What is Thin-Film Transistor(tft) monitors? All explained
Thin Film Transistor, or TFT for short, is a form of technology used in LCDs, or liquid demitasse displays. A subset of LCD displays, Thin-Film Transistor(tft) monitors are distinguished by their superior response pets and image quality. Here’s a comprehensive look at TFT monitors:
_monitors.webp)
Basics of Thin-Film Transistor(tft) Technology
- Transistors and Pixels: Thin film transistors (TFTs) are used in TFT technology to regulate each pixel on the screen. Every pixel has a transistor linked with it. It functions as a switch to regulate how much light enters the liquid crystal.
- Active Matrix: An active matrix technology is TFT. This indicates that one or more transistors are in charge of each pixel. This gives you more flexibility over how photos are displayed. more accuracy in color reproduction and a faster refresh rate than passive matrix LCDs.
Types of Thin-Film Transistor(tft) Panels:
1. TN (Twisted Nematic):
- Pros: Fast response times, low cost.
- Cons: the narrow viewing angle. less accurate portrayal of color.
2. IPS (In-Plane Switching):
- Pros: Excellent color accuracy. broad angle of view.
- Cons: Slower response times compared to TN, higher cost.
3. VA (Vertical Alignment):
- Pros: Good contrast ratios, better color reproduction than TN.
- Cons: Slower response times, limited viewing angles compared to IPS.
How Thin-Film Transistor(tft) monitors Work
In many contemporary computer and television screens, thin-film transistor (TFT) displays—a kind of liquid crystal display (LCD) technology—are employed. This is a thorough description of how it operates:
1. Basic Structure
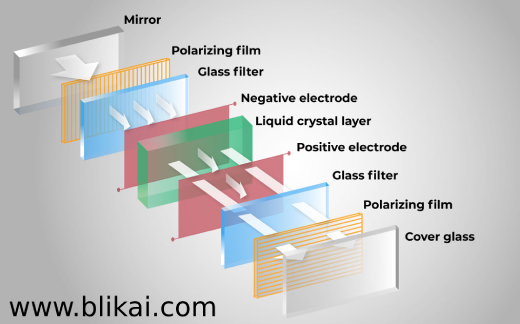
A TFT monitor consists of several key components:
- Liquid Crystal Layer: Made up of motes of liquid demitasse, this subcaste is deposited between two glass shells.
- Polarizing Filters: Situated on the liquid crystal layer's two sides. Only one direction of light wave passage is permitted by these filters.
- Color Filters: To form a color image, these filters — generally red, green, and blue, or RGB are piled in individual pixels.
- Thin Film Transistors (TFTs): Bitsy switches that regulate the liquid crystal's exposure are set up on every pixel.
- Backlight: Source of light Usually, the display is illuminated by this LED light.
2. Working Principle
The operation of a TFT monitor involves several steps:
a. Backlight Illumination
The backlight shines through the polarizing filter and the liquid crystal layer. This light is initially unpolarized.
b. Polarization of Light
The light waves are polarized by the first polarising filter, which causes them to vibrate in unison.
c. Control of Liquid Crystals
A thin film transistor governs each pixel in the liquid crystal layer. By putting voltage on the TFT, the liquid crystal's orientation can be altered.
- If no voltage is applied, the liquid crystal will disintegrate. Permitting the passage of light.
- When applying voltage, liquid crystals are organized to block light.
d. Modulation of Light
The direction of the liquid crystal modifies the intensity of light as it travels through the liquid crystal layer. This light is adjusted even more by a second polarization filter. based on the crystal alignment, permitting or obstructing the passage of light.
e. Color Creation
The modulated light then passes through the RGB color filters. By varying the intensity of red, green, and blue light for each pixel, a full diapason of colors can be displayed.
3. Pixel Control and Image Formation
By altering the voltage provided to the TFT corresponding to these sub-pixels, each pixel in a TFT display is made up of three sub-pixels (one pixel for each of the three colors: red, green, and blue). As a result, the monitor may display a variety of colors and tints.
A matrix of these TFTs controls the entire screen, rapidly turning on and off to depict the animation. The number of times per second that a TFT monitor updates is indicated by its refresh rate, which is commonly expressed in hertz (Hz).
Advantages of Thin-Film Transistor(tft) monitors
As a subset of LCD( liquid demitasse display) technology, thin film transistor( TFT) defenses are extensively used in numerous different operations due to their numerous benefits. The following are the principal advantages of TFT displays for both home and business use:
1. Superior Image Quality:
- Sharpness and Clarity: The TFT display offers high-resolution, clear images. For intricate tasks like graphic design and image editing, this makes it perfect.
- Color Accuracy and Consistency: This is pivotal for operations that need for precise color reduplication since it offers advanced color accuracy and consistency over former LCD technologies.
2. Response Time:
- Faster Response Times: The TFT monitor reacts more quickly. Minimize ghosting and motion blur. Because of this, it's perfect for gaming and watching quick videos.
