Capacitor Symbol: What Does It Really Mean?
What is a Capacitor?
A capacitor is an electrical element that acts as an electric field storehouse for energy. It features two conductive plates, called electrodes, separated by a dielectric, which is an electro-separating material. The operation of voltage across the plates causes an electric charge to accumulate between the plates, which leads to the conformation of an electric field. Capacitors perform a number of functions, including repression of voltage oscillations in power inventories, signal filtering, and timing in circuits.

Key Characteristics of Capacitors
- Capacitance (C): The charge accumulated by the capacitor per volt of electrical eventuality, measured in farads( F).
- Voltage rating: The maximum voltage under which a capacitor can work without breaking down.
- Dielectric type: Different dielectrics (like ceramic, electrolytic, or film) affect the capacitor's performance, size, and cost.
Types of Capacitors
Ceramic Capacitors
These types of capacitors have become very popular due to their stability and extreme reliability. Due to ceramics being dielectric, they are appropriate in high-frequency applications. They are sufficiently small and cheap for decoupling and filtering circuits.
Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors are similar capacitors that have been given opposition in order to achieve high capacitances- in a small volume. They are rated for smoothing out voltage fluctuations, especially in supply circuits. They are, however, severely constrained by their polarized nature and have shorter service lives than other varieties.
Film Capacitors
Film capacitors employ a plastic film as a dielectric and offer excellent stability coupled with low losses. They are used in audio applications, timing circuits, and signal processing. Their non-polarized nature allows for versatile applications across various electronic designs.
Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors have good reports for their small- size, low capacitance and high trustability. These are being employed in applications where the space warrants, such as in portable electronics, and yet, their heightened price, along with increased sensitivity to overvoltage, has driven their reduced use.
Supercapacitors
Supercapacitors are energy storage units with high energy, fast charge, and fast discharge. They are midway between conventional batteries and capacitors and are best for use in energy harvesting and backup. Their long cycle life makes them suitable for renewable energy systems.
The Capacitor Symbol in Circuit Diagrams
A. Description of the Standard Capacitor Symbol
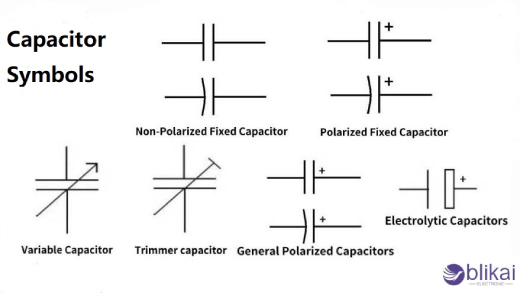
The standard symbol for a capacitor consists of two resemblant lines, which represent the plates of the capacitor. The lines are generally straight and may vary in length. In schematic diagrams, the symbol is often drawn as:
- A simple pair of parallel lines (for a non-polarized capacitor).
- A curved line on one side (for a polarized capacitor, indicating the positive plate).
B. Variations in Symbols Based on Capacitor Types
Different types of capacitors have variations in their symbols:
1. Non-Polarized Capacitors: Represented by two parallel lines.
2. Polarized Capacitors: Usually indicated with one plate marked (+) to denote the positive terminal.
3. Electrolytic Capacitors: Often shown with a curved line on one side and a straight line on the other, with the positive side indicated.
4. Variable Capacitors: Typically depicted with an arrow or additional markings to show adjustability.
5. Tantalum Capacitors: May be indicated with a specific symbol or color code.
C. Importance of the Symbol for Identification
The capacitor symbol is crucial for the following:
- Identification: Helps quickly identify the type of capacitor in a circuit, which is essential for understanding functionality and requirements.
- Circuit Design: Ensures proper placement and connections in circuit designs, affecting performance and reliability.
- Troubleshooting: Aids in diagnosing issues by allowing technicians to recognize capacitor types and their roles in a circuit.
Meaning Behind the Capacitor Symbol
A. Representation of Electrical Energy Storage
- The capacitor symbol also denotes an electrical energy-storing machine, paneling two parallel lines to present the capacitor plates and a void created between them to suggest a dielectric material.
