Chip Resistor: characteristics, Applications & Advantages
A resistor type with a square shape is called a chip resistor. They generally have a resistive element on the top face and are composed of glass or ceramic. Surface mount technology(SMT) operations on printed circuit boards(PCBs) constantly use these resistors.
Decipher the Resistance Value of Chip Resistors
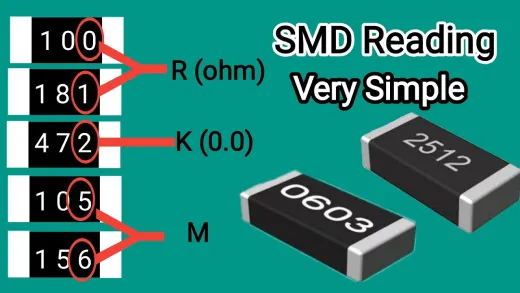
Understanding the Coding System: Chip resistors generally have a 3- number or 4- number law published on them.
For 3-digit codes: The resistance value's significant figures are represented by the first two integers. and the multiplier is represented by the third number.
For 4-digit codes: Important figures are represented by the first three integers. and the multiplier is represented by the fourth number.
Interpreting the Values:
Example 1 (3-digit code): If you see a code like "473", it translates to 47 10^3 ohms, which equals 47 kΩ (kiloohms).
- Here, "47"is the significant figure (first two digits).
- "3"is the multiplier(third number), which indicates 103(or 1000).
- So, the resistor value is 47 1000 ohms = 47000 ohms = 47 kΩ.
Example 2 (4-digit code): If you see a law like"1021", it translates to 102 101 ohms, which equals 102 ohms.
- Here, "102"is the significant figure (first three digits).
- "1"is the multiplier(fourth number), which indicates 101(or 10).
- So, the resistor value is 102 10 ohms = 1020 ohms = 1.02 kΩ.
Tolerance:
Sometimes, there might be a letter indicating the forbearance of the resistor(e.g.,"K"for ± 10,"J"for ± 5). This letter is typically found near the numerical code and tells you the tolerance of the resistor's rated value.
Reading Orientation:
The orientation of the resistor matters because it can affect the interpretation of the code. Ensure you are reading the code in the correct position, especially if the resistor is small and the code wraps around the component.
Color Coding (less common on chip resistors):
Some chip resistors may have color bands similar to through-hole resistors, but this method is less common for SMD components.
Types of Chip Resistors
Thin Film Resistors: These work by covering a ceramic foundation with a thin layer of a resistive substance, like nichrome. high stability and accuracy.
Thick Film Resistors: These employ a more substantial layer of resistive substance, often oxide of ruthenium. They are significantly less accurate than thin film resistors, but they are more affordable when placed on a ceramic basis.
Metal Film Resistors: Employ a metal film atop a ceramic foundation, often composed of tantalum nitride or nickel-chromium. Offers high precision and stability.
Carbon Film Resistors: Use a ceramic foundation with a carbon film placed on it. Although they are less expensive than metal film resistors, they are less accurate.
Structure and Composition
Substrate Material: It's frequently composed of alumina, a kind of ceramic that's both electrically conductive and thermally stable.
Resistive Element: A thin subcaste of a essence oxide or amalgamation, or other resistant material.
Protective Coating: Generally, defensive coatings are applied on resistor rudiments to guard against oxidation and damage.
Terminals: For electrical connections, the resistor has metal contacts on both ends. Usually, solderable metals like tin or silver are used to make them.
Characteristics
- Size: Chip resistors are small and come in conventional sizes, which are represented in elevation and include 0402, 0603, 0805, and 1206.
- Resistance Value: Milliohms to megaohms are just a many of the numerous resistance conditions available.
- Tolerance: There are differences in tolerance. The typical values have an accuracy of ±1%, ±5%, and occasionally ±0.1%.
- Temperature Coefficient: This figure shows the temperature-dependent variation in resistance. Corridor per million per degree centigrade(ppm/ °C) is the standard unit of dimension.
- Power Rating: Depending on size and material, the power standing generally ranges from 1/ 32W to 1W.
- Material: Typically composed of metallic, thin, or thick film materials.
- Packaging: Printed circuit boards(PCBs) can be fluently assembled with face mount technology(SMT) packaging.
Considerations When Using Chip Resistors
- Power Rating: Make sure the chip resistor is able of handling the quantum of power dispersion demanded for your operation.
- Tolerance: Corroborate that the resistor forbearance satisfy the circuit's delicacy conditions.
- Temperature Coefficient: Recognize how temperature affects a resistor's value. In the event that temperature stability is crucial.
