13003L Transistor: Specs, Pinout & Applications
What is the 13003L Transistor?
As an NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) the 13003L continues to function in switching functions and power supply operations with high voltages. The device functions as a versatile electronic device serving high-current and high-voltage operations in various systems.

Structure and Package
The 13003L transistor arrives in the TO-126 package because it functions as one of the standard medium-power transistor packages. The package features good thermal behavior that enables proper heat removal while operating. The TO-126 package includes convenient mounting features that enable its usage in through-hole bonding and surface-mount bonding applications for circuit board implementation.
13003L Transistor Pinout
Identification of Pins
The 13003L transistor operates as a three-pin device which belongs to the standard design of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). The device has three pins that function as Emitter (E), Base (B), and Collector (C). An accurate understanding of pinout structure remains essential to achieve correct circuit addition and operational performance.
Pin Configuration
When viewed from the front with the flat side facing you and the pins pointing downwards, the pinout of the 13003L transistor is as follows:
- The leftmost pin is the Emitter (E)
- The middle pin is the Base (B)
- The rightmost pin is the Collector (C)
13003L Transistor Specifications
Maximum voltage and current ratings
The 13003L transistor extends wide usability because of its elevated voltage and current capabilities. An optimal performance of the NPN bipolar junction transistor occurs under maximum collector-emitter voltage conditions up to 400 volts (VCEO). The device offers a VCBO rating of 700V, which extends design possibilities in circuit applications. The 13003L transistor maintains a continuous collector current at 1.5A and a short-duration peak collector current at 3A.
Power dissipation capabilities
The 13003L transistor shows sufficient power dissipation functionality for standard power consumption applications. Seventy-five Celsius degree cases assist the transistor to operate at a 20W total power dissipation level for different circuit applications. Standard heat sinks need to be installed for maximal power dissipation to maintain superb product performance while extending lifetime.
Operating temperature range
The 13003L transistor performs various functions because of its specification for high voltage and current. The optimal performance range of NPN bipolar junction transistors extends to maximum collector-emitter quantities of 400 volts (VCEO). The device offers a VCBO rating of 700V, which extends design possibilities in circuit applications. The 13003L transistor maintains a continuous collector current at 1.5A and a short-duration peak collector current at 3A.
Gain and frequency response
The 13003L transistor exceeds power dissipation requirements that support typical usage power levels in different applications. The 25°C case temperature enables the transistor to handle total power dissipation (Ptot) of 20W effectively for different circuit applications. Proper heat sinks must be applied to ensure excellent performance and product lifespan when operating at the maximum power dissipation thresholds.
13003L Transistor Features
Powerful Handling of High Voltage and Current
The transistor provides powerful handling of high voltage and current, which supports amplification tasks and power-switching operations. When utilizable between a 400V collector-emitter voltage range and 1.5A collector current, the 13003L transistor delivers efficient power load performance.
High Gain Performance
The 13003L demonstrates excellent current amplification features through its typical DC gain range which goes from 20 to 200. The transistor delivers dependable operations over various operational conditions due to its broad gain range.
Thermal Characteristics
The 13003L transistor performs exceptionally well for thermal management requirements. This transistor can function in hot environments because its maximum junction temperature rating reaches 150°C. The TO-126 design package serves as a critical feature because it enables efficient heat dissipation crucial in sustaining power application stability.
Switching Performance
The 13003L transistor stands out because it delivers rapid switching abilities. Fast on-off transitions find optimal use with this feature in switching power supplies as well as motor control circuits. The low saturation voltage of this transistor improves switching efficiency by minimizing power dissipation when it operates.
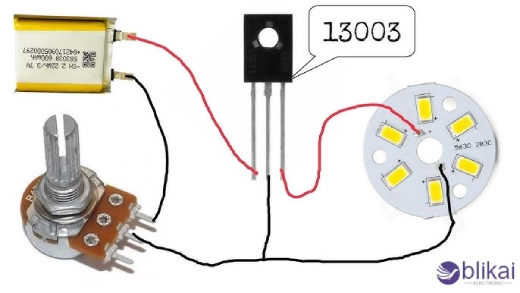
13003L Transistor Applications in Electronic Circuits
Audio amplification systems
The 13003L transistor functions indispensably to amplification systems from power amplifiers where it serves in their output stages. The device has outstanding current performance alongside high voltage endurance for optimal speaker operation in consumer electronics together with professional audio instruments. The 13003L shows superior performance when operated in a push-pull mode to provide clean output sound even at power levels reaching its upper reach.
