C Battery vs AA, AAA, D & 9V Battery: Differences
Introduction
A C battery is a regular cylindrical cell that is neither bigger nor smaller nor more powerful than an AA or D battery. The C battery has been a consistent compromise option over the decades, providing a middle ground in devices requiring more energy than can be provided by AA batteries but less bulk than a D cell would add.
Battery size is another important thing that a consumer must consider because compatibility determines the performance, safety, and convenience directly. What most individuals do not know is that like-appearing batteries cannot be used interchangeably, as disparity in the size, voltage, and capacity may lead to poor performance as well as damage to the device. Consequently, the paper makes a comparison between C-size batteries and other popular battery specifications in order to assist the consumer in making informed decisions and preventing unwarranted losses.
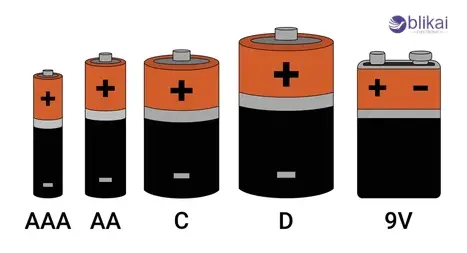
Size Comparison
C batteries are in a relative intermediate range between cylindrical batteries in size and weight. A typical C battery is approximately 50mm (1.97 inches) high and 26mm (1.02 inches) in diameter and weighs normally (6570 grams).
Compared to AA Battery: AA cells measure 50 mm (1.97 inches) tall, 14mm (0.55 inches) in diameter and have a mass of about 23 grams. They are identical in height, but much thinner and lighter, and this reduces their carrying capacity and present delivery.
Compared to AAA Battery: AAA batteries are taller with a height of 44.5 mm (1.75 inches) and a diameter of 10.5 mm (0.41 inches), with only a weight of 1112 grams, which is a lot thinner and lighter and only used in low-drain devices.
Compared to D Battery: D batteries are higher by 61.5 mm (2.42 inches) and have a larger diameter of 34.2 mm (1.34 inches) and a weight of 140 to 150 grams, significantly larger, and providing more energy storage to a device with a heavy load.
Compared to 9V Battery: 9V batteries are also rectangular with approximate dimensions of 48.5 mm x 26.5 mm x 17.5 mm (1.91 x 1.04 x 0.69 inches), weighing 45-50 grams, yet this battery type offers high voltage in a small size, but do not physically fit where C batteries are needed.
Capacity and Runtime Comparison
C batteries are usually 6000-8000mAh in the alkaline format, and are perfect for medium-drain gadgets. NiMH C batteries are generally able to supply 3000 or 4000mAh in accordance with alkaline, even though this can be charged many hundreds of times, thus the total price of the battery is cheaper and much more environmentally friendly long term.
The AA batteries normally supply alkaline 2000-2500mAh and NiMH 1900-2200mAh. Though AA batteries could be efficient to power low-drain devices like remotes or clocks, they are far less efficient than C batteries in medium-drain devices.
The AAA battery capacities are even less, at 800 to 1200mAh with alkaline power and at 600 to 1000mAh with NiMH power. They can only support small power electronics, and not devices that consume more current.
D batteries have a 12000-18000mAh rating, and NiMH have an 8000-10000mAh rating, yielding very extended run times in high-drain devices like a large lantern or handheld radio.
The 9V batteries would be able to do 500 to 600mAh of alkaline, and 170 to 250mAh of rechargeable. Their high voltage is applicable in specialized electronics, but they have a short run time as compared to cylindrical batteries.
Practically, it means that you need an intermediate amount of power to supply your device for a few hours, and a C battery is the best option between size and energy. The same device will drain its AA or AAA batteries sooner, but D batteries will last longer, but are larger, and 9V batteries, although of higher voltage, are not made to be on constant power-hungry duty.
