What’s the Difference Between LR44 and 357 ?

Description of LR44

The LR44 battery, a button cell powered by alkaline chemistry, distinguishes itself with its adaptable utility across a diverse array of devices. Boasting a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts and dimensions of 5.4mm in diameter and 11.6mm in height, it presents a commendable energy density. This battery variant commonly serves in compact electronic devices, wristwatches, electronic calculators, and medical apparatuses. Users should remain cognizant of its voltage decline characteristics, as its output gradually diminishes during discharge, potentially posing reliability challenges for some devices if the voltage dips below a specific threshold. Despite its extensive adoption, the LR44's taller stature might pose fitting concerns in select battery compartments, thus warranting careful consideration of compatibility issues.
Specifications
| Features | LR44 |
| Battery Type | Alkaline Manganese Batteries |
| Nominal Voltage | 1.5V |
| Nominal Capacity | 120mAh |
| Operating Temperature Range | -10℃ to 60℃ |
| Diameter (inch) | 0.457inch |
| Diameter (mm) | 11.6mm |
| Height (inch) | 0.213inch |
| Height (mm) | 5.4mm |
| IEC (JIS) | LR44 |
| Mass (oz) | 0.0705oz |
| Mass (g) | 2g |
LR44 Battery Substitutes
AG13: AG13 serves as a commonly recognized substitute for LR44, boasting identical size and voltage specifications, rendering it a suitable stand-in.
A76: A76 represents another designation interchangeable with LR44, featuring matching size and voltage parameters.
357: The 357 battery, alternatively labeled as SR44, is frequently deemed exchangeable with LR44 owing to its similar size and voltage ratings.
SR44: SR44 stands as another alternative synonymous with LR44, offering matching size and voltage attributes and frequently employed interchangeably.
G13: G13 provides yet another alternative designation for LR44, aligning closely with its size and voltage characteristics.
PX76A: PX76A emerges as another equivalent counterpart to LR44, commonly utilized in photography apparatuses.
Description of 357 battery
The 357 battery, categorized as a silver oxide cell, stands out for its dependable performance in precision instruments. Boasting a nominal voltage of 1.55 volts and typically offering a capacity of around 150mAh, the 357 demonstrates a steady and uniform voltage output over its lifespan, rendering it an optimal energy source for watches, calculators, toys, and diverse medical tools. Renowned for its prolonged longevity, spanning from 30% to 100% more than an LR44 battery, the 357 affords an extended operational span, thereby minimizing the need for frequent battery replacements. Its compact dimensions, measuring 11.6mm in diameter and 5.4mm in height, enhance its compatibility across various battery compartments.
Specifications
| Features | 357 |
| Battery Type | Silver Oxide |
| Nominal Voltage | 1.55V |
| Nominal Capacity | 150mAh |
| Operating Temperature Range | -28C to 55 C |
| Diameter (inch) | 0.457inch |
| Diameter (mm) | 11.6mm |
| Height (inch) | 0.213inch |
| Height (mm) | 5.4mm |
| IEC (JIS) | |
| Mass (oz) | |
| Mass (g) | 2.3g |
357 Battery Substitutes
SR44: SR44 emerges as one of the most prevalent alternatives for the 357 battery, boasting identical size and voltage specifications, facilitating seamless interchangeability.
AG13: AG13 represents another equivalent option for the 357 battery. Similar to SR44, it matches in size and voltage, commonly serving as a substitute.
A76: A76 stands as a designation interchangeable with the 357 battery, sharing congruent size and voltage characteristics.
SG13: SG13 provides an additional alternative designation for the 357 battery, aligning closely with its size and voltage attributes.
PX76A: PX76A presents yet another counterpart to the 357 battery, frequently employed in the realm of photography equipment.
LR44 vs. 357: Difference in Specifications
| lR44 | 357 | |
| Battery type | Alkaline Manganese | Silver Oxide |
| Nominal Voltage | 1.5V | 1.55V |
| Nominal Capacity | 120mAh | 150 mAh |
| Operating Temperature Range | -10℃ to 60℃ | |
| Diameter (inch) | 0.457inch | |
| Diameter (mm) | 11.6mm | 11.6mm |
| Height (inch) | 0.213inch | 0.213inch |
| Height (mm) | 5.4mm | 5.4mm |
| IEC (JIS) | LR44 | |
| Mass (oz) | 0.0705oz | |
| Mass (g) | 2g | 2.3g |
Chemical Contrasts: LR44 (Alkaline) vs. 357 (Silver Oxide)
Alkaline LR44 Battery
LR44 batteries harness alkaline chemistry, typically comprising zinc and manganese dioxide as core constituents.
Performance Traits:
Alkaline chemistry affords a relatively elevated energy density.
Voltage output gradually diminishes as the battery discharges.
