Voltage Amplifier vs Power Amplifier: What’s the Differences?
An amplifier functions as an electronic apparatus designed to augment the current, voltage, or power of a signal, thereby enhancing its strength while preserving its original shape. Amplifiers find extensive application across wireless communications, broadcasting, and various audio equipment. They manifest in diverse forms, spanning from Op-Amps and small signal amplifiers to larger-scale power amplifiers. Amplifiers are typically categorized into two primary types based on their function: voltage amplifiers and power amplifiers. The classification of an amplifier hinges predominantly on factors such as signal magnitude, physical configuration, and the manner in which it manipulates the input signal in relation to the current supplied to the load. This article furnishes concise insights into voltage amplifiers, elucidating their operation and applications.
What constitutes a Voltage Amplifier?
A voltage amplifier, as its name suggests, is a type of amplifier engineered to generate an elevated output voltage relative to the input voltage. It finds application in scenarios necessitating higher voltage transmission over extended distances. While augmenting the power of an electrical signal, this amplifier retains the essential characteristics of the original signal intact. In electronics, voltage amplifiers play a pivotal role in enhancing audio clarity, refining image quality, and facilitating precise sensor readings.
It's essential to note that while voltage amplifiers bolster the overall power within a circuit to achieve desired outcomes, they do not serve as power sources themselves. Consequently, while these amplifiers enhance the available voltage, they are generally unsuitable for powering devices such as motors. Nonetheless, their ability to elevate voltage levels proves invaluable in amplifying signals from various control mechanisms.

Voltage Amplification
A unit devised primarily to elevate the voltage level of an incoming signal directed into an amplifier is termed a voltage amplifier. The fundamental objective in the design of such amplifiers revolves around achieving maximum attainable voltage gain. Consequently, the gain of this amplifier is delineated as the ratio between the output value and the input value, equivalently represented as the ratio of output voltage to input voltage. The formula for voltage gain in voltage amplifiers is expressed as:
Av = Vout/Vin
These amplifiers exhibit a characteristic of drawing minute amounts of power from the connected load. Referred to as small-signal amplifiers, they are adept at amplifying signals characterized by exceedingly diminutive magnitudes, effectively amplifying them across the amplifier circuit.
Voltage Difference Amplifier Circuit
Creating the circuit for this amplifier is relatively straightforward, as it requires only basic electronic components. Often referred to as voltage difference amplifiers, these circuits specialize in magnifying disparities between voltages within an electronic setup. Consequently, the altered output voltage can be scrutinized and evaluated.
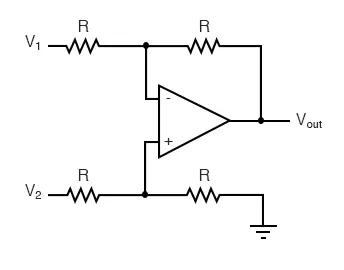
The depicted voltage amplifier circuit amplifies an input voltage signal and furnishes an output voltage signal. Functioning as a voltage-controlled voltage source, this amplifier necessitates a high input impedance and a low output impedance. In the provided circuit, when the input impedance Rin is significantly greater than the source resistance Rs, the input voltage Vin approximately equals the source voltage Vs. Moreover, if the load resistance RL is substantially greater than the output resistance Rout, the relationship between output voltage Vout and input voltage Vin can be approximated as:
Vout ≈ AvVin
Here, the voltage gain Av is calculated as the ratio of output voltage Vout to source voltage Vs, expressed as:
Av = Vout/Vin = Vout/Vs
An ideal amplifier adheres to the characteristics of infinite input resistance and zero output resistance. Such an amplifier yields an output voltage directly proportional to the input voltage, with the proportionality constant remaining unaffected by variations in source magnitudes or load resistances.
