What 1N5408 Power Diode is : Pinout & Applications
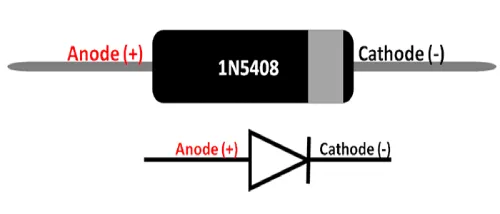
The 1n5408 power diode is a two-terminal component consisting of an anode and a cathode. Current flows through this diode in only one direction, from the anode to the cathode, making it function like an electronic check valve. It has low resistance in one direction and very high resistance in the opposite direction.
As indicated by its name, this diode can handle a high maximum repetitive reverse voltage and forward current. It is suitable for use in circuits operating below 3A. This article provides an overview of the 1N5408 power diode, including its pin configuration and applications.
What is the 1N5408 Power Diode?
The 1N5408 is a type of power diode from the 1N540x series. This general-purpose diode includes several features that make it suitable for a wide range of applications. It can handle up to 3000mA/3A of current and is available in the DO201 package, which is slightly superior to the DO-41 package. The 1N5408 can replace the DO-41 package if a bit more space is available.
If you need a diode that handles more current than the DO-41 type, such as the 1N4148 or 1N4007, the 1N5408 is a suitable replacement in most applications to achieve higher forward current.

However, the 1N5408 is becoming obsolete in modern electronic circuits due to its slow recovery time. It is being replaced by more advanced and efficient diodes. The VI characteristics of the 1N5408 power diode are non-linear, and it allows current to flow in only one direction once the fixed threshold voltage is reached in the forward direction.
Pin Configuration
The pin configuration of the 1N5408 power diode is shown below. This power diode has two terminals, each with a specific function:
- Pin1 (Anode): This terminal allows the flow of current into the diode.
- Pin2 (Cathode): The current exits through this terminal.
Features & Specifications
The features and specifications of the 1N5408 power diode include the following:
- - Available in a small size
- - Maximum surge current capacity
- - Low forward voltage drop
- - Available in volume quantities
- - Average forward current: 3A
- - Forward voltage drop: 1V at 3A
- - Maximum non-repetitive current: 200A
- - Maximum reverse current: 10µA
- - Cyclic reverse voltage: 1000V
- - Available in DO-201 package
- - General-purpose rectifier diode
- - Maximum reverse current: 10µA
- - Maximum non-repetitive forward current: 200A
- - Maximum operating and storage temperature range: -65°C to +175°C
Alternative 1N5408 power diodes include the 1N5400, 401, 402, 404, 406, and 407. Equivalent diodes are the CR3-100, P300M, CR3-120, FR307, G3M, FR607, V3510, and HER508. The main difference between these diodes lies in the PRRV (Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage) and RPRV (Non-repetitive Reverse Voltage). For circuits operating between 12V-24V, these differences are not critical, but for higher voltages, the PRRV and RPRV should be checked, and the diode with the highest PRRV should be chosen compared to the operating voltage.
1N5408 Equivalent Replacements
When replacing a 1N5408 power diode, it is essential to understand its key electrical characteristics and practical application details. Here’s how to select a suitable replacement for the 1N5408:
Direct Replacement Models
- **1N5400 to 1N5407 Series:** These diodes match the current handling and package type of the 1N5408. They have slightly different peak repetitive reverse voltage (PRRV) and non-repetitive reverse voltage (RPRV). They are suitable for 12V-24V circuit environments and are ideal for low to medium voltage levels.
Equivalent Replacement Models
- **CR3-100, CR3-120, FR307, G3M, FR607, V3510, HER508:** These diodes have similar physical size, current capacity, and voltage withstand capabilities to the 1N5408. They are used in rectification, surge protection, and high-frequency switching circuits.
Key Considerations for Selecting a Replacement
Voltage Range:
12V to 24V Applications: All of the above models work well within this range and can effectively handle normal operating stresses.
Above 24V:Double-check PRRV and RPRV to ensure the diode can handle higher voltages. PRRV should exceed the highest voltage in the system to prevent damage from voltage spikes.
Physical Dimensions and Footprints:
Compatibility: Select models with similar physical dimensions and footprints to avoid redesigning the board or soldering interfaces.
Ease of Installation:Ensure a direct replacement without major modifications.
Functional Testing:
Post-Replacement Testing: Perform simple tests to confirm the new diode is functioning properly.
Voltage Test:Ensure the diode maintains the proper voltage level.
Continuity Test:Verify the diode is conducting electricity properly.
Thermal Test: Check for overheating issues to ensure reliable operation.
Selecting the right replacement diode involves matching voltage ratings, ensuring physical compatibility, and performing thorough testing to ensure reliable performance.