- Mounting: Take heat control and soldering techniques into account.
Applications of Chip Resistors
Consumer Electronics
Smartphones, Tablets, and Laptops Used for colorful purposes similar as voltage regulation, signal filtering, and current limiting within the circuitry of these bias.
Televisions and Audio Equipment: Employed to guarantee reliable operation and performance in power force units, audio amplifiers, and signal processing outfit.
Automotive Industry
Electronic Control Units (ECUs): The functioning of the ECU in voltage dividers depends heavily on chip resistors. resistors that can be pulled up or down and a signal processing circuit.
Sensors and Actuators: Used in selector control circuits and sensor modules(e.g., pressure and temperature sensors) to cover and control electrical signals.
Industrial Equipment
Control Systems and Automation: Employed for controlling and regulating electrical signals in PLCs(programmable sense regulators), motor control circuits, and artificial robotization.
Power Supply Units: Utilized in the power supply unit for noise reduction, voltage regulation, and current detection. to guarantee dependable and steady functioning.
Medical Devices
Diagnostic Equipment: Utilized in gadgets like medical imaging systems (MRI, CT scanners) where electrical component precision and dependability are crucial.
Patient Monitoring Systems: Utilized in circuits that track vital signs. Make sure that data is acquired and transmitted accurately.
Telecommunications
Networking Equipment: Used for signal conditioning in modems, switches, and routers. matching of the impedance and noise reduction in the data transfer circuit.
Signal Processing: Used for signal processing and impedance matching in base station and communication equipment. to raise the signal's dependability and quality.
Advantages
- Compact Size: Smaller form factors allow for more efficient and compact designs by freeing up space on the PCB.
- High Reliability: Chip resistors are renowned for being dependable and stable. For applications requiring great performance, this is quite crucial.
- Ease of Manufacturing: Packaging using surface mount technology (SMT) streamlines the assembly procedure. suitable with alignment devices that operate automatically.
- Cost-Effective: Reasonably priced to make and market. For many applications, this makes it a cost-effective choice.
- Wide Range of Values: Accessible in a large variety of resistance levels. It offers accurate electrical parameter control.
- Thermal Stability: Good temperature coefficient characteristics ensure that the resistor's performance remains stable under varying thermal conditions.
- Compatibility: Can be easily integrated into various circuits and are compatible with other SMT components.
Disadvantages
- Limited Power Handling: Their modest size prevents them from dissipating a lot of electricity.
- Heat Dissipation: Because of its small size, it might be an issue in high power operations.
Summary
Chip resistors are essential corridor of contemporary electronic circuitry. It's useful in numerous different operations because of its small size, responsibility, and versatility. Their numerous advantages, including ease of fabrication, profitable effectiveness, and great thermal stability, extend to consumer electronics and aircraft systems.
FAQ
1. What materials are used in chip resistors?
Chip resistor rudiments are frequently composed of ceramic accoutrements , similar as alumina(Al2O3) or other ceramic composites. Generally, a binder and resistor material are combined, and the admixture is burned into the ceramic face.
2. What are the common sizes of chip resistors?
Standard sizes are available for chip resistors. The codes 0402, 0603, 0805, 1206,etc. stand for this. These values(0402,0.04"x0.02") indicate the resistor's size in hundreds of elevation, both in length and range.
3. How do I identify the resistance value of a chip resistor?
A numerical code written on the surface of chip resistors typically indicates the resistance value of the resistor. This code must be decoded using an internet calculator or resistor code table in order to comply with EIA-96 or EIA-24 standards.
4. Are chip resistors polarized?
No, chip resistors are not polarized components. They can be placed in a circuit in either orientation without affecting their performance.
5. How do temperature coefficients affect chip resistors?
A Temperature Coefficient of Resistance(TCR) is a dimension of how much the resistance of a chip resistor changes with temperature. Better stability across a broad temperature range is indicated by a lower TCR value.
6. What is the power rating of chip resistors?
The size and architecture of chip resistors will affect their power rating. For lower sizes, the typical power conditions range from1/16 watt(0.0625 watt) to several watts.
7. Can chip resistors be used in high-frequency circuits?
Chip resistors can be employed in circuits with high frequentness. At veritably high frequentness, still, parasitic inductance and capacitance can have an impact on performance. technical radio frequency(RF) chip resistors.
Related Articles
Decoding Resistor Color Bands: A Beginner's Guide
How Does a Resistor Work [Fully Explained]
Inductor vs Resistor: What’s the Differences?










