Motherboard: The Core of Computer Hardware
In the computer hardware system, the motherboard plays a core role. It carries most of the hardware devices in the computer and determines the computer's performance and functions. This article will introduce you to the basic knowledge of computer motherboards and help you better understand and use your computer.
Ⅰ.The composition and working principle of the motherboard

Figure1:motherboard
Computer motherboard is mainly composed of the following parts: processor, memory slot, chipset, expansion slot, interface slot, power interface, etc.
The processor is the brain of the computer, responsible for executing various instructions;
The memory slot is used to install memory modules and is responsible for storing operating data;
The chipset is the core of the motherboard, including the northbridge chip and the southbridge chip, which are connected to each other through a bus;
Expansion slots include PCI, PCI-E and other slots, which are used to install external devices such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards;
Interface slots include USB, serial port, parallel port, etc., providing various input and output interfaces;
The power interface supplies power to the motherboard and is responsible for providing stable power support for various hardware devices.
Ⅱ. Main functions of the motherboard
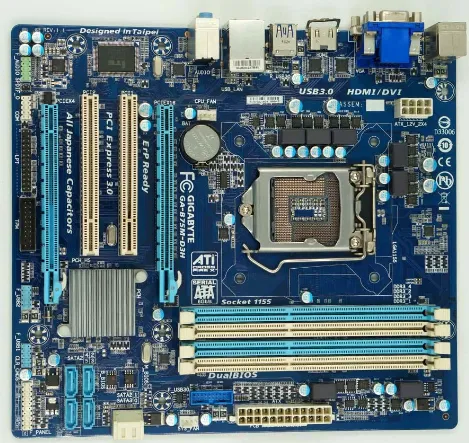

Figure2:motherboard
Processor support: The motherboard must be able to support different types of processors, including processors of different brands and models such as Intel and AMD.
Memory support: The motherboard must be able to support different types of memory, including DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, etc.
Storage support: The motherboard must be able to support external storage devices such as hard drives and optical drives, as well as USB storage devices such as USB flash drives and mobile hard drives.
Graphics card support: The motherboard must be able to support different types of graphics cards, including AGP, PCI-E and other graphics cards of different specifications.
Complete interfaces: The motherboard should provide a complete set of interface slots to facilitate users to connect various external devices.
Stable power supply: The motherboard must provide a stable power supply to ensure the stable operation of various hardware devices.
Figure3:motherboard
Ⅲ. Application scenarios of motherboard
Home applications: Home users use computers for entertainment, study, work and other activities, and the motherboard must be able to meet the various needs of users.
Office applications: Office users use computers for document processing, data analysis and other activities, and the motherboard must be able to provide efficient performance and a stable operating environment.
Industrial applications: Industrial users use computers for control, monitoring and other activities, and the motherboard must be able to provide a stable operating environment and strong expansion capabilities.
Ⅳ.The future development of motherboards
With the continuous development of technology, the performance and functions of motherboards are also constantly upgraded. In the future, motherboards will develop in a more efficient, stable, and intelligent direction. For example, the new generation of processors will have higher clock speeds and more cores, memory will have higher bandwidth and lower latency, and hard drives will have higher capacity and faster read and write speeds. At the same time, with the continuous development of emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things and cloud computing, motherboards will also be used in more fields, bringing more convenience to people's lives and work.
In short, the computer motherboard is the core of the computer hardware system, which determines the performance and functions of the computer. Understanding the basic knowledge and main functions of computer motherboards will help you use your computer better. At the same time, with the continuous development of technology, the future development of motherboards will also bring more convenience to people's lives and work.
Ⅴ.Motherboard form factors and types
Figure3:motherboard cpu
Motherboard form factors and types are an important part of a computer motherboard. Motherboard form factor refers to the size, shape, and other physical characteristics of the motherboard, while motherboard type refers to the motherboard's features and specifications. Currently, there are many different types and form factors of motherboards available on the market. Some common motherboard form factors include:
ATX (Advanced Technology Extended): This is one of the most common motherboard form factors and is commonly used in desktop computers. Standard ATX supports the most advanced graphics cards and has multiple RAM expansion slots.
Micro-ATX: This form factor is smaller than ATX and is typically used in lightly used computers. Micro-ATX motherboards are suitable for light users and only require up to four PCIe slots.
Mini-ITX: This form factor is smaller than Micro-ATX and is typically used in lightweight PCs used in homes or small offices. Mini-ITX motherboards are ideal for users who need a small, affordable and easy-to-install computer.
Nano-ITX: This form factor is designed for digital entertainment devices with smaller size and lower power consumption.
Ⅵ.FAQ
01How many connections, ports or slots are there on the motherboard?
The number of connections, ports, or slots on a motherboard can vary depending on the model and manufacturer. However, some common ports and slots found on most motherboards include USB ports, audio jacks, Ethernet ports, SATA ports for storage, PCI Express slots for expansion cards, and RAM slots for memory.
02Why are the slots and connectors different colors?
The different colors of slots and connectors on computer motherboards are used to differentiate between the various types of components that can be installed, such as RAM, graphics cards, and storage devices.
03How is the motherboard connected to the computer case?
The motherboard is connected to the computer case through a set of screws or standoffs that secure it to the case. These screws or standoffs are placed in specific locations on the case that correspond to the mounting holes on the motherboard.
04What did the first motherboard look like?
The first motherboard, invented in 1981, was the IBM PC motherboard. It was a large green board with various slots and connectors for the CPU, RAM, and other components.
05 Since there is a main board, is there a parent board?
The term "parent board" is not commonly used in the context of electronic circuit boards. The main board is typically the primary circuit board in a device, and it may have subsidiary boards that connect to it.
06Where does the name of the motherboard come from?
The name "motherboard" comes from the fact that it is the main circuit board in a computer system, which all other components connect to.
07What are the differences between Dell, HP and other OEM motherboards?
The main difference between Dell, HP and other OEM motherboards is that they are designed specifically for their respective brands and may not be compatible with other brands or generic components. They may also have different features, layouts, and BIOS configurations.
08Are there motherboards in laptops, smartphones and tablets?
Yes, laptops, smartphones, and tablets all have motherboards.
Related Articles
Variable Capacitors: A Complete Guide
Switching Diodes: Definitions, Principles, Applications, and Future Trends
Comparative Analysis of DC Transmission and AC Power
How Does a Single Phase Motor Work?
Regulated vs Unregulated Power Supply: What's the difference?
How does an Accelerometer Work?
NC7SZ125P5X Overview: Features, Applications and Datasheet
What is Buffer Amplifier?
STM32f401rct6: Explained with Applications, Features and Datasheet
FPGA vs ASIC: Which one should you Choose?
LMC555CN Timer: Applications, Features, and Datasheet
10k Resistor Color Code: Everything You Need to Know










