DC to AC Converter:Principle and Applications
In most mini electronic projects, converting DC voltage to AC voltage is a common issue. Typically, we design circuits that take AC input and provide DC output. However, if we need to convert DC to AC, a DC to AC Converter circuit is required. An inverter (converter) is frequently necessary in circuits where DC to AC conversion is not otherwise possible. Therefore, an inverter circuit is used for converting DC to AC.
A converter is a power electronic device used for DC to AC conversion. These devices utilize switching components. The conversion can range from 12V, 24V, 48V to 110V, 120V, 220V, 230V, 240V with supply frequencies of 50Hz/60Hz. To better understand this concept, here is a simple 12V DC to 220V AC Converter circuit designed for DC to AC conversion.
What is a DC to AC Converter?
DC to AC Converters are mainly designed to change a DC power supply to an AC power supply. In this context, the DC power supply is comparatively stable and provides a positive voltage source, whereas AC oscillates around a 0V base stage, typically in a sinusoidal or square mode.
The common inverter technology used in electronics converts a voltage source from a battery into an AC signal. Generally, they operate with 12 volts and are commonly used in applications like automotive, lead-acid technology, photovoltaic cells, etc.
A simple circuit used for an inverter includes a transformer coil system and a switch. A typical transformer can be connected to the DC signal’s input through a switch that oscillates back and forth quickly. Due to the bi-directional current flow in the primary coil of the transformer, an alternating current signal is produced as output throughout the secondary coils.
How to Make a DC to AC Converter?
The DC to AC Converter Circuit using Transistors is shown below. The primary function of an inverter circuit is to generate oscillations with the specified DC and apply these to the transformer’s primary winding, increasing the current. This primary voltage is then stepped up to a high voltage based on the number of twists in the primary and secondary coils.
The circuit diagram of a 12V DC to 220V AC Converter can be built using simple transistors. This circuit can power lamps up to 35 watts, although it can be designed to drive more powerful loads by utilizing more MOSFETs.
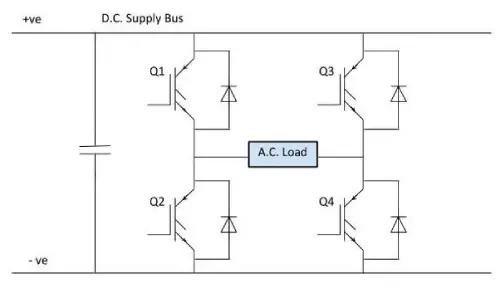
The inverter used in this circuit can generate a square wave and is suitable for devices that do not require a pure AC sine wave.
The components needed to build a DC to AC Converter circuit mainly include a 12V battery, 2N2222 transistors, two MOSFET IRF 630s, two 2.2µF capacitors, two 12k resistors, two 680 ohm resistors, and a center-tapped step-up transformer.
Circuit Working of DC to AC Converter
The DC to AC Converter circuit can be divided into three sections: amplifier, transistor, and oscillator. For an AC supply frequency of 50Hz, a 50Hz oscillator is used. This is achieved by designing an astable multivibrator, which generates a 50Hz square wave signal. The oscillator can be formed using resistors R1, R2, R3, R4, capacitors C1 and C2, and transistors T2 and T3.
Each transistor generates square waves (inverting), and the frequency is determined by the resistor and capacitor values. The frequency formula for the generated square wave with the astable multivibrator is F = 1/(1.38 * R2 * C1).
The oscillator's inverting signals are amplified by the two Power MOSFETs, T1 and T4, and these signals are supplied to the step-up transformer, with its center tap connected to 12V DC.
Disadvantage of DC to AC Converter
The Disadvantage of DC to AC Converter include the following:
The use of transistors can reduce the circuit efficiency.
Switching transistors can cause crossover distortion in the output signal. This limitation can be mitigated to some extent by using biasing diodes.
DC to AC Converter Applications
The applications of DC to AC Converter circuits include the following:
- DC to AC converters are used in vehicles to charge their batteries.
- These circuits are mainly used for driving low-power AC motors and are utilized in solar power systems.
In conclusion, DC to AC converters can be employed in DC transmission lines for transmitting power to loads. They are also used in uninterruptible power supplies to convert direct current to alternating current. Additionally, converters find applications in industries where consistency is critical.
Why Do We Require Changing from DC to AC?
Most vehicles use a 12V battery for power, though some may use a 24V battery. It is crucial to know the vehicle's voltage because the inverter's voltage rating must match the battery's voltage.
A battery provides DC power, meaning the current flows continuously from the battery's negative terminal to the positive terminal in a single direction. While DC is very useful, batteries typically provide low voltage DC power. Many devices require more power to function correctly than what DC alone can offer.
A DC to AC Converter increases the DC voltage and converts it into AC before supplying it to a device. Initially, these converters were designed to convert AC to DC. However, because these converters can work in reverse to achieve the opposite effect, they are also called inverters.
Related Articles
What is Analog to Digital Converter & How it works
Buck vs Boost Converter: Everything You Need to Know










