Why Do Capacitors Explode?

Why Do Capacitors Explode
You may be frightened by an explosion of a capacitor, especially if you weren't expecting it. You can save time and money by knowing the possible causes of capacitor explosions (you won't have to replace the blown capacitors as often). So, Why Do Capacitors Explode?
An explosion could be caused by a reverse polarity voltage or over-voltage (as little as 1 - 1.5 volts above the voltage can cause an explosion). As opposed to other types of capacitors, electrolytic capacitors are more likely to explode.
An examination of reverse polarity voltage and other causes of capacitor explosions is presented in this article. Don't worry we are going to discuss why capacitors explode and all the important things in detail!
What Does A Capacitor Do?
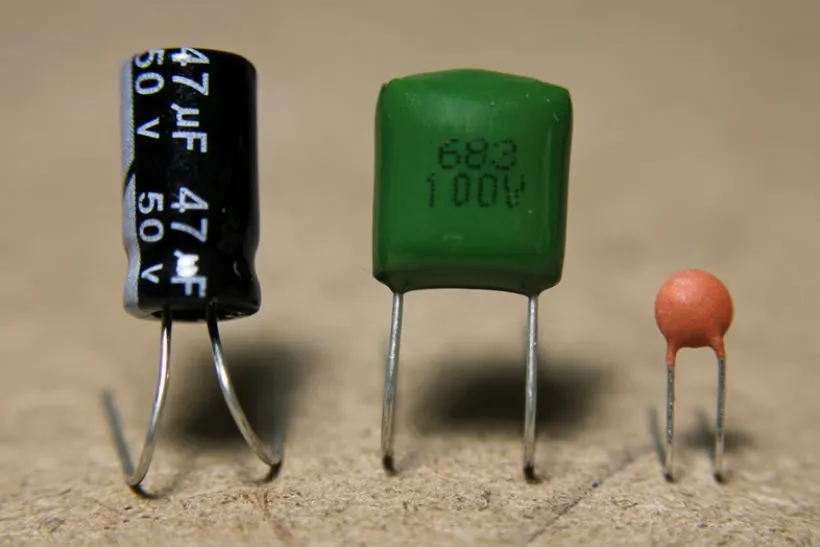
In countless electrical circuits and devices, capacitors play an essential role. An energy storage device serves as a temporary energy reservoir capable of storing and releasing electrical energy. The electronic world uses capacitors for a variety of purposes and applications due to their ability to store and discharge electrical charge.
In essence, a capacitor acts as a filter for electrical signals. A parallel connection stabilizes voltage levels and prevents sudden fluctuations when connected in parallel with a power supply. An electronic device's proper operation depends heavily on a steady and reliable voltage in power supply circuits.
Oscillators and timing circuits also use capacitors. Their ability to control frequency and duration of electrical pulses depends on how fast they charge and discharge. Tone generators, clocks, and timers use this feature to generate audio.
Why Do Capacitors Explode: Reasons
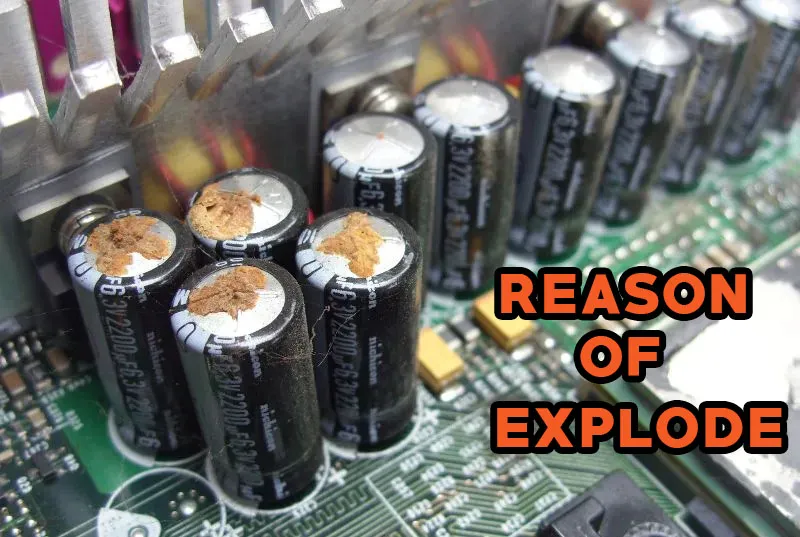
Reason of Capacitors Exploding
Electrolytic capacitors are more likely to cause spectacles when they explode compared to their predecessors. Many capacitors do not explode; instead, they burn, crack, pop, or smoke. Electrolytic capacitors fail when their oxide layer deteriorates.
Consequently, heavy current flows through the electrolyte. As a result, significant amounts of heat will be generated. A capacitor will eventually blow up because of this intense heat, which turns water into gas. Capacitor explosions can be caused by a variety of factors.
Overheating
A capacitor can become damaged and fail catastrophically if it produces excessive heat when in use. The capacitor may overheat and explode if temperatures are too high outside, if there is an excessive current flow, or if there is not adequate cooling.
Run for Longer Time
The equipment in which capacitors are installed can also cause them to overheat. Devices under heavy load conditions or those that operate for long periods often experience this problem. The internal temperature of capacitors can rise to unsafe levels with continuous use and high currents. A capacitor's capacitance can decrease due to overheating, and its internal resistance can increase, ultimately leading to its failure. It is possible to avoid overheating capacitors by using fans or heat sinks to dissipate heat.
