RS232C Pin Configuration: Guide to Wiring & Signal Connections
Introduction
RS232C- One of the oldest and most popular norms of periodical communication in electronics. RS232C was first offered in the 1960s and became a common standard in data transfer between computers and supplemental devices(modems, printers, artificial outlets, etc.) soon afterward.
Indeed, with the newer USB, Ethernet and wireless protocols becoming the standard in ultramodern electronics, RS232C continues to be demanded in aged systems, embedded operating systems, and artificial robotization.
A reliable RS232C connection cannot be established without knowledge about pin configuration and wiring techniques. This reference manual describes
RS232C Pinouts, wiring layouts, signal functionalities, troubleshooting and implementation examples.
What Is RS232C?
The electrical characteristics and timing of signals employed in periodical communication are specified in RS232C(Recommended Standard 232, modification C). The Electronic Diligence Association(EIA) was its original standard.
Key Features of RS232C
- Voltage Levels Logic 1(Mark) is represented by −3 V to −25 V, while sense 0(Space) is 3V to 25V.
- Transmission: Asynchronous periodical communication, transmitting one bit at a time.
- Distance supports up to 15 measures(50 feet) at standard baud rates.
- SpeedTypically over 20 kbps, though advanced pets may work with short cables.
- Connector TypesCommonly uses DB9 and DB25 connectors.
RS232C vs. Other Protocols
RS422: Balanced signals, longer distance support.
RS485: Multi-drop network support, industrial use.
USB: Faster, plug-and-play, but requires different drivers.
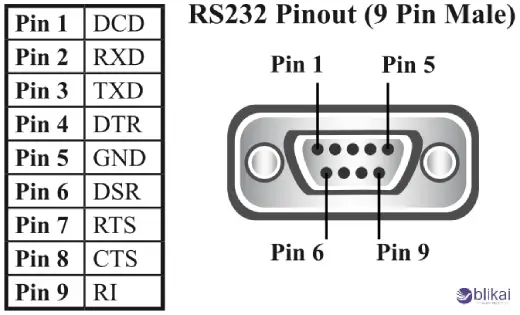
RS232C Pin Configuration Explained
RS232C connections use D-subminiature connectors, with DB9 (9-pin) and DB25 (25-pin) being the most common. Each pin has a specific signal role.
DB9 Pin Configuration
| Pin | Signal Name | Function | Direction |
| | - | -- | |
| 1 | DCD (Data Carrier Detect) | Detects modem connection | Input |
| 2 | RXD (Receive Data) | Receives data from remote device | Input |
| 3 | TXD (Transmit Data) | Sends data to remote device | Output |
| 4 | DTR (Data Terminal Ready) | Indicates terminal is ready | Output |
| 5 | GND (Ground) | Signal reference ground | — |
| 6 | DSR (Data Set Ready) | Indicates modem is ready | Input |
| 7 | RTS (Request to Send) | Requests permission to send data | Output |
| 8 | CTS (Clear to Send) | Grants permission to send data | Input |
| 9 | RI (Ring Indicator) | Detects incoming call signal | Input |
DB25 Pin Configuration
| Pin | Signal Name | Function | Direction |
| | -- | - | |
| 1 | GND | Frame ground | — |
| 2 | TXD | Transmit Data | Output |
| 3 | RXD | Receive Data | Input |
| 4 | RTS | Request to Send | Output |
| 5 | CTS | Clear to Send | Input |
| 6 | DSR | Data Set Ready | Input |
| 7 | GND | Signal ground | — |
| 8 | DCD | Data Carrier Detect | Input |
| 20 | DTR | Data Terminal Ready | Output |
| 22 | RI | Ring Indicator | Input |
RS232C Wiring and Signal Connections
Correct wiring ensures successful data transmission. RS232C supports different wiring methods depending on device roles.
Straight-Through Wiring
Used when connecting a DTE(Data Terminal Equipment) device, similar to a computer, to a DCE(Data Communication Equipment) device, similar to a modem.
Pin 2(RXD) connects to Pin 2, Pin 3(TXD) connects to Pin 3, etc.
