Brushed vs Brushless Motors: What's the Difference? (Guide)
Our daily lives are enhanced by the use of power tools, such as brushless and brushed DC motors. In order to have a better understanding of the performance of brushless and brushed DC motors, it is important to understand the differences between them. Among the many factors to consider when comparing brushless and brushed motors, being efficient, long-lasting, cost-effective, and various other characteristics are all important.
There are brushless DC motors as well as brushed DC motors, each of which is suitable for different types of applications. Understanding their differences will help you gain a better understanding of their uses. Users can select the right brushless motor for their application based on a few important factors of differences between brushed and brushless motors. Following is a detailed discussion of those factors.
What is a Brushed Motor?
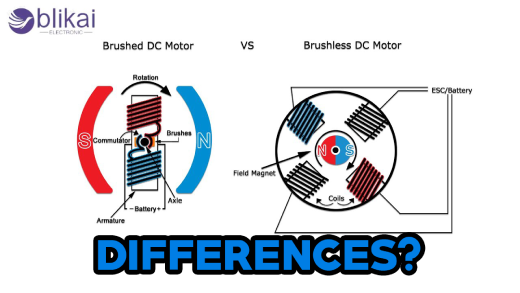
Brush motors are electric motors that deliver current to motor windings using brushes and commutators. A stator generates the magnetic field within which the coils of an armature (rotor) rotate. Commutator segments are physically contacted by carbon brushes as the rotor turns, changing the direction of current flow through the windings. Motor shafts are driven by this interaction, which creates rotational force. A brushless motor is quieter and produces fewer electrical noises than a motor with brushes. Brushes also require more maintenance and produce more heat.
What is a Brushless Motor?
In brushless motors, also called BLDCs (Brushless DC motors), no brushes and no commutators are used. In fact, the rotor is driven by a rotating magnetic field created by switching the current in the windings via an electronic controller. Permanent magnets are used in the rotor, while windings are used in the stator. In addition to being more efficient, less maintenance is required, these motors last longer, and they operate quieter because of the elimination of friction and wear caused by brushes. Drones, electric vehicles, and computer cooling fans all use brushless motors for their reliability and performance.
Brushed vs. Brushless Motors: Key Differences
Design and Construction
-
Brushed Motors: There is a physical contact between the brush and commutator in these motors in order to deliver current to the windings of each motor. There have been many years of use of this traditional design.
-
Brushless Motors: Brushes and commutators are not required in these motors. Current is delivered to the windings by electronic controllers instead. Permanent magnet rotors are combined with coils in the stator of the motor to produce electric current.
Efficiency
-
Brushed Motors: Friction and energy loss in brushes and commutators make them generally less efficient. Further reducing efficiency is the generation of heat by this friction.
-
Brushless Motors: The friction losses caused by brushes are eliminated, making them more efficient. Heat is generated less and energy is converted better without physical contact.
Maintenance
-
Brushed Motors: Replacement of worn-out brushes and cleaning of commutators are required on a regular basis. Depending on how the motor is used, maintenance can be frequent.
-
Brushless Motors: The brushes do not wear out, so they require minimal maintenance. Their reliability and suitability for maintenance-intensive applications are enhanced by this.
Lifespan
-
Brushed Motors: Because brushes and commutators wear out, their lifespan is typically shorter.
-
Brushless Motors: In contrast to brushes and commutators, they have a longer lifespan.
Performance
-
Brushed Motors: As brushes wear and commutators malfunction, performance can degrade over time. Noise and electrical interference may also be produced by them.
-
Brushless Motors: Providing consistent performance over time, keeping electrical noise to a minimum, and providing consistent performance over time. Compared to conventional engines, they offer higher speeds and torques.
Cost
-
Brushed Motors: For applications that must be cost-effective, they are generally less expensive up front.
-
Brushless Motors: Initially more expensive because of the complexity of the electronics, but less maintenance and higher efficiency can offset this cost in the long run.
Brushed vs Brushless Motor Torque
Motors with brushless motors are commonly misunderstood when it comes to torque. Torque is not necessarily determined by the design of brushed or brushless motors. For example, the first Milwaukee M18 FUEL hammer drill offered less torque in real-world situations compared to its predecessors. Manufacturers realized, however, that something very critical was at stake. Electric motors can be supplied with more power when needed due to the electronics used in brushless motors.
Electronic control technology now allows brushless motors to detect when they slow down under load. The brushless motor electronics can request and receive more current from the battery pack as long as the battery and motor are within the specified temperature range. It is possible to maintain higher speeds under load with tools like brushless drills and saws. They become faster as a result. It is often much faster. DeWalt Perform and Protect, Makita LXT Advantage, and Milwaukee RedLink Plus are a few examples. Performance and runtime are maximized by integrating motor, battery, and electronics seamlessly.
Advantages of Brushless and Brushed motors
Brushless Motors
Higher Efficiency: A brushless motor converts energy more efficiently because friction losses associated with brushes are eliminated, which results in a lower temperature generated and better energy conversion.
Longer Lifespan: In applications requiring durability and reliability, brushless motors are ideal because they do not require brushes to wear out.
Low Maintenance: There are no brushes, so maintenance and replacement parts aren't necessary as often.
Quiet Operation: Since brushless motors eliminate mechanical friction, they can be used in applications that require low noise levels.
High Performance: A drone, electric vehicle, or precision machine can benefit from these motors' superior speed and torque characteristics.
Brushed Motors
Cost-Effective: The cost-effectiveness of brushed motors makes them ideally suited to cost-sensitive applications.
Simple Control: There is less complexity and less cost associated with these motors' control circuitry than with brushless motors. When used in simple applications, they are less likely to fail.
Ease of Use: For simple tasks and projects, brushed motors are easy to use and control.
High Torque at Low Speeds: In applications such as power tools and automotive starters, these motors provide a high torque at low speeds.
Wide Availability: There are many types of brushed motors available, and they have been used for many years.
Which Is Better: Brushed or Brushless?
Brushed Motors
Brushed motors are highly efficient and cost-effective for household appliances, toys, and industrial tools. In applications where the motor won't run continuously and maintenance is possible, they are easier to control with simpler circuitry.
Brushless Motors
Since brushes and commutators are not present in brushless motors, they are more efficient, reliable, and have a longer lifespan. As a result, they are suitable for applications such as drones, electric vehicles, and advanced industrial machinery that require high performance and precision. Although they may have a higher initial cost, they often have lower operating costs and maintenance costs over time.
Final Verdict
The application's specific needs should be taken into account when choosing between brushless and brushed motors. A brushless motor is ideal for high-performance, continuous operation tasks due to its superior efficiency, longevity, and low maintenance requirements. Drones and electric vehicles benefit from their quieter and more reliable operation. Brush motors, on the other hand, are useful for basic projects and are more cost-effective and easier to operate than brushed motors. Performance and maintenance requirements must be balanced with cost. It is generally recommended to use brushless motors because of their long-term reliability and efficiency.
Related Articles
Servo Motor vs. Stepper Motor: Key Differences Explained
Applications of Induction Motor: And its Types
Electric Motors Applications and Features: Fully Explained
What is an Electric Motor? Explain its Types