3. Energy Efficiency:
- Low Power Consumption: Compared to CRT( Cathode Ray Tube) observers and earlier LCD technologies, TFT displays consume lower power, which lowers electricity costs and has a lower environmental effect.
4. Slim and Lightweight Design:
- Compact Form Factor: The TFT monitor's lightweight, thin design frees up desk space and makes it simple to move and put on a wall or movable stand.
5. Viewing Angles:
- Improved Viewing Angles: While viewing angles on early TFT displays were restricted, current TFT screens have much improved in this regard. It offers clear visibility from a variety of perspectives.
6. Durability and Longevity:
- Long Lifespan: Compared to CRT monitors, TFT monitors generally last longer and are less prone to burn in and picture retention.
7. Less Eye Strain:
- Reduced Flicker: Unlike CRT monitors, TFT monitors do not flitter, which lessens eye strain after extended use. Because of this, it's applicable for lengthy computer use and office work.
8. Versatility and Connectivity:
- Multiple Inputs: TFT displays can be used with a variety of bias because they generally have multitudinous input options( HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI, and VGA).
- Touchscreen Capabilities: Touchscreen functionality is available on certain TFT monitors. enhanced usability and commerce across a range of operations.
9. Better Contrast Ratios:
- Improved Contrast: The contrast ratio of contemporary TFT monitors is superior. Darker blacks and brighter whites are the effect of this. This enhances the whole experience of watching.
10. Eco-Friendliness:
- Less Hazardous Materials: Compared to CRT monitors, TFT monitors contain smaller dangerous accoutrements, which makes it easier to reclaim and dispose of them in an environmentally respectable way.
Applications of Thin-Film Transistor(tft) monitors
1. Consumer Electronics:
- Computers and Laptops: Both desktop and laptop computers typically include TFT monitors. gives a clear picture.
- Televisions: Utilized for high-definition viewing on contemporary flat screen TVs.
- Tablets and Smartphones: TFT LCDs are a common choice for mobile devices because they offer a good mix of performance and affordability.
2. Medical Field:
- Diagnostic Equipment: Clear imagery is handed by high- resolution displays in MRI scanners, ultrasound systems, andX-ray bias.
- Patient Monitoring Systems: Utilized in vital sign monitors to guarantee dependable and precise readings.
3. Automotive Industry:
- Dashboard Displays: Include a digital speed display integrated into the dashboard of the car. Gas gauge and additional crucial data.
- Infotainment Systems: Utilized on the center console display for navigation. Other features and controls for the audio.
4. Industrial Applications:
- Control Panels: Utilized in industrial control systems and machines for equipment monitoring and operation.
- HMI (Human-Machine Interface): TFT screens are a component of the interface that operators use in factories and manufacturing lines to monitor and control processes.
5. Gaming:
- Gaming Monitors: Its great quality and quick refresh rate make it recommended. The gaming experience will be improved by this.
- Portable Gaming Consoles: The majority of handheld gaming devices have TFT screens.
6. Retail and Advertising:
- Digital Signage: Used to display information boards, interactive kiosks, and digital advertisements.
- Point of Sale (POS) Systems: in retail systems such as cash registers. to conduct business and communicate with clients.
7. Aerospace and Defense:
- Cockpit Displays: Vital for aircraft navigation, control systems, and other critical information.
- Military Applications: Used in various military equipment for tactical displays and monitoring systems.
8. Education and Training:
- Interactive Whiteboards: TFT monitors are part of interactive teaching aids in classrooms. - -E-learning Devices: Tablets and e-readers used in education often employ TFT technology.
9. Entertainment:
- Portable Media Players: Many personal media players use TFT screens for video playback.
- VR Headsets: Some virtual reality headsets use TFT displays for immersive experiences.
10. Public Transportation:
- Information Displays: To put timetables, advertisements, and route information on buses, trains, and subways
Considerations When Buying a TFT Monitor:
1. Resolution: More resolution on a monitor yields sharper, more detailed images.
2. Panel Type: Select based on your main use case (e.g., IPS for work-related tasks, TN for gaming).
3. Refresh Rate: For gaming, higher refresh rates (such as 120Hz or 144Hz) are advantageous.
4. Response Time: Lower response times reduce motion blur.
5. Connectivity: Ensure the monitor has the necessary ports (HDMI, DisplayPort, etc.) for your devices.
6. Adjustability: Look for monitors with adjustable stands and VESA mount compatibility for ergonomic setup.
Because TFT monitors combine performance, quality, and affordability in a way that makes them ideal for most applications, they have become the industry standard. The type and features of the panel you choose should take your particular needs into account.
Related Articles
Varieties of Monitor Cables: A Beginner's Guide
Transistor Series Voltage Regulator:All You Need to Know
Junction Field-Effect Transistors: Principles, Applications, and Advantages










