Evaporator Coil: Function, Types & Troubleshooting Guide
Introduction to Evaporator Coils
The evaporator coil is a very important element of any cooling system that may be an air conditioner, heat pump or refrigeration. It will take a key position in the heat exchange process, which involves absorbing heat from the indoor environment and permitting the system to provide cool, conditioned air. HVAC systems would be unable to regulate the desired temperatures indoors without a properly functioning evaporator coil, which means that they would be less comfortable and consume more energy. Its importance can be known both by homeowners and technicians since timely identification of issues may save them money in terms of repairs. The evaporator coil guarantees energy efficiency and the maximum performance of the cooling system.
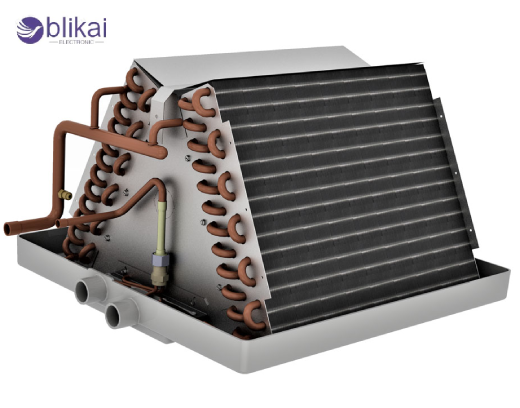
How an Evaporator Coil Works
A refrigeration cycle absorbs the heat in the indoor air into the evaporator coil. Refrigerant is a special fluid that is extremely heat absorbing and passed through the coil. When warm indoor air passes over the cold coil surface, refrigerant in the coil absorbs the heat which is converted to a gas. This plays a vital role during the cooling process as it cools the air and brings the temperature in the house to a low. The system has some form of a blower fan that recirculates the cooled air to the living space. The information about such a process will come in handy during troubleshooting of such questions as a lack of cooling or frozen coils that are likely to indicate a problem with air flow or refrigerant.
Main Types of Evaporator Coils
Evaporator coils are available in many different forms that are applied to specific performance requirements and performance needs. The choice of the proper type of the coil will ensure the efficiency and ease in the maintenance process, and compatibility with the HVAC system.
|
Type |
Structure & Material |
Applications |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
A-Coil |
“A”-shaped, often copper or aluminum |
Residential HVAC systems |
Compact, efficient |
Harder to clean |
|
N-Coil |
“N”-shaped configuration |
High-efficiency units |
Larger surface area |
More expensive |
|
Slab Coil |
Flat horizontal layout |
Ceiling or floor systems |
Easy installation |
Lower airflow |
|
Plate Coil |
Flat plate design |
Refrigeration units |
Good for compact designs |
Lower heat transfer efficiency |
The type of coil used ought to be dependent on the space and efficiency that is required as well as compatibility with the system. These are large coils and they should be installed and kept properly to achieve their maximum life and prevent the usual complications.
Common Problems and Symptoms
Frozen Evaporator Coil
The lack of heating capacity of an HVAC system with a frozen evaporator coil is the most frequent issue. This tends to happen because of lack of airflow as a result of dirty filters or blocked vents or lack of refrigerant. The coil is accumulated with ice that impairs its capacity to absorb and hence cooling performance of the coil is low as well as where there is no treatment compressor can be damaged.
Refrigerant Leaks
Breaks in the evaporator coil decrease the refrigerant charge, which leads to inadequate cooling and high usage of energy usage. The symptoms are warm air coming through vents, hissing around the coil, and lowered efficiency of the system. The detection and fixing of the leak is vital within a short time to avoid additional damage.
Dirty or Clogged Coils
The presence of dust, dirt and debris in the area surrounding the coil on its fins inhibits the movement of air and lowers the heat exchange capacity. The symptoms include uneven cooling, increased energy bills, and short-cycling of the system occasionally. Cleaning and inspection will avoid these problems.
Corrosion and Physical Damage
The corrosion of coils with time may occur because of moisture or exposure to chemical elements, particularly in rainy or seashore conditions. Physical damage, e.g., bent fins or punctures, may be a performance-destroying factor too, resulting in refrigerant leak or cooling capacity decrease.
Poor Cooling Performance
Without proper cooling of the rooms, the system can stop working in case the evaporator coil is faulty. The other signs are abnormal sounds, irregular breathing, or a high rate of cycling of the system. One should also determine the source of the problem, be it the airflow or the refrigerant or the location of the coils and then make the necessary repair.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance Guide
Inspecting the Coil
The first step is the visual inspection of the coil regarding dirt, ice, corrosion, or any other physical damage. Test the airflow and straightness of the coil fins. Sometimes with the turn of a cleaning needle or a micro adjustment of the fin, minor problems can be solved.