Internal Short Circuit
Physical harm or manufacturing flaws can cause the capacitor to short circuit. Capacitor short circuits allow large currents to pass through the shorted part due to the low resistance they create. As a result, energy may be released rapidly, and severe heat may be produced, which may result in an explosion.
Reversed Polarity
The connection of the positive terminal to the negative terminal reverses the polarity of a capacitor if it is wired incorrectly. Wiring it incorrectly and applying voltage for a short period of time shouldn't be a problem. Long-term reverse polarity exposure will, however, cause an electrolytic capacitor to blow up.
Age
The lifespan of capacitors is limited, just like that of all electronic components. As a capacitor ages, its materials may deteriorate due to electrical stress and temperature changes. During dielectric degradation, leakage currents may increase or capacitance may decrease.
Furthermore, repeated thermal cycles can damage the capacitor's electrical connections by weakening or cracking the solder joints. To ensure that electronic devices and systems perform optimally and last a long time, capacitors must be maintained regularly and replaced on a regular basis.
Gas release
Those capacitors that contain electrolytes or other volatile materials, such as high temperatures or excessive voltage, can experience chemical reactions if their internal electrolyte evaporates. A rise in pressure caused by the gas release could cause the capacitor casing to burst.
How to Know if Capacitor is Exploding?
Humming Noise
Unusual noises are often associated with capacitor failure. A humming noise is a common sign of a failing capacitor. Air conditioning units or capacitors can emit this noise. If the motor or compressor is not operating efficiently, it could be because of a humming noise made by a capacitor struggling to provide electrical energy.
Clicking Noise
There is also a clicking noise that can be heard when a capacitor is failing. Clicking noises can be caused by loose components or degradation in capacitors. When the equipment is under heavy load or during the startup phase, the clicking noise may be more pronounced.
Start and Stop
Air conditioning units can start and stop rapidly due to a failing capacitor. Because capacitors are becoming less capable of storing and discharging electrical energy, the system may be unable to supply electrical power continuously. An abrupt shutdown may occur, followed by a brief restart of the unit. There is a high probability that this capacitor is suffering from a compromised performance and needs to be replaced.
Can A Capacitor That Has Exploded Still Work?
If you learned why do electrolytic capacitors explode, then I think you also need to know whether they worked or not in this condition. RIght? Overvoltage, reverse polarity, or internal faults lead to capacitor explosions, which are usually the result of catastrophic failures. Capacitors explode when their casing ruptures and their internal components are released. It is highly unlikely that the capacitor will continue to function properly in such a situation. The extent of the damage, however, must be assessed in order to determine whether any residual functionality remains.
When capacitors explode, their internal structures and components have failed severely. Capacitors are frequently damaged by explosions, resulting in cracks and breaks in the casing. It is also possible to compromise or scatter other essential elements, such as the dielectric.
How To Prevent A Capacitor From Exploding?
If you learn why do capacitors explode, then you also need to learn how to prevent them from exploding. So for this reason, I have listed some of the important precautions which you can take to increase the lifespan of your capacitor.
Quality components:
Capacitors with good quality have a lower chance of failing or exploding. Capacitors from reputable manufacturers should be of high quality.
Maintenance:
By performing a regular inspection and maintenance, you can catch any potential problems early. Depending on the condition of the capacitor, this may include checking for signs of wear or damage
Use the right type:
The characteristics and capabilities of different types of capacitors differ. Explosion risks can be reduced by using the right type of capacitor.
Faqs
Question 1: Is it common for capacitors to explode?
Answer: It is relatively rare for capacitors to explode. The safety measures used in capacitor construction reduce the likelihood of failure. Following instructions and operating conditions appropriately reduces the risk of a capacitor bursting.
Question 2: What causes a capacitor to explode?
Answer: Electrolyte inside a capacitor breaks through the restraint of the shell and explodes if its temperature rises too high.
Question 3: Can capacitors explode?
Answer: Certain circumstances can cause capacitors to explode. An overvoltage, high temperature, or internal failure can cause a capacitor to explode. A capacitor explosion is generally a rare event and occurs only in very specific circumstances.
Question 4: What is the lifespan of a capacitor?
Answer: In addition to the quality and operation parameters of the capacitor, other factors can affect its lifespan. There is a wide range of life expectancy for capacitors, ranging from 10 to 20 years on average. Capacitors can be affected by electrical load, temperature, humidity, and voltage stress.
Question 5: Are blown capacitors toxic?
Answer: Chemicals and gasses released by blown capacitors can be dangerous or toxic. The electrolyte in electrolytic capacitors, for instance, can provoke skin irritation, eye irritation, and even death if ingested or inhaled. To avoid potential hazards, blown capacitors must be handled carefully and properly disposed of.
Final Verdict
A thorough understanding of the causes and risks of capacitor explosions is essential for the safety and reliability of electrical systems. In order to save yourself from any type of explosions, make sure to follow the usage guidelines, adhere to voltage ratings, and handle capacitors safely.
Moreover, in this article we discuss why do capacitors explode in detail. If you have any questions, then you can ask in the comment section. Thank You!
Related Articles
Tantalum vs Ceramic Capacitor: What's the Differences?
What Is CBB61 Capacitor - Function and Applications










