Shackle Insulator: Types, Applications Working Principles

A transmission line insulator can be found in different types, including pin, strain, suspension, solid core lines, guy strains, posts, stays, and shackles. Suspension and strain insulators are used in medium- and high-voltage systems. Insulators with stay & shackle are also used in low voltage systems. Insulators prevent conductors from carrying excessive electrical current toward the earth in electrical systems. In the power system, these devices are essential because of their high resistance. Shackle insulators are discussed in this article as well as their use in applications.
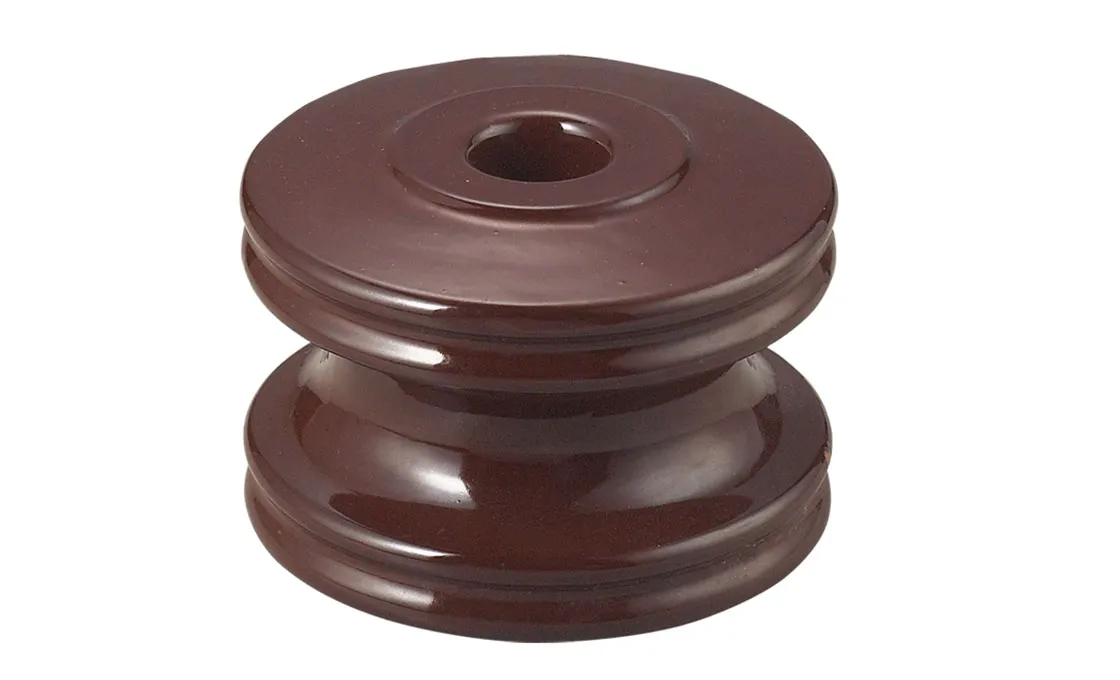
What is a Shackle Insulator?
What is a Shackle Insulator
The use of shackle insulators in electrical power transmission and distribution systems is common in order to support and insulate overhead power lines. Each end of the insulator resembles a shackle or loop and consists of a porcelain or glass insulator unit. Power line conductors are attached to one end of the insulator by means of a pole or tower and to the other end by means of a pole or tower.
They ensure safe and efficient transmission of electricity by preventing electrical current from leaking into supporting structures. Shackle insulators contribute to maintaining the integrity and reliability of power distribution networks by securely suspending electrical conductors and insulating them. In overhead power line installations, they are essential components because they can withstand temperatures of over 100 degrees Celsius, humidity, and mechanical stress.
Types of Shackle Insulators
Power transmission and distribution systems typically use a variety of different types of shackle insulators. The designs and characteristics of each type are suited for specific applications. Shackle insulators can be classified into the following types:
Glass Shackle Insulators
Tempered or toughened glass is used for glass shackle insulators. Thermal stress and environmental effects are not a problem for them because they are powerful and highly resistant to them. Metal end fittings are used to attach glass shackle insulators to supporting structures and conductors, similar to porcelain insulators. A glass insulator's mechanical strength and resistance to vandalism or harsh environmental conditions make it a popular choice for applications that require high mechanical strength. A common use for them is in coastal regions, industrial environments, and pollution-prone areas.
