15 Volt Regulator:Types, Features & Applications
What is 15 Volt Regulators?
An electronic element called a 15-volt regulator is made to keep the affair voltage of 15 volts constant, independent of changes in the input voltage or cargo situations. In power force circuits, these regulators are employed to guarantee that delicate electronic factors admit precise and steady voltage.

Types of 15 Volt Regulators
Linear Regulators
The foundation of voltage control is provided by linear regulators. In order to keep the output voltage constant, it adjusts the resistance. The fundamental idea is to adjust the amount of current passing through the regulator by means of a passive transistor. The output voltage will stabilize as a result. Two primary categories of linear regulators exist:
Fixed vs. Adjustable Linear Regulators: A fixed regulator yields a voltage that is constant. It is often adjusted to 15 volts in 15V regulators. With adjustable regulators, the output voltage can be varied within a predetermined range. This offers versatility for applications that need accurate voltage control.
Example:
- LM7815: Widely used linear voltage regulator with a 1V output that can handle up to 15A of current.
- LM7915: Its negative counterpart, providing -15V output.
Switching Regulators
Switch regulators work by rapidly turning on and off the input voltage in order to keep the output voltage constant. When compared to linear regulators, the efficiency of this switching mechanism is higher. This is so that the voltage can be effectively increased, decreased, or reversed.
Example:
- LM2576-15: A buck (step-down) switching regulator that efficiently converts a greater input voltage into an output of 15 volts.
- LM2596-15: Similar to the LM2576-15, but with a few minor variations.
Adjustable Regulators
These can be set to output a desired voltage by using external resistors.
Example:
- LM317: An adjustable linear regulator that can be configured to output 15V with appropriate resistors.
- LM337: Its negative adjustable counterpart.
Features of 15 Volt Regulators
Voltage Output
Stability and Accuracy: The purpose of the 15 volt regulator is to deliver a precise and consistent output voltage in the face of fluctuating load and input voltage circumstances. Sensitive electrical components are guaranteed constant voltage levels thanks to this stability. Prevent potential harm and commercial issues.
Ripple Rejection: Regulators also feature high ripple rejection capabilities, which refer to their ability to suppress AC ripple and noise from the DC output voltage. Low ripple ensures clean power supply to sensitive circuits, reducing interference and improving overall system performance.
Current Handling
Maximum Current Ratings: Each regulator specifies a maximum current it can reliably supply without overheating or exceeding safe operational limits. This rating is essential for figuring out whether regulators are suitable for a given application where high current demands could happen sometimes or all the time.
Thermal Considerations and Heat Dissipation: When designing a controller, heat dissipation is crucial. This is particularly valid for linear regulators, which release surplus voltage in the form of heat. Sufficient cooling and heat management strategies guarantee that the controller functions within safe temperature ranges, enhancing dependability and durability.
Protection Mechanisms
Overcurrent Protection: An overcurrent protection feature on the 15 volt regulator stops excessive current flow. Overheating or component damage may result from this. In order to protect the controller and any attached devices, this feature typically entails turning off the controller or limiting the output current.
Overtemperature Protection: In order to shield against heat damage. Controllers come with over-temperature protection as a result. With the help of this capability, the controller's temperature may be tracked and preventative conduct, similar lowering the affair current or temporarily turning off the device, can be done. when the temperature rises over the respectable position.
Short-Circuit Protection: In order to guard against detriment from unintentional short circuits in linked circuits or cables, regulators also have short circuit protection erected in. In the case of a short circuit, this function immediately disconnects the output. It shields the surrounding components, the controller, and the load from possible dangers.
Applications of 15 Volt Regulators
Power Supply Units (PSUs)
15 volt regulators play a crucial role in various power supply designs, providing stable voltage outputs required by sensitive electronic equipment. They are commonly used in:
- Bench Power Supplies: Employed to supply controlled DC power in labs and shops for the testing and prototyping of electrical circuits.
- Battery Chargers: Make that the charging voltage is applicable for rechargeable batteries, like those set up in electric buses or movable electronics.
Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, 15 volt regulators are integrated into devices to ensure reliable performance and longevity. Applications include:
- Televisions (TVs): Control the voltage to the display panels. amplifier and control system to ensure peak performance and audio/visual quality.