Null Modem Wiring
Used to connect two DTE devices directly(e.g., two PCs).
TXD and RXD lines are crossed: Pin 2 ↔ Pin 3, Pin 3 ↔ Pin 2.
RTS ↔ CTS and DTR ↔ DSR connections are also crossed.
Shielding and Grounding
Always connect GND(Pin 5 on DB9 or Pin 7 on DB25) to ensure a common reference.
Use shielded cables in noisy artificial surroundings to reduce hindrance.
Practical Applications of RS232C Connections
Although RS232C was formalized numerous decades ago, it remains a popular moment due to its simplicity, trustworthiness and use with aged tackle. Now we will look into some of the most common uses of RS232C connections.
Computers and Modems
RS232C was the most common way of connecting a computer to a dial-up internet modem or long-distance device in the early days of personal computing. The protocol also provided reliable data movement among PCs and telephone line modems. Some networking devices continue to use RS232 console ports to this day, to configure and diagnose them.
Industrial Automation
RS232C is widely embedded in industry control systems. Programming, monitoring, and diagnostics of many programmable logic controllers (PLCs), CNC machines, robotics systems, and motor drives are still done using RS232. That makes it a viable option in industrial machine equipment that does not require a fast-speed communications network, but one that is reliable in noisy conditions.
Laboratory and Test Equipment
Scientific instruments and test devices, such as oscilloscopes, diapason analyzers, multimeters, and data loggers, frequently have RS232 interfaces. This allows experimenters and masterminds to collect data directly into a computer, automate trials, or control devices. RS232 provides a straightforward way to link instruments without demanding complex networking setups.
Embedded Systems and Microcontrollers
RS232 is considered to be one of the simplest methods to make communication between a computer and a microcontroller. Developers frequently use RS232 to debug, upload firmware and observe serial output. Arduino and STM32 development boards communicate with PCs via RS274 (in some cases via level shifters, such as MAX232). This is why it can be useful in prototyping and electronics education.
Networking Devices and Consoles
A lot of routers, switches, and firewalls have an RS232 console port. It is used by technicians to initially configure, update firmware, and troubleshoot with no network access. In contrast to Ethernet, where an IP setup is needed, RS232 provides a low-level access point to the hardware.
Medical Equipment
RS232-based interfaces are still used with some medical devices, including patient monitors, diagnostic machines and infusion pumps, to transfer data to hospital systems. As a well-established and simple standard, RS232C has found favor in high-stability critical applications where performance is less important than reliability.
Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems and Printers
In retail environments, RS232 is used in barcode scanners, receipt printers, and cash registers. These devices don’t require high data transfer rates but must be extremely reliable. RS232 connections ensure transactions and printing occur smoothly without communication failures.
Testing and Troubleshooting RS232C Connections
Step 1: Verify Pinouts with a Multimeter
Use continuity mode to ensure correct wiring.
Check that TX ↔ RX connections are properly established.
Step 2: Loopback Test
Connect TXD to RXD on the same connector.
If characters typed echo back, the port is functional.
Step 3: Common Problems
No Communication: Wrong wiring (straight-through vs. null modem).
Data Errors: Cable too long or noisy environment.
Handshake Failures: RTS/CTS not connected when required.
RS232C vs. Modern Interfaces
Although RS232C is slower and limited in distance, it still has advantages.
Advantages
- Simple and reliable.
- Works without complex drivers.
- Compatible with older equipment.
Disadvantages
- Short distance and low speed.
- Bulky connectors.
- Not hot-swappable like USB.
Adapter Solutions
- RS232 to USB– Commonly used for laptops without serial ports.
- RS232 to TTL– For connecting to microcontrollers.
- RS232 to RS485– For long-distance industrial networking.
Conclusion
RS232C is conceivably an obsolete protocol, although it continues to be an important communications standard in electronics, automation, and embedded systems. It's better to know its pin layout, wiring, and signal connections so that data is transferred reliably, and common troubleshooting headaches are avoided.
RS232C is still useful whether you are linking a PC to a modem, debugging a microcontroller or servicing industrial equipment. It still connects the old and new technologies with the right wiring and adapters.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.