Distinction between Voltage Amplifier and Power Amplifier

Voltage amplifiers and power amplifiers serve the common purpose of augmenting the potency of an input signal. However, they diverge in their primary objectives and functionalities. While a voltage amplifier prioritizes the amplification of voltage without significant emphasis on power gain, a power amplifier is specifically engineered to deliver substantial power gain, facilitating the driving of high-power loads. Both types of amplifiers find utility across audio and radio frequency (RF) applications. Below, we delineate the disparities between these two amplifier variants.
| Voltage Amplifier | Power Amplifier |
| A device engineered to increase the voltage level of an input signal is referred to as a voltage amplifier. | A device tailored to furnish a substantial amount of power gain to the input signal is recognized as a power amplifier. |
| This amplifier elevates the amplitude of input signals without delivering significant power amplification. | This amplifier harnesses a low-power electrical signal and elevates its power level to a magnitude suitable for propelling high-power loads or loudspeakers. |
| It is alternatively referred to as a small-signal amplifier owing to its operation with low-magnitude input signals. | The power amplifier earns the moniker of a large-signal amplifier due to its requirement for high-magnitude input signals. |
| In this amplifier circuit, the transistor base is narrow as it is not intended to manage high currents. | The transistor base in this amplifier circuit is relatively broader to accommodate higher currents. |
| The transistor employed in this amplifier is a low- or medium-power transistor characterized by its compact physical dimensions. | The transistor utilized in this amplifier is a high-power transistor distinguished by its substantial physical dimensions. |
| The collector current value in this amplifier is relatively small, measuring at 1 mA. | The collector current value in this amplifier is significant, approximately 100 mA. |
| The output power provided by this amplifier in AC is relatively modest. | The output power delivered by this amplifier in AC is substantial. |
| The current amplification factor of this amplifier is small. | The current amplification factor of this amplifier is large. |
| The current amplifier is linked with the RC | The current amplifier is linked with the transformer. |
| Heat dissipation is minimal. | Heat dissipation is significant. |
| These amplifiers are commonly utilized in audio equipment to amplify the signal without substantially increasing its power. | Power amplifiers find frequent application in wireless communication systems, audio setups, and diverse scientific and industrial contexts whenever substantial output power is required. |
Distinction between Current Amplifier and Voltage Amplifier
Both the current amplifier and voltage amplifier are electronic apparatuses primarily employed for magnifying electrical signals, albeit functioning on disparate principles. The contrast between these two amplifiers is delineated below.
| Current Amplifier | Voltage Amplifier |
| A current amplifier is an electronic device utilized to boost the current of the input signal while ensuring a constant voltage level. | A voltage amplifier is an electronic device employed to increase the voltage of the input signal while keeping the current stable. |
| This amplifier enables a small input current to regulate a larger output current. | This amplifier enables a small input voltage to govern a larger output voltage. |
| The input and output of this amplifier are characterized by low input impedance and high output impedance, both in terms of current. | The input and output of this amplifier consist of voltage with high input impedance and low output impedance. |
| It is employed for amplifying voltage. | The current amplifier is utilized for amplifying current. |
| This amplifier exhibits exceedingly high voltage gain and input impedance, while delivering lower output current. | This amplifier features low voltage gain, substantial current gain, and moderate to high input impedance. |
The uses of voltage amplifiers encompass the following:
- Enhancing the amplitude of the output voltage of a signal.
- Widespread utilization in electronic devices.
- Employed across various applications such as wireless communication, signal broadcasting, and audio equipment like speakers.
- Application in scenarios necessitating signal transmission at maximum voltage over long distances.
- Integration in speakers to amplify audio signals and in radios to amplify weak radio signals received via an antenna.
Potential applications as impedance-matching circuits and switching circuits.
Therefore, this concludes an overview of voltage amplifiers, covering their circuits, operation, distinctions, and applications. These amplifiers yield an output signal with heightened voltage levels when presented with low voltage input signals, especially beneficial for scenarios demanding signal transmission over extended distances. As for your question, an amplifier is an electronic device designed to increase the magnitude or power of a signal, typically voltage or current, without substantially altering its other characteristics.
Related Articles
What is TL074 Operational Amplifier?
Microprocessor Vs Integrated Circuit: What’s the Differences?
Difference Btween Amplifier and Current-Sense Amplifier
Push-pull Amplifier :Overview and Working Principle