Cleaning the Coil
Sweep dust and other debris with a soft brush, vacuum or commercial coil cleaner. In an extreme deposition, the services of a professional coil cleaner may need to be hired. The cleaning has positive impacts such as the improvement of air circulation, cooling, and reduction of the frozen coils potential.
Checking Refrigerant Levels
Low refrigerant is a common cause of frozen or underperforming coils. Refrigerant levels should be checked and leaks monitored by technicians. Installing the right refrigerant in place of the old system will guarantee that the coils are operating correctly otherwise damage may be incurred in the long run.
Airflow Assessment
Vents, ducts and filters should not be blocked. There should be sufficient airflow to facilitate the heat exchange and prevent coil freezing. It is also possible to change and clean ducts with frequency that would aid in ensuring that there is a constant flow of air and systems are effective.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Have regular checkups done by professional staff members to determine any problems at an early age. Refrigerant charge is to be maintained, filters are to be kept clean, changed or maintained, and condensate drain to be clear. Preventive maintenance prolongs life of the coil, reduces energy costs as well and reduces unexpected repair.
Replacement and Cost Considerations
The coils of an evaporator can serve for many years, provided they are maintained, but it happens that sometimes the installations may need changing. Small leaks or accumulated dirt can be repaired; however, the corrosion, physical damage, and major refrigerant problems normally demand a complete coil replacement. The expenses differ by the type of coil, the size of the system and the costs of labor. An A-coil used in residential areas could be cheaper than an N-coil used in high-efficiency systems. It is important to make sure that it is compatible with the current condenser coil to prevent any performance problems. The replacement coils that will help to save money in the long term will be the ones that do not require a lot of electricity and also do not need any other repairs.
Evaporator Coil vs. Condenser Coil
|
Aspect |
Evaporator Coil |
Condenser Coil |
|
Function |
Absorbs indoor heat |
Releases outdoor heat |
|
Location |
Indoor unit |
Outdoor unit |
|
Temperature |
Cold (evaporating refrigerant) |
Hot (condensing refrigerant) |
|
Phase Change |
Liquid → Gas |
Gas → Liquid |
|
Maintenance Needs |
Prone to icing |
Prone to dust clogging |
The two coils are complementary despite the fact that they have a vital role to play in the refrigeration cycle. Both systems must also be maintained frequently to ensure that the efficiency of the systems as well as the wastage of energy is eliminated.
Best Practices for Longevity
In order to achieve the maximum life and performance of evaporator coils, there are some best practices that should be observed. The cleaning procedure and changing of air filters on a regular basis minimize dirt that may block airflow. The proper amount of refrigerant can prevent freezing or unproductive working. Coats or other protective materials that are corrosion resistant may also help increase the life of coils, particularly in salty or wet areas. Wear and tear are also minimized by avoiding short-cycling of the HVAC system and making sure that the condensate is drained away. These practices can be used to prevent expensive repairs that might be incurred by homeowners and technicians and also to maintain the comfort indoors.
FAQs About Evaporator Coils
Can I clean an evaporator coil myself?
Light cleaning does not require much, but it is only a licensed technician who can assist with deep cleaning or any other problems of the refrigerant.
Are evaporator and condenser coils interchangeable?
No, they are used for various purposes in the system and locations.
Conclusion
The evaporator coil is one of the key components of the HVAC system and refrigeration that has the responsibility to ensure that the interiors are cooled effectively. Regular maintenance, troubleshooting in time, and understanding the purpose and the type of the system would have prevented system failures to save energy. Regardless of cleaning, inspection or changing coils according to best practices is the way to achieve maximum performance, comfort and long life of the cooling system. Evaporator coils should be properly maintained, as this is a cost-saving investment that conserves energy and, at the same time, improves indoor air quality.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.
How does HMI Improve User Interaction in Control Systems?
What a Human Machine Interface system is and How it works
The Transmission System and Its Function
Types of Industrial Control Systems: Everything Explained
Distributed Power Management in Electronics: ICs & Systems Guide
How Does a Fuse Work? [Full Guide]
Air Conditioner Capacitor Basics: What You Need to Know
Unveiling Polypropylene Capacitors: Principles, Applications, and Future Trends
Motherboard: The Core of Computer Hardware
What do Microminiature and Ultraminiature RF connectors entail?










