Ballast Resistors: Operation, Applications, and Optimization
What is a Ballast Resistor?
Ballast resistors serve as imperative components within electrical circuits, giving solidity and control over current flow. These resistors are particularly designed to direct the flow of power, guaranteeing that the circuit works within secure parameters. By altering the resistance, balance resistors offer assistance to stabilize current levels, anticipating variances that might damage sensitive components or disturb system usefulness. Their presence is vital in different applications, extending from automotive lighting systems to mechanical warming components, where reliable and controlled current flow is essential for ideal execution and security.

Operation of Ballast Resistors
Explanation of Ballast Resistor Functionality
Ballast resistors are components inserted into electrical circuits to limit the flow of current, thereby stabilizing voltage across other components. They provide a fixed resistance that helps regulate the current passing through a circuit, ensuring consistent performance and preventing damage to sensitive electronic devices.
Role in Stabilizing Current
By offering resistance to the flow of electrical current, ballast resistors serve to stabilize the current within a circuit. This stability is pivotal in operations where oscillations in current could lead to malfunctions or failures of electronic factors. Ballast resistors help maintain a steady current level, ensuring reliable operation of the entire system.
Impact on Voltage Regulation
Ballast resistors have a significant function in regulating voltage by managing the level of current within a circuit. By keeping the current passing through the resistor relatively consistent, fluctuations in voltage across the remainder of the circuit are reduced. This helps ensure that devices receive a consistent voltage supply, leading to improved performance and longevity.
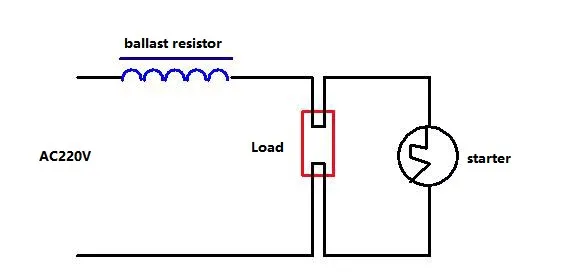
Applications of Ballast Resistors
Ballast resistors find diverse applications across various industries, showcasing their versatility and importance in electrical circuits.
Automotive Industry
Headlights: Headlights in the automotive industry serve the initial work of brightening for secure driving during low-light conditions, compared to darkness or serious weather.
Ignition Systems: Ballast resistors play a significant role in ignition systems by controlling the current stream to the start coil, ensuring a steady start, and securing the coil from damage due to overheating or expected current draw.
Lighting Systems
Fluorescent Lamps: Fluorescent lamps serve as complete light sources in lighting systems by changing electrical vitality into egregious light through the excitation of mercury vapor.
LED Arrays: LED technology offers benefits such as vitality effectiveness, long-life expectation, inflexibility in color, and concentrated control. LED arrays are astronomically employed in different operations, including inner and out-of-door lighting, automotive lighting, and display screens.
Heating Elements
Electric Heaters: Electric heaters, a subset of heating components, utilize balance resistors to control the stream of electrical current, guaranteeing controlled heat generation.
Industrial Furnaces: Mechanical furnaces depend on heating components prepared with ballast resistors to achieve high temperatures for different mechanical forms.
Optimization Strategies for Ballast Resistors
Selection Criteria
Resistance Value: Optimal resistance values ensure that the ballast resistor effectively stabilizes the current while minimizing power losses.
Power Rating: Selecting the appropriate power rating ensures that the resistor can handle the expected current flow without overheating or failing.
Thermal Considerations
Heat Dissipation: Optimizing heat dissipation is crucial to maximizing the performance and lifespan of ballast resistors. Enforcing effective thermal operation methods, similar to heat sinks or thermal pads, ensures effective dispersion of redundant heat generated during operation.
Thermal Management Techniques: By effectively managing thermal considerations, the longevity and trustability of ballast resistors can be significantly enhanced.
Efficiency Enhancement
Minimizing Power Losses: Utilizing resistors with appropriate resistance values and power ratings helps reduce unnecessary energy dissipation. Additionally, employing thermal management techniques such as heat sinks or airflow optimization aids in dissipating heat generated by the resistors more effectively.
Improving Circuit Performance: Improving circuit performance involves enhancing thermal management techniques to ensure effective heat dissipation.
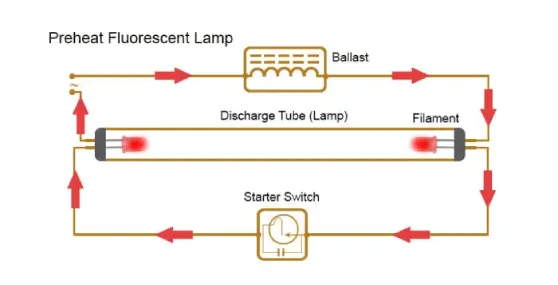
Case Studies with Ballast Resistors
In the automotive industry, ballast resistors play a fundamental role in ensuring the legitimate work of headlights and ignition systems. On occasion, in more seasoned vehicles equipped with gleaming headlights, ballast resistors are utilized to control the current streaming through the headlight filaments. This ensures steady brightness and extends the life expectancy of the bulbs. Essentially, in start systems, balance resistors offer assistance in controlling the voltage provided to the start coil, guaranteeing dependable start generation while anticipating overheating of the coil. These case studies highlight the indispensable role of ballast resistors in automotive applications, contributing to improved security and execution on the road.
FAQs of Ballast Resistors
What's a ballast resistor, and how does it work?
A ballast resistor serves to control the flow of electrical current in circuits by introducing resistance that restricts the passage of current. This helps stabilize current situations and prevents damage to factors.
Where are ballast resistors generally used?
Ballast resistors are generally used in colorful operations, including automotive lighting and ignition systems, fluorescent and LED lighting, and artificial heating rudiments.
How do I select the right ballast resistor for my operation?
When choosing a ballast resistor, factors such as resistance value, power standing, and thermal characteristics should be considered. It's essential to choose a resistor that can handle the anticipated current situations while dissipating heat effectively to help with overheating.
Are there any maintenance considerations for ballast resistors?
While ballast resistors are generally reliable components, periodic inspection for signs of damage or overheating is recommended. Replacing worn or damaged resistors promptly can help prevent circuit failures and ensure continued operation of the system.
Final Thoughts on Ballast Resistor
Ballast resistors serve as unsung heroes in the domain of electrical engineering, quietly guaranteeing the solidity and reliability of endless circuits and systems. Whereas they are regularly neglected, their significance cannot be exaggerated. From automotive lighting to mechanical warming, balance resistors provide crucial current direction and voltage stabilization, contributing to the productivity and longevity of electrical components. As innovation progresses, their part may advance, but their crucial work as guardians of circuit integrity remains unaltered. In conclusion, the humble balance resistor deserves acknowledgment for its important commitment to the world of electronics.
Related articles
Is a Fuse a Resistor? [Everything Explained]
Resistor Transistor Logic (RTL): Operation, Variations, Traits & Uses
How Does a Resistor Work [Fully Explained]
Is a Fuse a Resistor? [Everything Explained]
Inductor vs Resistor: What’s the Differences?
Does a Resistor Reduce Voltage
Carbon Film vs Metal Film Resistor
Capacitor vs Resistor: What's the Differences?
How to Charge Capacitor Without Resistor?
Wirewound Resistor: An In-Depth Overview
What are Metal Posters? All Explained
BSS138 MOSFET : Principle,Features & Applications
AC Capacitor Keeps Blowing: What to Do Next?










