MPSA92 Transistor: Pin Configuration and Applications
With a trigger voltage of just 5V, MPSA92 transistors are capable of switching 300V of loads. Since this transistor operates with 5V, it is used in digital electronics. Generally, transistors are used as amplifiers or switches, but this transistor is only used as a switch due to its low gain. Additionally, this transistor is rated for a maximum voltage of 50 volts and a maximum operating speed of 50 MHz through a 3pF reduction in output capacitance. The purpose of this article is to examine the datasheet, specifications, and circuit application of the MPSA92 PNP transistor.
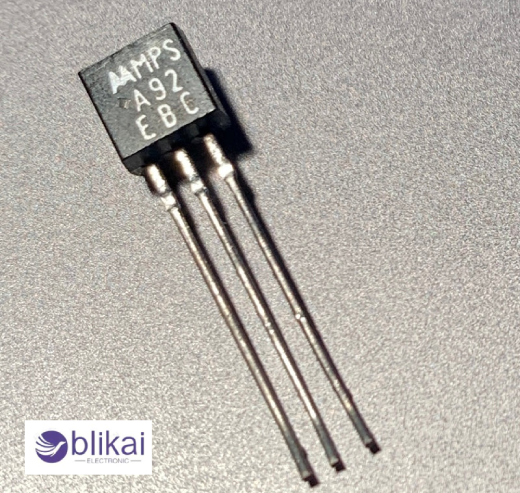
What is an MPSA92 Transistor?
A BJT of this type is commonly used in switching applications and general-purpose amplification. As compared to standard small-signal transistors, it can handle relatively high voltages and currents. The TO-92 package houses the transistor, making it suitable for various electronic circuits that require space efficiency and ease of handling.
Specifications show that the MPSA92 transistor can typically handle voltages between 200V and 300V at the collector-emitter and collector-base, making it suitable for applications that require higher voltages. As well as being able to handle moderate current loads, its collector current rating is 500mA. Its characteristics make the MPSA92 transistor ideal for power supply circuits, audio amplifiers, voltage regulators, and other applications with moderate power amplification or switching requirements.
Pin Configuration
PNP bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) such as the MPSA92 are commonly used in electronics. This is how the pins are configured in detail:
Collector (C): When the transistor is in active mode, current flows through this terminal. Collectors of PNP transistors like MPSA92 are typically connected to more positive voltage supplies than emitters.
Base (B): Emitter and collector currents are controlled by the base terminal. A transistor MPSA92 looks like this:
-
PNP Transistor: It is possible for current to flow from the emitter to the collector when a positive voltage is applied to the base compared to the emitter.
-
NPN Transistor (not applicable for MPSA92): Current flows from the collector to the emitter when a positive voltage is applied to the base.
Emitter (E): Active transistors receive current through their emitters when they are in active mode. When a PNP transistor is used, the emitter is usually connected more negatively to the collector supply than the collector is to the emitter supply.
Features
Known for its robust performance in various electronic applications, the MPSA92 transistor is a high-voltage NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT). A detailed description of the MPSA92 transistor can be found below:
Type and Package: MPSA92 transistors come in TO-92 packages and are NPN transistors. A variety of electronic projects and applications are suitable for this compact package format (TO-92), which makes it easy to handle and mount on circuit boards.
Voltage Ratings: As compared with standard small-signal transistors, MPSA92 can handle relatively high voltages. V_CEO is usually rated at 200V, while V_CBO is usually rated at 300V. The transistor can handle higher voltages because of these voltage ratings.
Current Ratings: MPSA92 transistors are capable of handling a maximum collector current (I_C) of 500mA. In applications requiring power amplification or switching of moderate loads, the transistor can handle moderate to high current levels.
Gain (hFE): According to the operating conditions and circuit configuration, the MPSA92 transistor's current gain is typically between 40 and 250. Signals in various electronic circuits are amplified efficiently with this moderate gain.
Frequency Response: In typical audio and low- to moderate-frequency applications, the MPSA92 transistor exhibits good frequency response characteristics. As an audio amplifier, signal processing circuit, etc., it is good at reliable signal amplification.
