How Does a Potentiometer Work? Function & Circuit Explained
As a basic analog electronic component, Potentiometers are used frequently to adjust the level or strength of a signal in a circuit. Potentiometers provide a specific resistance that can be adjusted; they can be used when setting an audio volume, tuning a sensor, or creating elements of an interface, such as knobs. This paper examines the meaning of a potentiometer, its operation and its application in real-life circuits.
What Is a Potentiometer?
A potentiometer, or commonly abbreviated as a pot, is a variable resistor (three-terminal) that serves as a voltage divider. The user can change their desired output voltage by turning or sliding a control device.
A potentiometer in a circuit diagram is normally signified using a resistor symbol and an arrow (which contacts the wiper). It includes:
- Two fixed terminals are connected to the ends of a resistive track.
- One movable terminal (wiper) that slides across the resistive material to tap a variable voltage.
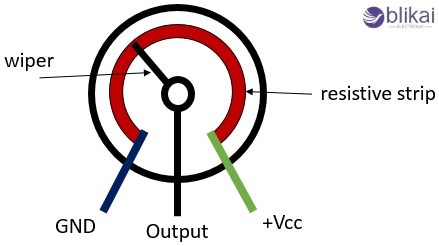
Basic Construction of a Potentiometer
A potentiometer consists of three main parts:
1. Resistive Element – A track made from carbon, cermet, conductive plastic, or wire.
2. Wiper – A contact arm that slides along the resistive track and taps voltage.
3. Housing & Terminals – External casing and electrical connections.
There are two major types of mechanical action:
- Rotary Potentiometers, which use a rotating knob.
- Linear Potentiometers, which use a sliding mechanism.
Working Principle: How Does a Potentiometer Work?
The potentiometer works on the basis of the principle of a voltage divider. Applying a voltage across the two fixed terminals moves the wiper across the resistive track, stealing off the voltage according to its position.
Voltage Divider Formula:
Vout=Vin×(R2/R1+R2)
Where:
- Vin is the supply voltage,
- R1 is the resistance between the wiper and one end,
- R2 is the resistance between the other end and the wiper.
The wiper causes the change of R1 and R2, thus adjusting Vout.
This is why potentiometers are ideal when it comes to parameter action in real time, e.g.:
- Audio volume
- Sensor sensitivity
- Motor speed
- Light dimming
Potentiometer in a Circuit
Potentiometers are commonly used in circuits as:
- Variable voltage dividers (3-terminal configuration)
- Rheostats or variable resistors (2-terminal configuration)
Basic Circuit Example:
Imagine a potentiometer connected between 5V and GND. If the wiper is at the middle point, the output voltage will be approximately 2.5V.
Types of Potentiometers
There are several types of potentiometers tailored for specific applications:
Rotary Potentiometers
Most common type
Used in volume knobs, tuning dials
Linear Potentiometers
Used in faders, sliders, and control panels
Motion is straight, not rotary
Trimmer Potentiometers
Small, adjustable resistors for calibration
Set during manufacturing or maintenance
Digital Potentiometers
Electronically controlled via SPI or I2C
Used in embedded systems for precision tuning
Key Applications of Potentiometers
These are multipurpose components known as potentiometers, which find application in a multitude of systems in the field of electronics and electricity. Their capability to offer variable resistance and perform the role of voltage dividers is making them indispensable both in consumer goods and industrial use. Major areas of use where potentiometers are highly important are presented below:
Volume and Tone Control in Audio Equipment
The most widely used potentiometers are found in audio systems, in controlling volume, bass, treble and balance. Rotary and slide potentiometers give users customisation of audio output by adjusting the amplitude of the signal or messing around with the frequency response. This makes them their smooth and accurate control, so they continue to be standard in analog stereo systems and guitar amplifiers and mixers.
Position and Motion Sensing
As a part of applications such as joysticks, servo mechanisms and robotic arms, potentiometers are used as position sensors. They transform mechanical displacement when it comes in the form of angular or linear displacement into a change of resistance, measurable to be read as position data. This is an essential role in CNC Machines, automobiles (Throttle position sensor), TPS and industrial automation.
Calibration and Tuning of Circuits
Circuit boards often use internal adjustments in the form of trimmers or preset potentiometers. They are applied to adjust sensitivity, gain, voltages and response timing to sensors, comparators, and analog signal processing circuits. They are used in the testing and production calibration processes of engineers.
Light and Temperature Controls
Potentiometers can be used to control light intensity (dimming) in home automation and lighting systems or to set a device threshold level that will actuate other devices, such as thermostats. Simple dimmer switches and more complex analog control systems also make use of them.
User Interface Controls in Appliances
Potentiometers typically form a part of the interface with microwave ovens, washing machines, air conditioners and other domestic appliances. Users turn a knob or push a bar to control power level, time and mode. These controls have a user-friendly interface and analog input.
Feedback Devices in Servo Systems
In closed-loop systems such as servos or motor controls, potentiometers are used to provide position feedback. This enables precise control of movement by constantly comparing the desired position to the actual one, as indicated by the potentiometer’s voltage output.
Educational and Prototyping Tools
Potentiometers are breadboarding and electronics classics. Associated students and engineers with the usage of resistance, difference voltages, elements of control, and analog signals. Their simple design and real-time adjustability make them ideal for circuit experimentation.
Advantages of Potentiometer
Simple and low-cost
Easy to integrate into analog systems
Offers manual and intuitive control
No power required to operate
Disadvantages of Potentiometer
Mechanical wear over time
Susceptible to dust and environmental factors
Not suitable for high-frequency or high-current use
Lower precision compared to digital alternatives
FAQs About Potentiometers
Can a potentiometer be used as a rheostat?
Indeed, when only two terminals (wiper and one end) are conjoined, a potentiometer may be used as a variable resistor (rheostat).
How long do potentiometers last?
Most mechanical pots have a lifetime of 10,000 to 1,000,000 switch cycles, depending on manufacture quality and application.
What’s the difference between a potentiometer and a variable resistor?
A potentiometer has three terminals and can be used to measure voltages, dividing them, whereas variable resistors (rheostats) are used to control either current or resistance to voltage.
Conclusion
A potentiometer is one of the starting points of the analog electronic field, which provides variable resistance and a voltage division in a mechanical implementation. The knowledge of the operation of a potentiometer assists you in the adoption of its functionality in a broad coverage of uses, such as audio volume controls, tuning circuits or creating your interface. As a hobbyist or engineer, this handy device should be in every toolbox, though it is still a common way to solve the problem of controlling something in real time in an analog way.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.










