What Steering Angle Sensor is :Principle,Features and Applications
Currently, most vehicles are equipped with ESC (Electronic Stability Control) for overall security. ESC comprises a series of sensors that work with a computer to enhance vehicle stability by detecting and reducing traction loss. Key sensors in the ESC system include the wheel speed sensor, yaw rate sensor, steering angle sensor, and lateral acceleration sensor. These sensors depend on each other to provide precise data to the ESC module, connecting the vehicle’s steering wheel to the wheels to control turning speed and traction. Modern vehicles often feature systems such as Electric Power Steering (EPS), Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), Variable Effort Power Steering, and Lane Keep Assist (LKA), which all rely on accurate data from the steering angle sensor. This article offers an overview of the steering angle sensor (SAS), its operation, and its applications.
What is a Steering Angle sensor?
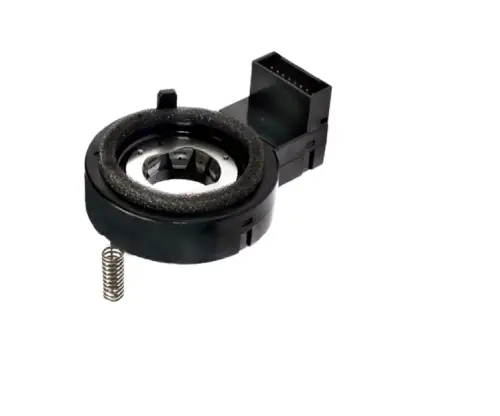

A steering angle sensor in a vehicle acts as a communication link between the vehicle’s computer system and the steering wheel. These sensors are crucial for modern vehicle security, aiding in maintaining the stability and control of the vehicle.
This sensor measures the position, angle, and speed of the steering wheel's turn. It is installed in the vehicle’s steering column to ensure data accuracy and validation. Typically, the steering control program requires signals from two sensors to confirm the steering wheel's position. These sensors usually operate on magnetic, inductive, or optical principles.
Steering Angle Sensor Diagram
The steering angle sensor features a slit disc that rotates with the steering wheel, along with a set of photo interrupters. This sensor is attached to the assembly of the turn signal switch, which detects the direction and angle of the steering rotation.
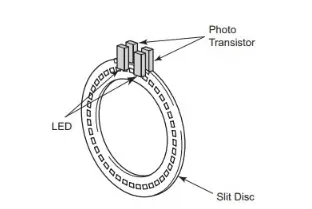
Each photo interrupter consists of an LED and a photo transistor positioned facing each other. The sensor converts changes in light irradiation between these two elements into ON/OFF signals. As the slit disc rotates between the phototransistor and LED pair of photo interrupters, it modulates the light transmission between them.
When the steering wheel operates, the slit disc rotates with the wheel, blocking and allowing light transmission between the two elements. The photo interrupters detect these changes, and the suspension control ECU determines the steering direction and angle based on the output variations. If the steering wheel's turning angle is large and the wheel speed exceeds a set value, the ECU increases the damping power.
Steering Angle Sensor Working Principle
The steering angle sensor operates by determining the direction in which the driver intends to steer and aligning the steering wheel with the vehicle's wheels. This sensor is installed in the steering column, typically as part of a single unit that includes multiple sensors for accuracy, diagnostics, and redundancy.
The steering angle sensor also provides critical information about the speed at which the steering wheel is being turned. During low-speed maneuvers, the steering wheel is often rotated very quickly, which is not typical at highway speeds. If the driver rotates the wheel rapidly while driving at highway speeds, the ESC interprets this as an indication that the vehicle may have lost control.
Conflicting Steering Reaction
A conflicting steering reaction is another indication of a faulty sensor. This issue is common when the wheel position causes the vehicle's steering to feel unusually light or heavy on one side.
Stability Control Loss
A loss of stability control can also indicate a defective sensor. Systems such as electronic stability control, active steering, and traction control may malfunction as a result.
Functions
The steering angle sensor monitors the position and movement of the vehicle’s steering wheel. It provides essential information for various systems within the vehicle, including the adaptive cruise control system, stability control system, and lane departure warning system. The functions of the steering angle sensor are discussed below.
Traction Control
SAS data aids in controlling traction by determining whether there is understeer or oversteer, enabling the traction control system to make necessary adjustments.
Stability Control
The SAS is a crucial component of the vehicle's electronic stability control system. It continuously measures and reports the position and angle of the steering wheel to the vehicle's onboard computer.