Versatile suitability across a broad spectrum of applications with varying power requisites.
Common Usages:
LR44 batteries find widespread application in small electronic devices, watches, calculators, and medical apparatuses.
Silver-Oxide 357 Battery
357 batteries employ silver oxide chemistry, featuring silver oxide as the positive electrode, zinc as the negative electrode, and an alkaline electrolyte.
Performance Traits:
Silver oxide chemistry ensures a stable and comparatively consistent voltage output for the majority of the battery's lifespan.
Enhanced energy density compared to alkaline counterparts, rendering them apt for precision-demanding devices.
Typically deployed in applications necessitating unwavering and dependable power provision, such as watches and medical instruments.
Common Usages:
357 batteries are prevalent in watches, calculators, toys, and various medical instruments.
Factors Influencing Choice Between LR44 and 357:
Voltage Stability: The silver oxide chemistry of 357 batteries yields a more stable voltage output, making them preferable for precision instruments.
Energy Density: Silver oxide batteries typically boast higher energy densities, enabling them to power devices with elevated energy requirements.
Voltage Comparison: LR44 vs. 357 Batteries
LR44 is specified at 1.5v, whereas 357 is specified at 1.55v.
Device Compatibility:
LR44 Batteries:
Suitable for devices compatible with a 1.5-volt power source.
Commonly utilized in diverse electronic devices, watches, calculators, and medical instruments.
357 Batteries:
Optimal for devices requiring a slightly elevated voltage of 1.55 volts.
Frequently employed in precision tools like watches, calculators, and medical apparatuses.
Voltage Stability:
LR44 Batteries:
Voltage output gradually declines as the battery discharges.
May be suitable for applications tolerant of gradual voltage reduction.
357 Batteries:
Silver oxide chemistry ensures a steadfast and relatively uniform voltage output over the majority of the battery's life.
Beneficial for precision devices necessitating consistent power delivery.
Voltage Sensitivity:
LR44 Batteries:
Certain devices may encounter reliability issues if the battery voltage drops below a specific threshold (e.g., 1.2 volts).
357 Batteries:
Preferable for applications demanding precise voltage levels, such as watches, where steady and accurate voltage is critical for precise timekeeping.
Energy Density:
LR44 Batteries:
Deliver a commendable energy density at 1.5 volts, suitable for various applications.
357 Batteries:
Higher voltage rating (1.55 volts) potentially contributes to increased energy density, catering to devices with heightened energy requirements.
Understanding the voltage disparities between LR44 and 357 batteries is crucial for selecting the appropriate power source for specific devices. The marginally higher voltage of the 357 battery, coupled with its consistent output, renders it particularly apt for precision instruments and applications necessitating precise voltage regulation. It's essential to consider the device's voltage sensitivity and select the battery accordingly to ensure optimal performance.
Voltage Decline
The silver oxide 357 maintains a more steadfast voltage until reaching 1.2v at the end of its lifespan, while the alkaline LR44 declines to 1.0v.
Alkaline LR44 Battery:
Voltage Deterioration Attributes:
During discharge, the LR44 battery experiences a gradual and relatively linear reduction in voltage output.
Voltage may decrease to 1.0 volts or lower as the battery nears depletion.
Implications:
Devices relying on LR44 batteries may encounter a consistent voltage decline, potentially affecting performance in applications sensitive to voltage fluctuations.
Certain devices may exhibit reliability issues if voltage falls below a specific threshold.
Silver Oxide 357 Battery:
Voltage Deterioration Attributes:
The silver oxide chemistry in 357 batteries ensures a more uniform voltage output throughout most of the battery's life.
Voltage remains stable until the final stages, where it may decline to 1.2 volts.
Implications:
Devices powered by 357 batteries enjoy a steadier and more consistent voltage supply.
Precision instruments, like watches, calculators, and medical devices, can uphold accurate functionality until the battery nears depletion.
Considerations and Applications:
Precision Devices
LR44 Batteries:
Suited for applications tolerating a gradual voltage decrease.
May suffice for applications with lower precision demands.
357 Batteries:
Optimal for precision instruments requiring a stable and unwavering voltage supply.
Frequently utilized in watches and medical devices demanding precision.
Device Reliability
LR44 Batteries:
Concerns regarding reliability may arise in devices sensitive to voltage drops below a specified threshold, such as 1.0 volts.
357 Batteries:
The consistent voltage output enhances device performance reliability.
End-of-Life Voltage:
LR44 Batteries:
Voltage may decline to 1.0 volts or lower, indicating the conclusion of its usable lifespan.
357 Batteries:
Maintains a steady voltage until the end, with a decline to 1.2 volts, offering extended and more predictable functionality.