- Audio Equipment: Inventories DACs( digital-to-analogue transformers) and other audio processing factors with steady power. In order to lessen noise and deformation, this guarantees excellent sound reduplication.
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, 15 volt regulators are employed in critical control systems and instrumentation where precision and reliability are paramount. Typical uses include:
- Control Systems: Regulating voltage for PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), motor drives, and sensors in automated manufacturing processes to maintain consistent operation and data accuracy.
- Instrumentation: Providing stable voltage to measurement instruments, data acquisition systems, and analytical equipment used in research labs, industrial monitoring, and quality control.
Communications
The 15 Volt Voltage Regulator is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and ongoing functioning in the context of communication technology for:
- Telecom Equipment: Gives electricity to base stations, routers, and modems in the communications infrastructure to ensure dependable network connectivity and data transfer.
- Networking Devices: In wired and wireless networks, control voltage for switches, hubs, and access points. allows for dependable data transfer and continuous device and user connectivity.
Selection Criteria for 15V Regulators
To guarantee optimal performance and dependability, it is crucial to take into account a number of significant variables when choosing a 15V regulator for a particular application:
Voltage and Current Requirements
Voltage Requirements: Find out the precise output voltage needed in your application. Verify that a 15V regulator can consistently deliver 15 volts within the given limits.to fulfill the linked devices' operational requirements.
Current Requirements: Assess the maximum current demand of your circuit or system. Choose a regulator with a current rating that exceeds your peak current requirements to prevent overheating and ensure stable operation under load.
Thermal Management
Heat Dissipation: Think about how well the controller dissipates heat. particularly if it's the linear kind that converts surplus electricity to heat. sufficient thermal control using cooling fans or heat sinks This can be required to keep the cooling system working at a safe temperature and avoid system damage or shutdown.
Size and Form Factor
Physical Space: Evaluate the available space for installing the regulator. Choose a regulator that fits within the constraints of your application, considering both PCB layout and enclosure dimensions.
Form Factor: Consider whether a surface-mount or through-hole package is more suitable for your assembly process and space requirements. Surface-mount packages are often preferred for compact designs and automated assembly.
Cost Considerations
Initial Cost: Compare the initial cost of the regulator with your budget constraints. While quality and reliability are paramount, consider whether higher-cost regulators offer additional features or performance benefits that justify their price.
Operating Cost: Factor in the efficiency of the regulator, especially in applications where power consumption directly impacts operating costs. Switching regulators, for example, offer higher efficiency than linear regulators, potentially reducing long-term energy expenses despite higher initial costs.
Advantages
- Provides a stable and clean voltage output.
- Guards against voltage variations for downstream components.
Disadvantages
- Inefficient linear regulators are possible. particularly when the input and output voltages differ significantly. As a result, a lot of heat is produced.
- Regulator switches can introduce noise into the circuit despite being more efficient.
Example Circuit for LM7815
Here’s a basic circuit example for a 15V linear regulator using the LM7815:
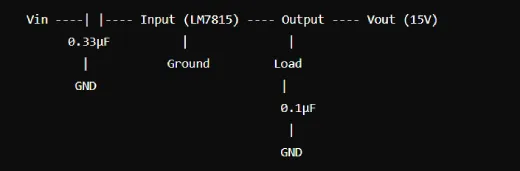
Components:
- LM7815 regulator
- Capacitors (0.33µF and 0.1µF)
- Heat sink (if required)
Circuit Diagram:
1. Input: Attach the input pin of the LM7815 to the input voltage (18–35 V DC).
2. Ground: Attach the earth pin to the ground of the power supply.
3. Output: Connect the output pin to your load requiring 15V.
4. Capacitors: Put a 0.33 µF capacitor in between the ground and the input pin. and to filter noise, place a 0.1 µF capacitor between the output pin and ground.
Considerations
- Heat Dissipation: Higher current applications may necessitate the use of a heat sink for linear regulators like the LM7815 since they can get hot.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of switch controllers is higher. The design, though, might be more intricate.
Would you like more detailed information on any specific type of 15-volt regulator? Visit Blikai.com to learn more.
Related Articles
Voltage Regulators: Types, Applications and Working
Transistor Series Voltage Regulator:All You Need to Know










