Does a Resistor Reduce Voltage
It is often unclear how resistors reduce voltage in electronic circuits, but they are fundamental components. Designing and analyzing circuits effectively requires an understanding of resistor behavior. The role of resistors in voltage division and current control is vital even though they do not actively reduce voltage like voltage regulators or transformers.
We will explore voltage reduction with resistors in this article. The various techniques used to achieve voltage reduction in practical applications, along with the principles behind voltage drop, will be discussed in this section. This article will explain Does a Resistor Reduce Voltage or not in electronic circuits. So stick with you till the end of the article to clear all your confusion!
How Does a Resistor Reduce Voltage?
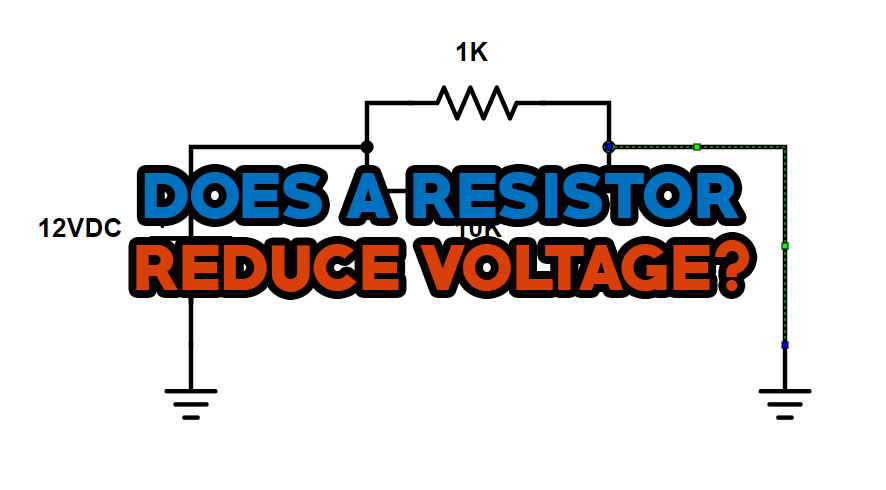
Voltage Divider
Voltage divider circuits can also use resistors to reduce voltage. Series or parallel networks of resistors compose the voltage divider. In the divider, the voltage across a particular resistor can be reduced by strategically selecting the resistance values. Various circuit applications can be performed with the reduced voltage.
Potentiometers or variable resistors often use the voltage divider configuration. Wiper elements change their resistance ratio over time, which affects the output voltage. There are many applications that require variable voltage levels, such as controlling volume and brightness, that utilize potentiometers.
Important Parameters Of A Resistor
Parameters of Resistor
Resistance
Among all the parameters of a resistor, resistance is the most fundamental. The flow of current in a circuit is opposed by resistance, measured in ohms (Ω). Per Ohm's Law (V = IR), the resistance determines the amount of current flowing through a resistor. A circuit's voltage drop and current levels can be controlled with different resistor values.
Inductance and capacitance
Resistance is the primary function of a resistor; however, parasitic capacitance and inductance can also be present in them. Materials and design play a role in determining these properties. Resistors have small capacitances and inductors, which are usually insignificant for most applications. It may, however, be necessary to consider these parameters in circuits with high frequencies or applications that require precise impedance matching.
Power Rating
Resistors are rated according to their power dissipation capacity. Watts (W) are usually used to specify it. Resistors can fail or even burn if they are overpowered. If a resistor is to operate at an expected current or voltage level, the power rating must be considered.
What Causes Voltage to Drop After a Resistor?
Whenever electrons pass through a resistance, some of their energy is lost. Thermal energy is accumulated as a result of energy being given up by material, and therefore the temperature rises. There is a voltage drop when electrons are moving because they lose energy.
Voltage and Current Reduction Resistors Types
There are a wide variety of resistors that can be used to reduce current and voltage, including carbon composition resistors, metal film resistors, and wirewound resistors. There is a wide variety of types, each of which has unique characteristics.
How is a Resistor Constructed to Reduce Current?
High-resistance materials are used in the construction of resistors, such as carbon-based materials, metal films, or wire woven around a core. A resistor's resistance value is determined by its length, thickness, and composition. To meet specific current-reduction requirements, resistors can be manufactured with different resistance values by varying these parameters during construction.
How Does a Resistor Reduce Current?
As a result of providing resistance, resistors limit the flow of electrons through a circuit, thereby reducing current flow. It is determined by the resistance value how much current is reduced. To protect components from excessive current flow, this property is used in current-limiting applications.
Faqs
Question 1: Does voltage decrease across a resistor?
Answer: When a resistor is connected to a source of current, the voltage decreases. Resistance introduced by a resistor converts electrical energy into heat when current flows through it. Ohm's Law (V = IR) states that the voltage dropped across the resistor is due to this conversion.
Question 2: Does a resistor reduce power?
Answer: Power is reduced by resistors. By virtue of its resistance, a resistor dissipates power as heat when current flows through it. Using the formula P = IV, one can calculate the power dissipated in a resistor, where P represents power, I represents current, and V represents voltage. Resistors deplete circuit power as they dissipate power.
Question 3: A resistor doesn't change the voltage, does it?
Answer: There is no such thing as a constant voltage after a resistor. By introducing resistance, a resistor converts electrical energy into heat when current flows through it. A voltage drop is caused by this conversion. Resistance and current flow through a resistor determine the magnitude of the voltage drop. As a result, a resistor reduces the voltage.
Question 4: Does a resistor reduce voltage or current?
Answer: When electrons attempt to flow through a resistor, it delays or resists them, causing a voltage drop. Voltage overload can damage or damage components. In other words, yes, voltage is reduced by the resistor.
Question 5: What causes a voltage drop?
Answer: A voltage drop is usually caused by a current flowing through a cable in an electrical circuit. Current flow has resistance and impedance due to passive components, such as cables, connectors, and contacts.
Final Thoughts
When a component in your circuit requires less voltage than the rest of the circuit, a resistor will provide a voltage drop to ensure it does not receive too much electricity. The component's current would also increase if the voltage remained constant but the resistance increased. So i hope after reading the article which is about Does a Resistor Reduce Voltage, you got the answer to all your questions. If you still want to ask, then you can comment below. Thank You!