Understanding voltage deterioration attributes is pivotal in selecting the appropriate battery for specific applications, particularly those necessitating precision and reliability. The choice between LR44 and 357 batteries should align with the voltage requisites and sensitivity of the devices they power.
Lifespan: LR44 vs. 357 Batteries
Alkaline LR44 Battery:
Lifespan Attributes:
The longevity of LR44 batteries is influenced by factors like discharge rate, usage patterns, and the specific requirements of the devices they power.
Typically possess an average nominal capacity ranging from 110 to 130 mAh.
Implications:
Suitable for a diverse array of applications with moderate energy requirements.
Performance may vary depending on usage patterns and device specifications.
Silver Oxide 357 Battery:
Lifespan Attributes:
The silver oxide composition in 357 batteries often affords a lengthier lifespan compared to LR44 batteries.
Boasting a higher nominal capacity, typically falling within the range of 150 to 200 mAh or even higher, contingent on discharge currents.
Implications:
Well-suited for applications demanding higher energy and prolonged operational durations.
Preferred for precision instruments necessitating a dependable and enduring power source.
Percentage Difference in Lifespan:
The assertion that "357 typically lasts 30% to 100% longer than the LR44" underscores a substantial advantage favoring the 357 battery.
Considerations and Applications:
Devices with High Energy Demands:
LR44 Batteries:
Suitable for devices with moderate energy requirements.
357 Batteries:
Preferred for devices with elevated energy needs owing to their higher nominal capacity.
Precision Instruments:
LR44 Batteries:
Sufficient for applications with less stringent precision demands.
357 Batteries:
Optimal for precision instruments like watches and medical devices, where durability and stable voltage are paramount.
Impact on Frequency of Battery Replacement:
LR44 Batteries:
May necessitate more frequent replacements in devices with heightened energy demands.
357 Batteries:
Extended lifespan reduces the frequency of battery replacements, offering convenience and potentially lowering long-term expenses.
Shelf Life:
LR44 Batteries:
Typically possess an average shelf life of around 3 years, although newer versions may offer extended shelf lives (4-5 years).
357 Batteries:
Standard 357 models often boast a 5-year shelf life, showcasing their longevity on the shelf.
LR44 vs. 357 :The Difference in Dimensions
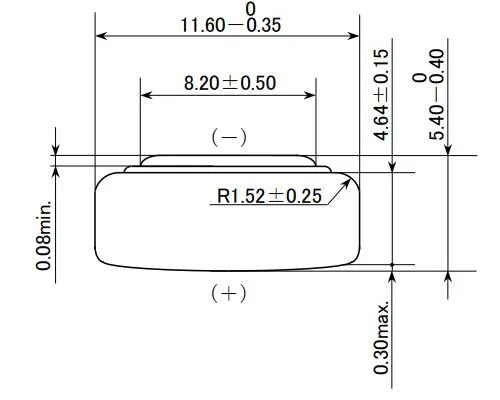
LR44 Dimensions
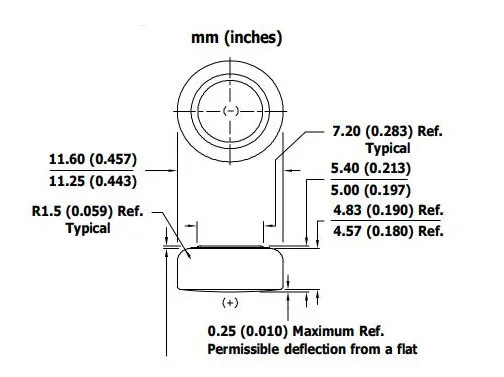
LR44 Battery Manufacturer
Murata stands as a prominent firm dedicated to crafting, producing, and delivering cutting-edge electronic materials, state-of-the-art electronic components, and versatile, high-density modules. Our groundbreaking advancements find application across a broad spectrum, spanning from mobile phones, household appliances, and automotive systems to energy management solutions and healthcare apparatuses.
Final Words
Although these button cells exhibit similarities in size and external dimensions, their internal chemical makeup and performance attributes distinguish them from each other. LR44, featuring an alkaline formulation, serves a variety of devices with moderate energy requirements, ensuring stable discharge and cost-efficient operation. Conversely, the 357, powered by silver oxide chemistry, distinguishes itself with its elevated nominal voltage, extended lifespan, and aptness for precision instruments.
Exploring Electronic Components(Guide)
Automotive Relays: Types, Advantages & Applications
Human-Machine Interface(HMI) Technology [Explained]
Digital Comparator and Magnitude Comparator Guide
Introduction to Flash Memory
How to Test Automotive Relays (Guide)
Top 10 Common Electronic Components Guide
Exploring Electronic Components: Innovations and Applications
DC Transmission: Types, Applications & Advantages
What TLV3201AQDCKRQ1 Voltage Comparator is and How It works