Common Device Applications
Medium-drain devices require a higher energy level than can be delivered by AA or AAA batteries and use C batteries. Such applications include handheld fans, medium-sized flashlights, portables like radios, battery-operated toys, lanterns, and a portion of a camping outfit. NiMH C batteries can be recharged and are used on a regular basis in a device such as a rechargeable drill. The benefit of this is that they can be charged numerous times and save money in the long term.
AA batteries are the most widespread form of cylindrical battery, and may be used in low- to moderate-drain devices. It would find use in remote control, wall clocks, wireless mice and keyboards, digital cameras, little handheld flashlights and toys. Battery AA is the best size, capacity, and convenience mix in terms of day-to-day electronics.
AAA batteries are smaller in size than AA, and they are intended to power low-drain compact devices. They are present in most TV remotes, small flashlights with LED lamps, calculators, wireless computer peripherals, portable medical gadgets such as thermometers, and mini toys.
D batteries are the largest conventional cylindrical batteries, and are used in high-drain or long-run devices. Common uses are large lanterns, boom boxes, portable radios, outdoor lights, medical equipment, and industrial equipment. Their high capacity makes them reliable over a long period and are therefore suitable during camping, during emergencies, or during the use of devices with a high current demand.
9V batteries are a rectangular design that offers a lot of power in a small size, but with a small capacity. They have applications in smoke detectors, carbon monoxide detectors, wireless microphones, guitar pedals, portable test instruments, and some small electronic kits or experimental electronics. They can be used in gadgets where higher voltage bursts are required, as opposed to high current.
Compatibility and Substitution
Two batteries of the same voltage can be compatible, but their size, capacity, and terminal format can often cause substitution to be impossible. AA or AAA batteries cannot be substituted directly in place of C batteries without an adapter, since, although they do offer a current of 1.5 volts, the lower relative size and reduced capacity cannot maintain the sustained current demanded by medium-drain devices. AA and AAA use the same nominal voltage as C batteries (1.5V on alkaline, 1.2V on NiMH), but are smaller in size and offer less capacity. Although adapters are available that may enable AA batteries to fit into a C battery compartment, these are intended to be used only in low-drain applications.
D batteries are bigger than C batteries and provide greater capacity. D cells in certain designs may be used in place of C batteries with an adapter sleeve, although the reverse is, in practice, impractical. A D battery might give better runtime and performance with high-drain devices because a smaller C battery can be used instead.
9V batteries are totally different in terms of shape and voltage. They cannot replace cylindrical batteries like C, AA, AAA or D. Attempting to do so may destroy the device or may be a safety hazard due to the difference in voltage.
Practical Takeaways
C batteries suit medium-drain devices and would need constant power at moderate levels. The battery should be selected based on matching the physical dimensions so as to fit well in the device and the right chemistry.
It is always advisable to check your device manual to find out what type of battery is recommended. Medium-drain devices such as flashlights, radios or toys usually require C batteries to work properly. Remote controls, clocks, wireless mice, etc., that are powered by AA or AAA batteries are the best use of these batteries. D batteries are used with high-drain devices, such as large lanterns or industrial equipment, and with special devices such as smoke detectors or guitar pedals.
Take into consideration Capacity and Runtime: When using devices with a long usage period, select the batteries with higher capacity. C batteries typically offer 6000-8000mAh with longer run time than an AA or AAA battery. Rechargeable NiMH C cells are economical to use on a regular basis and may be a bit less efficient in capacity per charge than alkalines.
Safe Substitution Practices: Only use adapters if recommended and for low-drain devices. Never attempt to replace cylindrical batteries with a 9V battery or vice versa. For D to C or AA to C substitutions, ensure the device’s power demand is considered.
Conclusion
C batteries offer an ideal performance of size, capacity, and voltage to suit medium-drain applications like flashlights, radios, and battery-operated toys. By selecting the right type of battery, which is consistent with the size and the type of chemistry of the physical device it must operate in, we can prevent problems with performance, prevent early depletion, and guarantee its safe use.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.