Switching and control circuits
A switching application benefits greatly from the 13003L because of its ability to switch quickly and produce minimal saturation across the device. Because of its quick on-off performance capabilities, the device finds application in circuits that implement pulse-width modulation (PWM) controllers and digital logic interfaces. The transistor demonstrates exceptional high-frequency switching dependability that designers use as their primary option for power management systems.
Power supply regulation
The 13003L maintains widespread applications for linear voltage regulators together with power supply circuits. The device successfully maintains stable output voltages because it operates with high voltages and currents. The device finds valuable application in industrial equipment along with telecommunications systems because it maintains constant voltage output.
Motor control applications
In motor control circuits, the 13003L serves as an excellent driver for small to medium-sized DC motors. Its high gain and current capabilities enable precise speed control and efficient power delivery. The transistor's durability under inductive loads makes it suitable for applications ranging from automotive systems to robotics and automation equipment.
Advantages in specific use cases
The 13003L shows its flexibility as a reliable solution when key applications need maximum performance. Fluctuating voltage conditions and harsh environmental conditions do not affect this device's operation in automotive electronics systems. The 13003L proves to be a well-liked solution among consumer electronics companies because of its affordability and dependable performance. The 13003L maintains long-lasting, reliable performance because of its sturdy construction, which withstands challenging operating environments in industrial control systems.
13003L Transistor Alternatives and Equivalents
|
Transistor |
Type |
Vce (max) |
Ic (max) |
hFE (gain) |
Package |
Typical Use |
|
13003L |
NPN |
400V |
1.5A |
40–250 |
TO-220 |
SMPS, CFL, LED drivers |
|
NPN |
400V |
1.5A |
40–250 |
TO-220 |
Power switching, general use |
|
|
NPN |
400V |
1.5A |
40–200 |
TO-220 |
High-voltage switching |
|
|
NPN |
400V |
1.5A |
40–250 |
TO-220 |
General purpose |
|
|
FJP13003H |
NPN |
400V |
1.5A |
40–250 |
TO-220F |
Energy-efficient SMPS |
|
NPN |
450V |
4A |
15–75 |
TO-220 |
High-power switching |
Troubleshooting and Testing
Common issues with 13003L transistors
Several performance-related issues may appear during the use of 13003L transistors. The primary problem among 13003L transistors consists of overheating that emerges from insufficient cooling systems or excessive current levels. The transistor will suffer permanent damage together with reduced operating efficiency because of these events. The transistor faces failure due to voltage breakdown because it fails to sustain proper voltage-blocking capacity. In high-frequency operations leakage current poses a major issue since it generates unneeded power dissipation together with signal degradation.
Using multimeters for diagnostics
The 13003L transistor needs multimeters as required equipment for diagnostic tests. The initial examination for functional integrity requires testers to use the diode test mode to assess base-emitter and base-collector junctions. The forward voltage reading of a functional transistor ranges between 0.6V to 0.7V while showing a complete break in the opposite direction. Measure the transistor current gain with the hFE (gain) test function while making sure the measured value stays within the recommended parameters. The oscilloscope provides detailed observation of transistor switching dynamics when performing diagnostics work in a circuit.
Replacing faulty transistors
The proper insertion of a replacement 13003L transistor becomes necessary after it has been found defective. You must choose replacement transistors with exactly matching specifications, focusing on their voltage ratings and current handling capability alongside gain characteristics. Careful verification of pinout connections should be performed prior to insertion due to safety reasons. Appropriate heat-sinking methods should be applied during new transistor soldering operations in order to avoid thermal damage. Test the circuit completely to validate its proper functionality while updating any biasing components if required.
Related Articles
Transistor Symbol Explained: Understanding the Basics and Types
5477 Transistor Types: Variants, Features & Applications Guide
Infineon IRF3808PBF MOSFET – High Power N-Channel Transistor
IRLZ44N MOSFET Transistor: Specs, Features, and Applications
BC557 Transistor Pinout, Features & Applications [Electronics Guide]
2N4401 NPN Transistor: Datasheet, Applications, and Features
C945 Transistor: Features, Applications, and Price
Thyristor vs Transistor: What are the Differences?
NPN Transistor? Construction, Working & Applications
2N2222 Transistor: Applications, Features, and Specifications
2SA733 Transistor: Applications, Features, and Specifications
13009D Transistor: Applications, Equivalent and Specifications
2N3904S Transistor: Features, Applications, and Datasheet
PNP Transistor? Construction, Working & Applications
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor:Features and Pinout










