Magnetic vs Dynamic Transducer: Key Differences & Applications
An electroacoustic device that transforms electrical energy into sound is called a magnetic dynamic transducer.(as well as the other way around) generally set up in speakers, microphones, and other audio outfit.
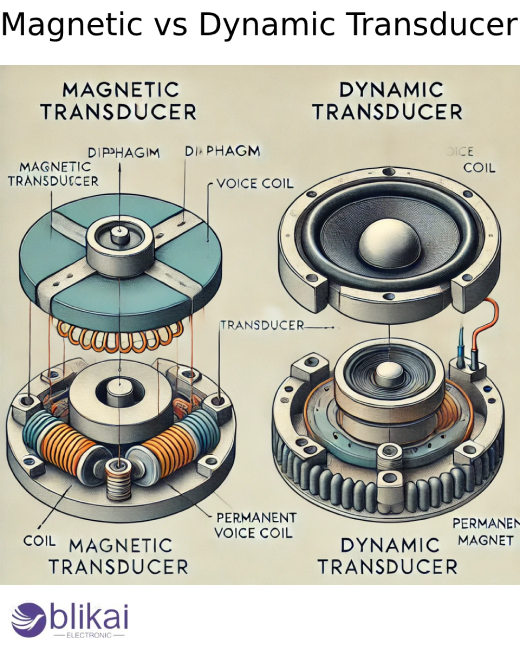
What is Magnetic Transducer?
An outfit that transforms an electrical signal into a magnetic signal or a magnetic signal into an electrical signal is called a magnetic transducer. Magnetic field measurements are usually done with magnetic sensors. either motion and location detection or magnetic material detection. Magnetic sensors are frequently employed in equipment like transducers, audio systems, and measuring tools. They operate on electromagnetic principles.
Types of Magnetic Transducer
Hall Effect Sensors: Detectors These sensors cover magnetic fields by using the Hall effect proposition. A voltage known as the Hall voltage is produced across a captain when a magnetic field flows vertical to the current in the wire. Hall effect sensors are employed in current, speed, and propinquity discovery.
Magnetoresistive Sensors: When there's a magnetic field present, these sensors alter their resistance. These sensors are employed in navigation systems, position discovery, magnetic data storehouse, and other operations that bear accurate magnetic field dimension.
Inductive Sensors: The electromagnetic induction principle underlies the operation of inductive sensors. There's an electric potential(EMF) created when a captain moves in a magnetic field. Operations including essence discovery, propinquity discovery, and speed discovery are common uses for inductive sensors.
Fluxgate Sensors: Using a magnetic core, these incredibly sensitive magnetic field sensors pick up on indeed the lowest changes in the magnetic field. Operations including geophysics, navigation, and space disquisition constantly make use of them.
Magnetic Pickup Sensors: By covering variations in magnetic magnet, these sensors are suitable to identify the motion of magnetic accoutrements. Speed sensors, such those in machineanti-lock retardation systems(ABS), constantly use them.
Working Principle of Magnetic Transducer
1. Magnetic Field Interaction: A magnetic substance or sensor element interacts with the magnetic field in sensors. Depending on the kind of magnetic sensor, several mechanisms(similar as the Hall effect, magnetoresistive, or inductive) may be involved in this commerce.
2. Detection of Magnetic Changes: The magnetic material in the transducer, similar as Hall effect sensors, is impacted by changes in the magnetic field. On the sensor material, the magnetic field induces a voltage that's vertical to both the current and the magnetic field.
3. Signal Conversion: An electrical signal is then produced from magnetic alterations. For Hall effect sensors, this signal consists of voltage. This change will cause a change in resistance in the case of magnetoresistive sensors.
4. Output Signal: The electrical signal is processed, amplified, and output as a quantifiable value. This signal can be used to detect changes in the magnetic field, monitor other relevant parameters, or gauge the strength of the magnetic field.
Applications of Magnetic Transducer
- Automotive Systems: Utilized in systems including transmission, engine control, and ABS to detect position, speed, and proximity.
- Consumer Electronics: Or wearable technology, tablets, and cellphones' compass and navigation features.
- Industrial Automation: For determining the position and speed of robotic systems and ministry.
- Medical Devices: For magnetic resonance imaging(MRI), imaging systems, and other medical bias.
- Aerospace and Navigation: Magnetometers and other navigation bias employ gyroscopes to deliver precise position data.
What is Dynamic Transducer?
A sensor or actuator that transforms one type of energy into another stoutly is called a dynamic transducer. When agitating audio and acoustics, it generally refers to a particular kind of loudspeaker or microphone that uses electromagnetic principles to restate sound into an electrical signal, or the other way around.