B. Indication of Polarity in Polarized Capacitors
- In the case of polarized capacitors (like electrolytic capacitors), the symbol often has a little "+" sign to indicate its positive terminal; thus, it has to be respected in circuit construction since reversing polarity could destroy the capacitor or failure in the operation of the circuit.
C. Role in Circuit Behavior (e.g., Filtering, Timing)
Capacitors are key components in various applications, including:
- Filtering: Used in power supply circuits to smooth out voltage fluctuations.
- Timing: In conjunction with resistors, capacitors can create time delays in circuits, crucial for applications like oscillators or timers.
Real-World Applications of Capacitors
Power Supply Filtering
Capacitors make a major player in the power supply circuits, with their primary role being that of voltage smoothing. As time passes, they charge, discharge, and stabilize the output voltage, thereby improving the performance and reliability of electronic devices supplied with power from these capacitors.
Signal Coupling and Decoupling
Capacitors are used in a wide variety of coupling and decoupling applications in audio and communication circuits. They allow AC signals to pass from one stage to the next while blocking DC components, ensuring signal integrity and minimizing noise in electronic systems.
Timing Circuits
Timing circuits, such as oscillators and timers, use capacitors to store energy for pre-set intervals and release it for a specified time duration, thus allowing timing devices such as clocks, flash units, and sequencers to be operated on a timed basis.
Energy Storage in Renewable Systems
Capacities, majorly supercapacitors, are available in renewable energy systems increasingly. The working is that they hold power generated excess by solar panels or wind turbines and could deliver energy surges when demand for power suddenly spikes, thereby increasing energy efficiency.
Motor Start and Run Applications
In electric motors, capacitors assist with starting and running operations. Start capacitors are temporary circuits that provide the extra torque needed to start the motor spinning, while run capacitors allow the operation to run smoothly and efficiently, improving its overall performance.
Conclusion
Understanding capacitor symbols will guide the interpretation of the circuit diagrams and give an understanding of the various roles the capacitors undertake in the electronic design. This goes a long way in troubleshooting and understanding circuit functionality. Continue to find understanding in this wide field of electronics and circuit design by expanding your supply of knowledge about different components and their interactions. That will enrich your whole view of electronics while equipping you with the skills through which you could originate commendable and effective electronic solutions. Keep experimenting and learning!
Faqs of Capacitor Symbol
1. What is the symbol for a capacitor?
- The basic symbol of a capacitor is two parallel lines with some gap in between. The lines may be either curved or straight, according to schematic style. In some cases, the lines may be shown with one vertical and one horizontal line to indicate polarized capacitors.
2. What does a polarized capacitor symbol look like?
- The standardized way to portray a polarized capacitor is with one straight line and one curved line. The straight line represents a positive terminal, whereas the curved line stands for a negative terminal.
3. Are there different symbols for different types of capacitors?
- There are analogous diverse groups of capacitors (for instance, ceramic, electrolytic, or tantalum), which may be represented along with other polarized symbols in schematics.
4. How do you distinguish between different capacitance values in symbols?
- The symbols themselves (that is, the letter's construction is generally the same) are often affixed next to the symbol by a value of a capacitor, either in microfarads (µF), nanofarads (nF), or picofarads (pF).
5. What does a capacitor symbol with a line crossing it mean?
- A line crossing through the capacitor symbol generally means that that capacitor is conservative. There is no direct polarity, and it is able to be wired in the reverse direction in the circuit.
6. Why do some capacitor symbols have a voltage rating next to them?
- The voltage rating gives and indicates the exact value of voltage allowed or applied on the body. This is done to prevent unforeseen situations of failing a capacitor.
7. What does the abbreviation "C" signify in circuit diagrams?
- The letter "C" with a number following it (such as C1, C2, ..., etc.) represents capacitors in the circuit.
Related Articles
What is Tantalum Capacitor: Design, Construction and Applications
Capacitor Tester: Types, Applications & Advantages
How to Test a Capacitor: Simple Steps and Tools










