LC Oscillator Circuits
LC oscillators use inductors and capacitors to form a resonant tank circuit, making them suitable for high-frequency and RF applications.
Hartley Oscillator
The Hartley oscillator utilizes a tapped inductor/two inductors in series to an inductor coupled with a capacitor to vary the frequency of oscillation. It is normally used in radio transmitters and receivers as it is easy and works well at high frequencies.
Colpitts Oscillator
The Colpitts oscillator involves the use of a capacitive voltage divider and one inductor. This design offers improved frequency stability and is widely used in RF signal generation and communication equipment.
RC Oscillator Circuits
RC oscillators are based on networks of resistors and capacitors and are used well in low- to mid-frequency.
Phase Shift Oscillator
A phase shift oscillator involves several RC stages to obtain the desired phase shift for oscillation. It is often implemented with transistors or operational amplifiers and is suitable for audio-frequency applications.
Wien Bridge Oscillator
The Wien bridge oscillator is known to produce a sine wave of low distortion. It is also highly employed in audio testing, signal generators and measurement equipment.
Crystal Oscillator Circuits
Crystal oscillators use piezoelectric quartz crystals as frequency-determining elements. These oscillators provide exceptional frequency accuracy and stability, making them ideal for microcontrollers, CPUs, and communication systems.
Relaxation Oscillators
Non-sinusoidal waveforms that are generated by relaxation oscillators comprise a square wave, sawtooth wave. They typically use comparators, timers, or Schmitt triggers and are common in timing and pulse-generation applications.
Key Components Used in Oscillator Circuits
Components of an oscillator circuit are very important as far as performance and stability are concerned.
Active Components (Transistors, Op-Amps, ICs)
Active elements offer the required gain and feedback control to be able to start and maintain the oscillation. Depending on the usage, transistors, operational amplifiers, and dedicated oscillator ICs are usually applied.
Passive Components (Resistors, Capacitors, Inductors)
Passive components can build frequency-selective networks that characterize the frequency of oscillation and the shape of waveforms. Their tolerances and temperature characteristics directly affect circuit stability.
Frequency-Determining Networks
The frequency-determining elements are LC tanks, RC networks and crystal resonators, which make the behaviour of oscillators predictable and repeatable.
Common Electrical Oscillator Circuit Diagrams
Circuit diagrams are used to plot the interaction of components in designs of oscillators.
Simple RC Oscillator Circuit Example
RC oscillator diagrams illustrate how resistor-capacitor networks interact with amplifiers to generate stable low-frequency signals.
Basic LC Oscillator Circuit Example
LC oscillator diagrams show resonant tank behavior, highlighting how energy oscillates between inductors and capacitors.
Crystal Oscillator Circuit Overview
Crystal oscillator diagrams show the application of the quartz crystals together with amplifying circuits to have very accurate frequency control.
Applications of Electrical Oscillator Circuits
Circuit Electrical oscillators, or EC, have applications in almost all branches of electronics.
Signal Generation and Testing
Oscillators are used in supplying interceptive signals to testing apparatus, waveform generators, and calibration instruments.
Clock Circuits in Digital Electronics
They produce microcontroller, processor, and digital logic system clock signals so as to provide coordinated action.
Communication Systems and RF Applications
Oscillator circuits create carrier frequencies for transmitters, receivers, and modulation systems in wireless communication.
Audio and Tone Generation Circuits
In audio electronics, oscillators generate tones for musical instruments, alarms, and sound effect circuits.
Advantages of Electrical Oscillator Circuits
Continuous Signal Generation
Oscillator circuits are designed to put out a constant and steady signal (rather than a DC signal) and do not require an external AC signal, able to make them useful as timing and frequency references in electronic systems.
Flexible Frequency Control
In RC, LC or crystal networks, the designers can easily change the frequency of the output to modify the values of components to suit specific application requirements.
Simple Circuit Structure
Other types of oscillator circuits, such as the RC or Hartley oscillators, are simple circuits that are relatively easy to construct with electronics that are available off-the-shelf.
Versatility Across Applications
The oscillators find extensive application in audio circuits, digital clocks, communication systems and RF devices, indicating their flexibility in various electronic applications.
Disadvantages of Electrical Oscillator Circuits
Frequency Drift
Temperature variations, component aging and variations in voltages can cause oscillator frequency drifts, so timing in sensitive systems is likely to be inaccurate.
Temperature Sensitivity
Passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors can change their values with temperature, impacting oscillator stability.
Noise and Distortion
Signal distortion or phase noise can be caused by electrical noise, variation in power supply and inappropriate feedback and impair the purity of the waveforms.
Component Tolerances
The difference in component specification may result in inconsistency in output frequency, and therefore, precision components should be chosen carefully in critical applications.
Practical Design Tips for Oscillator Circuits
Good design practices improve reliability and signal quality.
Frequency Stability and Component Selection
Using precision components and temperature-stable elements improves long-term frequency accuracy.
Power Supply and Noise Considerations
Proper power decoupling, grounding, and layout reduce phase noise and interference.
Common Design Mistakes to Avoid
Wrong levels of feedback, bad PCB layout and the use of wrong component values may inhibit oscillation or even distort.
Electrical Oscillator Circuit vs Signal Generator
A signal source that is commonly an electrical oscillator circuit is a fixed-function source of signal intended to be incorporated into a system, whereas a signal generator is a test instrument with flexible frequency, amplitude, and waveform control.
FAQs
What is the simplest oscillator circuit?
A basic RC relaxation oscillator using a comparator or timer IC is one of the simplest oscillator circuits.
Can an oscillator circuit work without an inductor?
Yes, the inductors are not needed in RC oscillators and crystal oscillators.
How is oscillator frequency controlled?
Frequency is controlled by adjusting component values in the frequency-determining network.
Which oscillator type is the most stable?
The stability and accuracy of frequency are the greatest in crystal oscillators.
Conclusion
Circuits based on electrical oscillators are very important electronic elements that allow timing, signal creation and frequency control in numerous applications. Knowing their principles of working, the type of circuit, and their most important components, engineers and designers can choose and realize the oscillator circuits, which meet the challenging requirements of the contemporary electronic system.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.