Types of Dynamic Transducer
1. Dynamic Microphones: Use an electromagnetic principle where a diaphragm moves within a magnetic field to induce an electrical signal. They are durable and handle high sound pressure situations well, making them popular for live sound.
2. Dynamic Loudspeakers: Also appertained to as a moving coil speaker, it produces sound by converting electrical signals using a coil and magnet. Sound swells are produced by the diaphragm, which is attached to the coil and moves back and forth.
3. Dynamic Headphones: It employs a coil and a diaphragm to transform electrical information into sound, important as moving coil speakers. They’re commonly used for their reliability and sound quality.
4. Dynamic Actuators: These are gadgets used in automation or vibration applications, including voice coils or solenoids. The same mechanism that powers loudspeakers also powers these actuators. Rather, it generates mechanical motion.
Working Principle of Dynamic Transducer
1. Electromagnetic Induction: The abecedarian idea is to attach a coil in a magnetic field to a diaphragm. The coil moves inside the glamorous field in response to movements of the diaphragm. This results in the coil producing an electric current in agreement with Faraday's Law of Induction.
2. Dynamic Microphone:
-Sound Waves: When sound waves hit the diaphragm, vibration results.
-Movement: A endless magnetic field is applied to a coil that's attached to the diaphragm.
-Induced Current: The diaphragm moves in response to sound swells, and the coil moves in the magnetic field. This creates a fluctuating current that is a representation of the sound wave.
3. Dynamic Loudspeaker:
-Electrical Signal: Through the coil, electrical sound waves are conveyed. within a continuous magnetic field.
-Coil Movement: The coil(together with the attached diaphragm) moves back and forth as a result of an electric current's creation of a magnetic field around it that interacts with the endless magnetic field.
-Sound Production: The sound surge that results from the diaphragm's movement pushes and pulls on the air, matching the electrical signal.
Applications of Dynamic Transducer
In audio and communication systems, dynamic codecs are frequently utilized. Because it can transfigure sound into electrical impulses and vice versa, it has a wide range of uses. Here are some key applications:
- Microphones
- Speakers
- Headphones
- Telecommunications
- Hearing Aids
- Sound Recording
Key Differences Between Magnetic and Dynamic Transducers
Sensitivity and Sound Quality:
Dynamic transducers are generally less sensitive than magnetic transducers. They are therefore appropriate for in-studio detailed recording. Conversely, dynamic codecs offer superior audio quality and are more versatile, even though they are marginally less accurate.
Durability and Robustness:
Dynamic transducers are typically more rugged and can handle rough conditions better than magnetic transducers. This makes them ideal for live performances and portable audio equipment.
Cost and Accessibility:
Dynamic transducers can withstand hostile environments better than magnetic transducers and are often more durable. They are therefore perfect for portable audio equipment and live performances.
Magnetic vs Dynamic Transducer
|
Feature |
Magnetic Transducer |
Dynamic Transducer |
|
Principle |
Electromagnetic induction |
Electromagnetic induction |
|
Types |
Moving coil, ribbon |
Moving coil microphones and loudspeakers |
|
Frequency Response |
Good, especially in mid-range |
Wide range, accurate sound reproduction |
|
Construction |
Simple and durable |
Simple, robust, and cost-effective |
|
Power Requirements |
Passive (no external power needed) |
Passive (no external power needed) |
|
Typical Applications |
Microphones, headphones, speakers |
Microphones, studio monitors, PA systems |
Advantages of Magnetic Transducers
1. Durability: Magnetic transducers are known for their robustness and long lifetime.
2. Efficiency: Generally more energy-effective than dynamic codecs, taking lower energy to induce the same volume of sound.
3. Clear Treble: The ability to produce high frequency sound is exclusive to magnetic transducers. It is thus appropriate for specific uses.
Disadvantages of Magnetic Transducers
1. Limited Bass Response: Due to their design, magnetic transducers may struggle with low-frequency sounds.
2. Potential for Distortion: At high volumes, magnetic transducers can sometimes produce distorted sound.
Advantages of Dynamic Transducers
1. Full-Range Sound: Dynamic transducers are able of reproducing a wide range of frequentness, from deep bass to high treble.
2. Power Handling: They can generally handle higher power inputs without distorting.
3. Cost-Effective: Dynamic transducers are often less expensive to manufacture, making them a popular choice for many audio devices.
Disadvantages of Dynamic Transducers
1. Lower Efficiency: Dynamic codecs could need more power to generate the same quantity of sound than magnetic transducers.
2. Potential for Wear: The moving components of a dynamic transducer may deteriorate with time. This could degrade the audio quality.
Related Articles
What is a Piezoelectric Transducer?Features, Specification and Applications
Active Transducer:Overview,Principle and Applications
Piezoelectric Actuator transducer : Principle & Its Applications