Applications
Power Supply Regulators and Drivers: Power supply regulator circuits use the MPSA92 transistor for voltage control and stabilization. By adjusting current flow through the load based on control signals, it can be used as a series pass element in linear voltage regulators. As a switching transistor in switch-mode power supplies (SMPS), MPSA92 ensures efficient power conversion by controlling the operation of switching regulators.
Audio Amplifiers and Preamplifiers: Audio amplifiers and preamplifiers can benefit from the MPSA92 transistor's moderate gain and good frequency response characteristics. Small audio signals can be amplified so they can be driven by speakers or other audio output devices with satisfactory power and fidelity. Before being amplified by power amplifiers, weak signals from microphones or other input sources are boosted with the MPSA92 in audio preamplifier stages.
Switching Circuits for Moderate Loads: MPSA92 transistors can operate at moderate currents (up to 500mA), making them ideal for switching applications. In addition to controlling current flow, it can also control relays, motors, LEDs, and other components. Microcontroller-based systems can utilize the MPSA92 in digital logic circuits to switch between logic states and facilitate digital signal processing.
Voltage Regulators and Control Circuits: By controlling the current flow in response to changes in input or load conditions, the MPSA92 transistor adjusts and stabilizes voltage in voltage regulator circuits. Electronic circuits and components require a steady output voltage to function properly. A wide range of input voltages and load conditions can be handled by the transistor's high voltage rating.
Oscillator Circuits and Signal Generators: An MPSA92 transistor can be used to generate precise waveform signals at specific frequencies by incorporating it into oscillators and signal generators. Combining this circuitry with capacitors and resistors will produce the oscillations necessary in digital circuits, communication systems, and test equipment, as well as waveform generation.
General-Purpose Amplification and Signal Processing: Other than specific applications, the MPSA92 transistor can be used in general-purpose amplification tasks that require high gain and stable operation. Circuits using this component include amplifiers for sensor signals, voltage level shifting circuits, and active filters, which amplify and condition signals.
Lighting Control Circuits: As a switch, the MPSA92 transistor controls the operation of LEDs and incandescent bulbs in lighting control circuits. These lighting elements can be driven efficiently with the currents it can handle. Modulate LED brightness or control lighting fixture on/off cycles by using the MPSA92, which can be used in dimming circuits.
Temperature Control Systems: Various temperature control systems can make use of the MPSA92 transistor to regulate heating or cooling elements. In response to temperature sensor feedback, the transistor switches current to these elements in order to maintain a desired temperature setpoint. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, thermostats, incubators, and other appliances requiring precise temperature control utilize this application.
Motor Drive Circuits: In motor drive circuits, the MPSA92 transistor controls the operation of small motors or actuators by acting as a switch. By controlling the speed and direction of these motors, it can handle the currents required to drive them efficiently. In robotics, automated systems, and small-scale electromechanical applications, MPSA92 transistors are commonly found in circuits that control motors precisely.
Wrapping Up
MPSA92 transistors are versatile components, capable of high voltages and delivering reliable performance. This semiconductor is primarily used for amplification and switching tasks, especially in low-power and medium-power circuits where it exhibits low noise and high current gain (hFE). Its durability and consistent behavior are especially appreciated by engineers and hobbyists. As a result, MPSA92 transistors are preferred in audio amplifiers, voltage regulators, and other electronic devices requiring reliable transistor performance. Popularity among electronics enthusiasts and professionals is also attributed to its widespread availability and affordability.
Related Articles
TIP31C NPN Transistor: Working Principle and Applications
2N5306 Transistor: Features and Application
What is BC547 Transistor: Applications and Working Principle
2N7000 Transistor: Applications, Features and Datasheet
2N3904 Transistor: Features, Applications and Datasheet
2N5088 Transistor : Pinout, Equivalent, Datasheet
2N5551 Transistor:Features,Applications and Pinout
Phototransistor : Circuit Pinout & Principle
What is Thin-Film Transistor(tft) monitors? All explained
Transistor Series Voltage Regulator:All You Need to Know
Junction Field-Effect Transistors: Principles, Applications, and Advantages
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor:Features and Pinout
PNP Transistor? Construction, Working & Applications
2N3904S Transistor: Features, Applications, and Datasheet










