Camshaft Position Sensor: Function, Symptoms & Replacement Guide
Introduction to Camshaft Position Sensors
A camshaft position sensor (CMP sensor) is one electronic component that is very important in the modern engine. It primarily monitors the rotational shaft positioning of the camshaft and conveys the signal to the engine control unit (ECU). The information will allow the ECU to synchronize fuel injection and ignition within the engine for optimal performance. Without a proper working camshaft position sensor, your car might be hard to start or run and consume a lot of fuel.
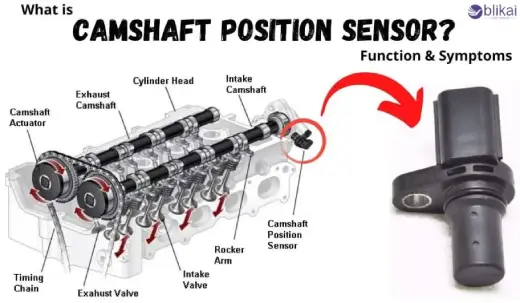
Function of a Camshaft Position Sensor
The role of the camshaft position sensor is based on the accuracy of timing. The rotation of the camshaft drives the intake valves and exhaust valves on the engine open and shut. The CMP sensor reports the precise position of the camshaft relative to the crankshaft and reports this back to the ECU.
Fuel Injection Timing: Injection of fuel into individual cylinders at the most effective stage of the combustion process is done using CMP sensor data entered into the ECU.
Ignition Timing: The ignition firing sequence is varied based on the position of the camshaft so that the combustion happens efficiently and provides optimum power.
Variable Valve Timing (VVT) Adjustment: In engines that have been fitted with this VVT technology, the system operates in tuning up engine-powertrain use under varying conditions of driving to enhance engine performance as well as efficiency in the use of fuel.
Should the CMP sensor relay improper data or fail to communicate, the ECU will not be able to coordinate the functions of the engine effectively hence resulting in poor performance, low fuel economy, and possible engine destruction.
Common Symptoms of a Faulty Camshaft Position Sensor
Engine Misfires and Rough Idling
Ignition and fuel timing can be disturbed with a faulty camshaft position sensor. This may result in engine misfires in that combustion occurs at the wrong moment, which results in jerkiness, hesitation or sputtering during idle. When the vehicle is at rest, the drivers will find that the car shakes or the RPM needle moves positively.
Hard Starting or No-Start Condition
In the absence of proper camshaft position information, the ECU would not know when to control the ignition of the fuel mixture. This may complicate or make it hard to start the machine. On other occasions, the vehicle may coil but may not start at each, particularly when the rainfall is cold.
Reduced Engine Power and Acceleration Issues
When the CMP sensor fails, the engine control unit (ECU) may go into what is known as “limp mode,” a protective measure which reduces power by limiting it so as not to cause damage. When the limp mode is enabled, acceleration is torpid and the vehicle can have problems attaining higher velocities.
Check Engine Light (CEL) Activation
One of the most popular symptoms of the bad camshaft sensor is the Check Engine Light on the dashboard. DTCs such as P0340 (Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction), P0341 (Camshaft Position Sensor Range/Performance Problem) will be found stored under the ECU.
Poor Fuel Economy
Improper timing would lead to inefficient combustion, and thus it would require an additional amount of fuel to attain the same power. With time, this may cause a significant increase in fuel consumption.
Causes of Camshaft Position Sensor Failure
Heat and Vibration Damage: Machine heat and vibration constantly expose the sensor to this stress, which can affect long- term damage to internal circuitry.
Wiring Harness or Connector Issues: loose, eroded or bare cables could intrude that signal before it gets to the ECU.
Oil Contamination: Oil contamination in the oil that would possibly be leaking onto the engine valve covers or seal can enter the sensor housings, and this would interfere with its precision of transmitting the signals.
Internal Component Failure: The sensor suffers magnetic and optical interiors that can fail due to the fact that they get worn out or poorly constructed.