Polymer Shackle Insulators
A polymer shackle insulator is typically made from a high-quality polymer material such as silicone rubber or a composite material. In addition to being lighter, more flexible, and more resistant to contamination and tracking, these insulators offer several advantages over traditional porcelain and glass insulators. Since polymer shackle insulators are less likely to break and vandalize, they are suitable for challenging environments and applications. In areas with high pollution levels or seismic activity, they are increasingly being used in overhead power line installations.
Porcelain Shackle Insulators:
Ceramic shackle insulators feature excellent electrical insulation properties and mechanical strength, making them an ideal choice for high-quality applications. Porcelain units are generally accompanied by metal fittings at each end of these insulators. Furthermore, porcelain bodies allow connections to supporting structures and power line conductors, besides providing electrical insulation. Unlike steel shackle insulators, porcelain shackle insulators can withstand high mechanical loads, making them highly useful for overhead power line installations.
Note: Various types of shackle insulators are suitable for different applications and operating conditions due to different characteristics and advantages. Glass insulators are highly resistant to environmental factors, whereas porcelain insulators have higher mechanical strength and durability. In contrast, polymer insulators are lightweight and resist contamination better. It is important to take into account a variety of factors when selecting the best shackle insulator, such as the operating voltage and mechanical load requirements, as well as cost and environmental conditions.
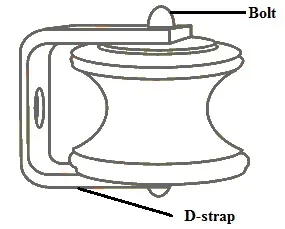
Shackle Insulator Construction
A hole in the middle of the shackle insulator allows it to be bolted together. Each side of the insulator is covered with a 25mm galvanized plate. Plates are arranged on the other side in the region of the pole. With the help of soft binding wires, the conductor is fixed within the channel. When the distribution line's angle changes, these insulators are more effective than strain insulators.
Construction
Their shackle insulators come in three sizes: (50mm x 65mm), (75mm x 90mm) & (100mm x 115mm). Main lines usually require 75 mm x 90 mm & 100 mm x 115 mm insulators, while low voltage connections in houses require 50 mm x 65 mm insulators.
Working Principle
In electrical transmission and distribution systems, shackle insulators provide mechanical support and electrical insulation for overhead power lines. An explanation of how a shackle insulator works can be found here:
Electrical Insulation
In addition to protecting power line conductors, shackle insulators also provide electrical insulation between the conductor and structures such as poles, towers, and crossarms. Conductors and their supporting structures are protected by this insulation, which prevents electrical current from flowing between them, preventing short circuits and ensuring safe and efficient transmission.
Dielectric Properties
Materials with high dielectric strength are typically used for shaker insulators, such as porcelain, glass, or polymer. It is possible to pass electrical current through these materials even at high voltages. It creates a barrier that prevents electrical leakage and ensures the integrity of the electrical insulation system by effectively separating the energized power line conductor from the grounded support structure.
Mechanical Support
Additionally, power line conductor shackle insulators provide mechanical support as well as electrical insulation. Conductor and environmental factors, such as wind, ice, and snow, exert mechanical loads on the insulator body and metal end fittings. The integrity of the insulator prevents the power line from sagging, swinging, or being mechanically disturbed because of its structural integrity.
Attachment to Conductor and Structure
Power line conductors and supporting structures are attached to shackle insulators through metal end fittings. In contrast, the attachment fitting facilitates mounting the insulator to the supporting structure while the conductor fitting secures the conductor to the insulator. Overhead power lines operate efficiently and reliably with these fittings, providing reliable electrical and mechanical connections.
Environmental Resistance
Moisture, pollution, ultraviolet radiation, and temperature fluctuations are all conditions that these insulators are designed to hold up to. Corrosion- and degradation-resistant materials are used for the insulator body and metal end fittings in outdoor environments. To further enhance its resistance to environmental hazards, waterproofing materials can also be applied to the insulator.
