Top 10 Common Electronic Components Guide
Electronic components are the fundamental elements of electronic technology and act as the essential building blocks of electronic circuits. As electronic technology and its applications rapidly advance, the number of components used in design processes continues to grow. It is vital for electronic engineers and enthusiasts to understand the characteristics and applications of commonly used electronic components. This article introduces the top ten electronic components frequently utilized by engineers and offers guidance on selecting the appropriate components.
Resistor
The resistor is the most commonly used component in a circuit. It functions as a current-limiting component and has a resistance effect on current. By adjusting the resistance value, the current flowing through the connected branch can be controlled, ensuring that various components in electronic equipment operate steadily at their rated current. Common types of resistors include thermistors, varistors, voltage divider resistors, color ring resistors, power resistors, and photoresistors. Resistors can be represented by the symbol Ω or the letter R.
.webp)
Capacitors of Electronic Components
In the realm of circuitry, a capacitor possesses the capacity to retain electric charge at a designated voltage. This property is known as capacitance, denoted by C. The farad, abbreviated as F, serves as the standard unit for capacitance. The capacitance value of a capacitor dictates its charge-storing capability. In circuit diagrams, capacitors are typically denoted with the identifier starting with the letter C, for instance C01, C02, C03, C100, and so forth.
.webp)
Diode of Electronic Components
A diode, also referred to as a crystal diode or simply diode, comprises two electrodes (terminals). It exhibits unidirectional conductive characteristics, permitting current flow exclusively in one direction. It finds applications in tasks such as rectification, protection, switching, and detection.
.webp)
Zener Diode of Electronic Components
A Zener diode possesses unidirectional conduction properties, primarily intended to channel current in a specific direction. Various types of diodes exist, including forward-conducting and reverse-blocking diodes. Its applications span voltage stabilization, power conditioning, overvoltage protection, and more. Zener diodes provide diverse voltage stabilization choices through appropriate breakdown voltage and power rating selection. They are crucial components widely employed in electronic circuits to ensure circuit reliability and voltage stability.
.webp)
Inductor of Electronic Components
An inductor is a vital electronic component utilized for storing and releasing electrical energy. It typically comprises one or more coils crafted from conductive material, wound in a spiral or ring configuration. Inductors operate by converting current into magnetic fields through electromagnetic induction, generating a counter electromotive force in response to fluctuating currents. They primarily function to impede changes in current and regulate the rate at which current rises and falls. Inductors play essential roles in filtering, current and voltage adjustment, and energy storage within circuits. Common types encompass coil inductors, inductive sensors, and transformers. Key characteristics of an inductor, such as inductance value, current handling capacity, and frequency response, determine its performance. Widely integrated across electronic equipment, communication systems, power supplies, automation control, and other domains, inductors serve pivotal roles in diverse applications.
.webp)
Varicap Diode of Electronic Components
A varicap diode is a specialized diode that modulates its capacitance by adjusting the reverse voltage applied to it. Primarily employed in applications like tuned circuits and frequency synthesizers, it is prized for its rapid response, high reliability, and compact dimensions, rendering it ideal for wireless communications, broadcasting, and related domains. This component offers flexibility and adjustability, facilitating precise frequency tuning capabilities within circuits.
.webp)
Transistor of Electronic Components
The transistor, a semiconductor device, regulates and can amplify current. Its primary role is transforming weak signals into electrical signals with greater amplitudes. Widely applied in electronic equipment, communication systems, computers, power control, and other domains, its small size and reliability establish it as an indispensable component in modern electronic technology.
.webp)
Field Effect Transistor of Electronic Components
.webp)
Also known as FET (Field Effect Transistor), this type is prevalent in electronic circuits for amplification and switching tasks. Field-effect transistors feature high input impedance, low output impedance, and minimal power consumption. They also offer high gain and rapid switching capabilities. Variants include MOSFET (metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor) and JFET (junction field effect transistor), tailored to different structural needs. Field-effect transistors find extensive use in analog circuits, digital circuits, power amplifiers, and related fields, pivotal to contemporary electronic equipment.
Sensor of Electronic Components
A sensor, or transducer, detects physical quantities and converts them into electrical signals or other discernible forms for analysis, processing, and control applications. Found across industries such as industrial automation, medical equipment, automotive, aerospace, environmental monitoring, and consumer electronics, sensors vary by type depending on the measured physical quantity. These include temperature, pressure, light, acceleration, humidity sensors, and more. Renowned for their precision, sensitivity, and reliability, sensors play a critical role in achieving intelligence, automation, and unmanned operational capabilities.
.webp)
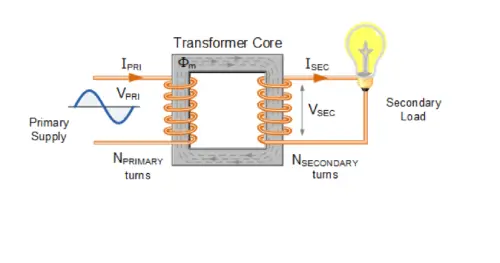
Transformer of Electronic Components
A transformer is an electrical apparatus designed to alter the voltage of alternating current. It comprises two or more coils, termed primary and secondary coils, wound around a magnetic iron core. Utilizing electromagnetic induction principles, a transformer converts input voltage into the desired output voltage while maintaining the electrical energy's power balance. Widely employed in power systems, electronic equipment, communication networks, and industrial applications, transformers are valued for their high efficiency, reliability, and energy conservation attributes. They play a crucial role in power transmission and distribution, and can also serve isolation purposes due to the complete electrical isolation between their input and output coils.
How to Purchase Electronic Components?
As the electronic components industry evolves swiftly, engineers face numerous challenges in sourcing suitable components. With a plethora of component types, multiple brands and manufacturers, and occasional shortages, engineers must navigate these complexities effectively.
BLIKAI stands out as a premier PCB manufacturer, offering top-notch PCB manufacturing and assembly solutions. Their comprehensive services encompass PCB design and layout, manufacturing, assembly, and testing, providing engineers with streamlined solutions.
BLIKAI boasts an extensive inventory of over 430,000 components, empowering engineers with ample choices. Engineers can pre-order components prior to placing a PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) order, mitigating concerns about last-minute component shortages. Furthermore, BLIKAI offers a free private warehouse service, alleviating worries about inventory costs and labor fees.
Choosing BLIKAI enables engineers to save considerable time, money, and effort, allowing them to concentrate on other critical project facets. Simply provide the PCB design files and a list of required components, and BLIKAI will manage the sourcing and assembly process.
In today's dynamic electronic components industry, engineers confront the challenge of procuring the right components. As a leading PCB manufacturer, BLIKAI offers comprehensive PCB assembly services. Engineers can rely on BLIKAI's extensive inventory and expert team to efficiently procure necessary components and benefit from dependable, high-quality assembly services. Opting for BLIKAI empowers engineers to focus on other project aspects, ensuring successful implementation.
Related Articles
Exploring Electronic Components - Their Varieties, Roles, and Future Directions
What are Audio Transformers for?
Comprehensive Guide to Common Sensors
PNP Transistor? Construction, Working & Applications
What is an Air Core Inductor? [Everything Explained]
Diode:Construction,Types & Working
How Does a Resistor Work [Fully Explained]