How to Diagnose a Faulty Camshaft Position Sensor
Step 1: Scan for Error Codes
Inspect stored fault codes that concern the camshaft timing, using an OBD-II scanner. The strong indication concerning the CMP sensor is codes such as the P0340 and P0341 codes.
Step 2: Visual Inspection
Looking at the sensor, looking at it physically, is it damaged? Is it contaminated with oil? Does it have plugs pulled off it? Look at the wiring harness to ensure there is no fraying or melting as a result of heat exposure.
Step 3: Multimeter Testing
Measure the values of voltage or resistance of the sensor using a multimeter. They need to be compared with the specifications given by the manufacturer to ascertain whether it is working correctly.
Step 4: Oscilloscope Testing (Advanced)
Using an oscilloscope will help you to fantasize the waveform of the affair signal of the sensor in real time. The sensor sends steady, invariant signals when it's healthy. Non normally occurring irregularities signify the malfunction.
Step-by-Step Camshaft Position Sensor Replacement Guide
Tools and Safety Precautions
- Socket set and ratchet
- Screwdrivers
- Gloves and safety glasses
- OBD-II scanner for resetting codes
Locate the Camshaft Position Sensor
Typically found near the cylinder head, timing cover, or camshaft gear.
Remove the Old Sensor
- Disconnect the battery.
- Unplug the sensor’s electrical connector.
- Remove mounting bolts and carefully extract the sensor.
Install the New Sensor
- Position the new sensor in place.
- Secure with bolts and reconnect the electrical plug.
Reset the ECU and Clear Error Codes
Reconnect the battery, start the engine, and use an OBD-II scanner to clear stored codes.
Tips for Prolonging Camshaft Position Sensor Life
- Keep up with regular oil changes to prevent sludge buildup.
- Check for oil leaks near the timing cover.
- Ensure wiring harnesses are secured away from excessive heat sources.
Camshaft Position Sensor vs. Crankshaft Position Sensor
|
Feature |
Camshaft Position Sensor |
Crankshaft Position Sensor |
|
Location |
Near camshaft or timing cover |
Near crankshaft or flywheel |
|
Role |
Synchronizes fuel injection & ignition |
Monitors crankshaft speed & position |
|
Failure Symptoms |
Misfires, rough idle, hard starting |
No start, stalling, wrong RPM readings |
|
Relation |
Works with crank sensor for timing sync |
Works with cam sensor for timing sync |
Both sensors work together, and a fault in either can cause similar performance issues.
Conclusion
The camshaft position sensor is crucial in tuning the engines, fuel consumption, and performance. Moreover, by knowing some symptoms early and changing a faulty sensor in time, you will not be forced to perform costly repairs and keep your engine in good operation. No matter what option you adopt, to DIY or take a car to a mechanic, your camshaft position sensor will operate well and last as long as you properly maintain and replace it.
FAQs of Camshaft Position Sensor
What happens if the camshaft position sensor fails?
Breakage of the sensor makes the ECU unable to inject fuel or to time the ignition correctly. This is capable of causing engine misfires, poor acceleration, stalling or engine malfunctions in starting.
Can you drive with a bad camshaft position sensor?
It can be done, but it cannot be recommended. With a false feedback sensor, the engine could malfunction and cause irregular performance of the engine and low fuel usage, besides the breaking of other engine components.
How long does it take to replace a camshaft position sensor?
Most cars differ in how wide the replacement is given only a matter of minutes or up to 2 hours depending on how easily accessible the replacer is and how well designed the vehicle is.
What codes indicate a bad camshaft position sensor?
These typical individual trouble codes are a law P0340( Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction) and a law P0341( Camshaft Position Sensor Range/ Performance Problem).
Is the camshaft position sensor the same as the crankshaft position sensor?
No. It contains a camshaft sensor which monitors the position of the camshaft so it can be corrected and the stopcock timing is correct and the crankshaft sensor which deals with speed and position of the crankshaft regarding correct ignition timing. They're coordinated in a manner that they give accurate timings to the machine.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.










