What is GBU6M? All You Need to Know
A single-phase glass bridge rectifier is the GBU6M. In many different types of electronic equipment, this part is utilized to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). What you should know about it is as follows:
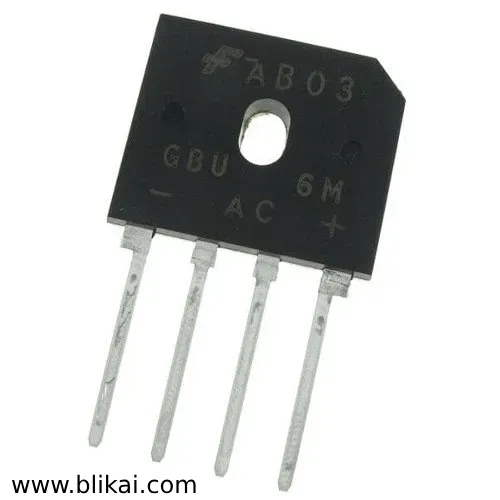

Specifications
- Maximum Repetitive Reverse Voltage (VRRM): 1000V
- Maximum RMS Bridge Input Voltage (VRMS): 700V
- Average Rectified Forward Current (IF(AV)): 6A
- Surge Overload Rating: 175A peak
- Construction: Reliable low-cost construction utilizing a molded plastic technique
- Junction: Glass-passivated, which enhances reliability and performance
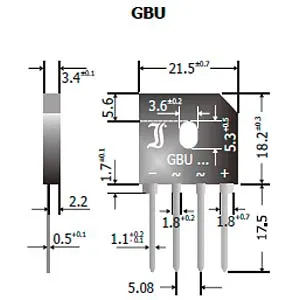
Features
- High Surge Current Capability: High surge currents are manageable for the GBU6M. It is therefore perfect for applications that encounter power spikes.
- UL Certification: It satisfies particular safety and quality requirements because it is UL approved (UL #E258596).
- Ideal for Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): Made to fit into PCBs with ease of integration. It can therefore be applied to a variety of electronic applications.
Components of GBU6M
- Rectifier Diodes: Four diodes stacked in a bridge configuration make up a bridge rectifier. When it comes to GBU6M, these diodes are often high power rectifier diodes that can manage sizable current.
- Bridge Configuration: A bridge-like arrangement of the diodes is used. This enables the rectifier to provide a pulsed DC output by converting the positive and negative loop portions of the AC waveform.
- Mounting Base: Bridge rectifiers, like the GBU6M, are typically sold as single in-line packages (SIP) or dual in-line packages (DIP) with a mounting base that helps dissipate heat and provide mechanical support.
- Terminals: Four connectors make up the GBU6M: two for the AC power supply (for AC input) and two for the DC output (rectified DC output).
- Heat Sink: To guarantee correct operation and extended life, particularly under heavy load situations, the GBU6M may need a heat sink, depending on the current rating and power distribution capacity.
- Insulating Material: To guarantee safety and electrical isolation. Insulating materials or coatings may be present on bridge rectifiers, like the GBU6M, to help prevent short circuits and guarantee dependable performance.
Applications of GBU6M
The GBU6M is used in general-purpose AC/DC bridge full-wave rectification for various electronic devices, including:
- Monitors
- Televisions
- Printers
- Switching mode power supplies
- Adapters
- Audio equipment
- Home appliances
Case studies and examples
-
Power Supply for LED Lighting:
- Application: LED street lighting systems.
- Challenge: In order to successfully eliminate harmonic distortion, it converts the AC mains voltage to DC for LED lighting while maintaining a high power factor.
- Solution: A GBU6M bridge rectifier is built into the power supply circuit of the LED driver to rectify the AC voltage and produce a constant DC output. This ensures that the street light will last longer and that energy savings are possible.
-
Battery Charger for Electric Vehicles:
- Application: Electric vehicle (EV) charging station.
- Challenge: Transforming AC mains electricity into DC voltage that can be used to safely and effectively charge EV batteries.
- Solution: GBU6M rectifiers are integrated into the power supply units of EV chargers to rectify AC voltage from the grid, delivering controlled DC output to charge EV batteries quickly and reliably.
-
Industrial Motor Drive Systems:
- Application: Industrial motor drive systems for conveyor belts.
- Challenge: Transforming mains AC electricity into DC voltage to enable the smooth and effective operation of a DC motor.
- Solution: The drive motor's power supply circuit uses a GBU6M bridge rectifier. It changes AC voltage to DC voltage, which is useful for regulating industrial motor torque and speed. to guarantee dependable conveyor system performance.
-
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS):
- Application: Data centers requiring reliable backup power.
- Challenge: Providing uninterrupted power to critical equipment during mains power failures.
- Solution: A UPS system's rectification process includes the GBU6M rectifier, which transforms primary AC power into DC so that the backup battery may be charged. In the event of a power loss, servers and other vital IT infrastructure continue to function because the Battery provides DC power to the inverter, which produces AC power.