How to Long Run this Diode within a Circuit?
To ensure the 1N5408 power diode operates safely and lasts a long time in various applications, follow these precautions:
- - Use this diode in circuits, devices, and projects that operate under 1000V.
- - Always keep the operation within the maximum characteristic or specification values for optimal performance.
- - Do not drive or operate loads above 3A with this diode.
- - Store and operate this diode within the temperature range of -65°C to +175°C.
How to Use 1N5408 Power Diode/Circuit Diagram
The reverse polarity protection circuit using a 1N5408 power diode is shown below. If you connect your MST and DDS VFO to a power supply with incorrect polarity, the circuit will blow. To protect the circuit from reverse polarity, the following method is used. In this technique, a diode and a fuse are used within the circuit as illustrated below.
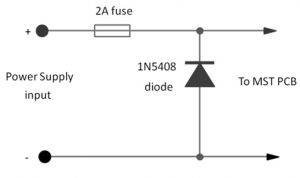
Once the polarity of the power supply is correct, the 1N5408 power diode is connected in reverse bias and does not conduct. However, if the polarity is reversed, this diode becomes forward biased and restricts the reverse voltage to approximately 0.8V across the MST.
If the circuit's power supply provides more than 2 Amps, the fuse within the circuit will blow, completely disconnecting the power supply. This simple yet effective circuit has the drawback of requiring a replacement fuse when it blows. The 1N5408 power diode is robust and will handle the current from the short circuit until the fuse is damaged.
To set up the circuit:
- - Fix a fuse holder, such as the M205 holder, on the rear panel near the input connectors of the power supply.
- - Connect the positive power supply connector to the supply side of the fuse holder.
- - Connect the load side of the fuse holder to the MST PCB.
- - Solder the power diode between the load side of the fuse holder and the negative power supply input connector. The cathode terminal end goes toward the positive connector.
Where to Use 1N5408 Power Diode/Applications
The applications of the 1N5408 power diode include the following:
- - Performing rectification within power supplies, battery chargers, voltage boosters, and more
- - Blocking the flow of current in the preferred direction within a circuit
- - Voltage doubler circuits
- - Current supply regulators
- - Adapters
- - Used as a protection device
- - Circuits for rectification
- - Half-wave rectifiers (HWRs) and full-wave rectifiers (FWRs)
- - Protection of components
- - High-voltage (HV) supplies
- - Regulating current and voltage in any required direction
- - Resolving reverse polarity issues
Thus, this overview of the 1N5408 diode datasheet highlights its design for maximum forward current and reverse voltage, with a power dissipation of 6.25W. The maximum current capacity of this diode is 3A, and it can withstand up to 200A. Due to its slow recovery time, it is often replaced by other diodes in modern electronics. These power diodes are designed in the DO-201 package and offer a repetitive reverse voltage of 1000V. Here is a question for you: What are the advantages of the 1N5408 power diode?
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1.What is the difference between a power diode and a normal diode?
Power diodes and normal diodes both allow electricity to flow in one direction. However, power diodes are designed to handle higher current and voltage levels compared to normal diodes. They are typically used in applications where large amounts of power need to be controlled, such as power supplies and converters. In contrast, normal diodes, often seen in signal processing circuits, manage much smaller currents and voltages.
2. What is the purpose of a pin diode?
A pin diode is primarily used to control RF (radio frequency) signals. Its structure differs from regular diodes because it includes an intrinsic layer between the p-type and n-type layers. This configuration makes the pin diode very effective at changing its resistance when exposed to different levels of voltage, which is useful for adjusting signal levels in RF applications, such as switches and attenuators.
3. What is the difference between 1N5406 and 1N5408?
Both 1N5406 and 1N5408 are power diodes, but they differ in their maximum repetitive reverse voltage. The 1N5406 can handle up to 600 volts, while the 1N5408 can handle up to 1000 volts. This makes the 1N5408 suitable for circuits where a higher voltage handling capability is required.
4. What is the voltage drop of a 1N5408 diode?
The voltage drop of a 1N5408 diode is typically about 1.2 volts when conducting forward current. This is a crucial parameter to consider in power applications because it affects the efficiency of the circuit, especially in high-current environments.
5. What will happen if the diode is connected in reverse polarity?
If a diode is connected in reverse polarity, it will not conduct under normal circumstances. The diode effectively blocks current flow, which can protect circuits from incorrect voltage polarity. However, if the reverse voltage exceeds the diode's reverse breakdown voltage, the diode may start to conduct, potentially leading to circuit damage or failure.
Related Articles
2N5551 Transistor:Features,Applications and Pinout
What 74LS138 IC is and How it works