Applications of Shackle Type Insulators
Electric power transmission and distribution systems commonly use shackle type insulators, also called shackle insulators. They ensure safe and reliable transmission of electricity by providing electrical insulation and mechanical support. The following are some examples of how shackle type insulators are used:
Overhead Power Transmission Lines
Often, bare conductors or insulated cables are supported and insulated with shaker insulators in overhead power lines. Transmission line crossarms are typically attached to poles, towers, or other supporting structures along the transmission line. A shackle insulator prevents electrical leaks, short circuits, and ground faults. Electrical clearance is maintained between grounded structures and energized conductors.
Distribution Lines
Electric current is distributed to homes, businesses, and industrial facilities by means of overhead power lines that utilize shackle insulators to support and insulate them. Distribution conductors are insulated and mechanically supported by these insulators mounted on distribution poles or transformers. In addition to reducing the risk of electrical accidents and service interruptions, shackle insulators ensure reliable and efficient delivery of electricity to end users.
Substation Equipment
Various equipment components, including busbars, switches, and disconnectors, are also insulated and supported by shackle insulators in electrical substations. In addition to maintaining electrical isolation within the substation, they prevent current flow and ensure that equipment operates safely. Insulators in substations provide critical protection against electrical faults and system failures due to their ability to withstand high voltages and mechanical stresses.
Railway Electrification
Overhead catenary wires that supply electric trains with power are supported and insulated by shaker insulators. This insulator ensures electrical isolation of catenary wires while maintaining clearances necessary for safe train operation. By contributing to the sustainable and modernization of rail transportation, shackle insulators play a crucial role in railway electrification systems.
Telecommunication Infrastructure
Overhead fiber optic cables and communication wires use shaker insulators as part of their infrastructure. Insulators protect communication cables from external interference by providing electrical isolation and mechanical support. Business and consumer communication services are supported by shackle insulators in telecommunication networks.
Faqs
Question 1: How do shackle insulators prevent electrical leakage?
Answer: Using a shank insulator prevents the flow of electrical current between the grounded supporting structure and the energized conductor, avoiding short circuits and ground faults. Conductors are effectively isolated from structures due to the dielectric properties of insulators.
Question 2: What factors should be considered when selecting shackle insulators?
Answer: Insulators used for shackles should be selected according to factors such as the operating voltage, the demand for mechanical load, the environmental conditions, and compatibility with mounting hardware. A high voltage, mechanical stress, and environmental factors have to be able to penetrate the insulators in order for reliability to be maintained.
Question 3: How are shackle insulators installed in power transmission and distribution systems?
Answer: Typically, shaker insulators are mounted on poles, towers, or crossarms that support overhead power lines. Conductor fittings on the insulators are connected to the conductor connections of the insulators using appropriate hardware.
Question 4: Can shackle insulators be used in harsh environmental conditions?
Answer: A variety of environmental conditions can be tolerated by shackle insulators. Their moisture resistance, pollution resistance, UV resistance, and temperature resistance make them ideal for outdoor use. The durability, corrosion resistance, and tracking resistance of porcelain, glass, or polymer insulation makes them ideal for outdoor use.
Question 5: What maintenance is required for shackle insulators?
Answer: Periodic inspections of shaker insulators are required to ensure that they are not damaged, contaminated, or deteriorating. Electrical systems should be maintained by replacing any damaged or faulty insulators as soon as possible.
Final Thoughts
Among the many types, applications, and working principles of shaker insulators in electrical engineering, they represent an integral part of power transmission and distribution systems. In addition to providing robust electrical insulation and mechanical support, they are composed of porcelain, glass, and polymer compounds. Electricity and communication signals are safely and reliably conveyed through shackle insulators in overhead transmission lines, railway electrification, and telecommunication networks.
These materials are resilient in diverse environmental conditions due to their dielectric properties and mechanical reinforcement. A shackle insulator is a linchpin supporting modern society's technological advancements and connectivity by combining engineering precision with practical utility. Check out more on: https://www.blikai.com/.
Active vs Passive Components: What's the Differences? (Guide)
Top 10 Common Electronic Components Guide
Exploring Electronic Components: Innovations and Applications
Exploring Electronic Components(Guide)
Inductor vs Resistor: What’s the Differences?
What Is CBB61 Capacitor - Function and Applications
Switching Diodes: Definitions, Principles, Applications, and Future Trends
The Automotive PCB Market Seizes Fresh Opportunities
Cross Sectional Area of Wire: Everything You Need to Know
Difference Between Serial and Parallel Communication