-
Home Appliance Power Supplies:
- Application: Refrigerator power supply.
- Challenge: To change the primary AC voltage into a steady DC voltage so that electronics may be controlled and a refrigerator compressor can be powered.
- Solution: Refrigerator power supply circuits use GBU6M bridge rectifiers to rectify AC voltage. It supplies the DC voltage needed for the motor, compressor, and control system to run effectively.
How GBU6M Works
One kind of bridge rectifier is the GBU6M. The GBU6M bridge rectifier, which is specifically made to change alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), functions as follows:
Bridge Rectifier Configuration:
The GBU6M is made up of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration. The labels for the diodes are D1, D2, D3, and D4.
AC Input:
An AC power supply is attached to the GBU6M's AC input connection, which is typically labeled AC or ~. This AC source typically supplies mains voltage (such as 110V or 220V AC).
Diode Operation:
- During the positive half-cycle of the AC input voltage:
- Diodes D1 and D2 conduct, allowing current to flow through the load in one direction (from +AC to -AC).
- Diodes D3 and D4 do not conduct current since they have reverse polarity.
- During the negative half-cycle of the AC input voltage:
- Diodes D3 and D4 conduct, allowing current to flow through the load in the opposite direction (from -AC to +AC).
- Diodes D1 and D2 do not conduct current since they have reverse polarity.
Output Voltage:
The output terminals (usually labeled as +DC and -DC or simply + and -) of the GBU6M provide a rectified DC voltage. This DC voltage is not perfectly smooth and contains ripple due to the pulsating nature of the rectification process.
Filtering:
To get a DC voltage that is smoother. At the output terminal, an extra filtering element, like a capacitor, is typically utilized. These capacitors charge at the peaks and discharge at the troughs to help even out pulsing DC voltages.
Output Characteristics:
The maximum value of the input AC voltage is roughly equivalent to the output voltage of the GBU6M bridge rectifier. The voltage across the conducting diode is subtracted. (Typically, silicon diodes operate at roughly 0.7V.) For instance, the peak voltage will be roughly 170V if the input AC voltage is 120V RMS. After adjustment, the DC output voltage would be roughly 170V - 0.7V = 169.3V DC (the ripple voltage).
Advantages of GBU6M
High Voltage and Current Ratings:
Relatively high voltage and current levels are supported by the GBU6M. Because of this, it can be used in applications that need robust regulating capabilities. Because of this, it can be utilized in industrial equipment and power supplies that handle crucial power levels.
Compact Design:
Despite its high power handling capabilities, the GBU6M typically comes in a compact package, which helps save space in circuit designs and facilitates easier integration into various electronic and electrical systems.
Bridge Configuration:
Full-wave AC input voltage rectification is provided by the GBU6M bridge rectifier, which leads to a more efficient conversion than half-wave rectifiers. Only half of the AC waveform is used in this.
Reliability:
Bridge rectifiers with a reputation for dependability and longevity include the GBU6M. They are made to run effectively for extended periods of time without seeing appreciable performance deterioration. For applications that need to run continuously, this is crucial.
Ease of Use:
By combining all necessary components for an AC to DC conversion into one unit, the GBU6M streamlines circuit design. As a result, the power supply circuit requires fewer components. Because there are fewer possible sources of failure, reliability is increased and overall costs are decreased.
Heat Dissipation:
To help with heat dissipation, the GBU6M package typically comes with a metal base or mounting surface. This feature allows the rectifier to handle high currents without overheating, ensuring stable operation under varying load conditions.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Compared to alternative rectification methods or individual diode assemblies, the GBU6M can offer cost savings due to its integrated design and high efficiency, providing good value for applications requiring AC to DC conversion.
Wide Range of Applications:
Owing to its robust performance and adaptability, GBU6M finds extensive usage across multiple sectors in applications like motor drivers, UPS systems, power supplies, battery chargers, and more. from industrial automation to consumer electronics.
In conclusion, a key component of power electronics is the GBU6M bridge rectifier. It provides a dependable method of converting AC to DC. that satisfies the requirements of current electronic systems and gadgets. The significance of electrical engineering and technology advancements is emphasized by the need to provide effective power distribution and management.
Related Articles
Understanding Rectifiers: How Do They Convert AC to DC?
Bridge Rectifier: Construction, Working, and Applications
2P4M Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR): Pinout and Application
Multimeter Not Reading DC Voltage: How to Fix it?
Comparative Analysis of DC Transmission and AC Power
DC Machine : Construction & Its Principle
Advancing ADC Converters: Innovations and Applications
DC Transmission: Types, Applications & Advantages
MBRS140T3G Diodes: Applications, Features, and Datasheet
Explanation of the Working Principle of Photodiodes
Switching Diodes: Definitions, Principles, Applications, and Future Trends
Capacitor vs Resistor: What's the Differences?
How to Dispose of Capacitors?