Yaw Rate & Lateral Acceleration Sensors
The SAS data is combined with information from yaw rate and lateral acceleration sensors to determine the vehicle's actual direction and movement. This helps the stability control system respond appropriately to sudden changes in steering or road conditions.
SAS Calibration
The steering angle sensor calibration is a crucial step for the proper functioning of ESC and ADAS systems. Calibration ensures precise measurements by accounting for real-world variables such as alignment issues, tire wear, or road curvature. Without proper calibration, ADAS might misinterpret steering inputs, leading to inappropriate vehicle reactions or false warnings.
Calibration of the SAS involves adjusting or resetting the sensor to accurately detect the steering angle and provide correct and consistent information to the vehicle's systems.
Under What Conditions is it Necessary to Calibrate the Steering Angle?
Calibration of the vehicle’s steering angle is required to ensure that the wheels are properly aligned and that the vehicle stays straight on the road. It is essential to calibrate the steering angle under the following conditions:
After the Alignment of the Wheel
Whenever the vehicle's wheels are aligned, it is essential to calibrate the steering angle to ensure the vehicle's path is straight.
After Replacing the SAS
If the SAS fails or needs to be replaced, the new sensor must be calibrated to provide accurate data for the vehicle's stability control system.
After Steering Components Replacement or Suspension
If steering components such as ball joints, tie rods, or control arms are replaced, the SAS needs to be calibrated to ensure the wheels remain properly aligned.
After a Collision
If the vehicle has been in a crash, it is crucial to calibrate the steering angle to ensure the vehicle can drive straight.
SAS calibration is necessary whenever there is a change in wheel alignment or steering components. During the calibration process, manufacturers must follow calibration guidelines to ensure the standard is properly executed.
How to Calibrate SAS?
The process of calibrating the SAS varies depending on the model and brand of the vehicle. Here is a general guide on the calibration process of a steering angle sensor.
Connect the Scanner Tool to the Car
First, connect the scanner to the OBD-II port of the vehicle and select the appropriate function for calibrating the SAS.
Place the Steering Wheel of the Vehicle
Ensure the steering wheel is centered and the wheels are pointing straight ahead. Follow the prompts on the scan tool to initiate the calibration procedure. Some vehicles may require rotating the steering wheel in a specific manner or driving in a straight line at a certain speed.
Completion Procedure
Once the calibration process is complete, the scan tool will indicate whether the sensor calibration was successful. If successful, disconnect the scan tool and test drive the vehicle to ensure the steering is functioning correctly.
There are various tools for calibrating this sensor, including automotive scan tools, wheel alignment equipment, turntable wheel chocks, torque wrenches, iSmartLink D01, and iSmartIMMO 801.
Characteristics
The characteristics of the steering angle sensor include the following:
- The steering angle sensor (SAS) is based on Giant Magnetoresistance technology and provides a complete steering-angle value across the entire steering-angle range.
- The sensor outputs the exact angle in the measurement range immediately after ignition-on.
- Steering wheel movement is not necessary even after disconnection and reconnection of the power supply.
- It does not require a standby current.
- Steering angle and steering-angle velocity are made available through the CAN interface.
- In safety systems, sensor-internal plausibility tests and special self-diagnostic functions allow the use of this sensor.
- The sensor also permits the integration of a second microprocessor for security-related applications.
How to Reset Steering Angle Sensor without Scanner?
To reset the SAS without a scanner, you need to perform a self-calibration process. This process varies based on the vehicle model, but it generally involves the following steps:
- Find a level surface to park your vehicle on.
- Turn the ignition to the ON position, but do not start the engine.
- Turn the steering wheel fully to the left and then fully to the right.
- Repeat the third step three times.
- Turn the ignition to the OFF position.
This process should reset the SAS. If you still encounter issues, you may need to take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis or repair.
Steering Angle Sensor Role in Vehicle Security
Steering angle sensors play a crucial role in modern vehicle security by contributing to vehicle stability and control.
ESC (Electronic Stability Control)
These systems utilize data from the SAS to detect instances where the driver loses control of steering. They automatically apply brakes to help steer the vehicle in the intended direction. By monitoring the vehicle’s steering angle and comparing it to the actual lane, electronic stability control identifies situations where the intended path differs from the actual one. This typically occurs during sudden maneuvers or on slippery surfaces. When this happens, electronic stability control intervenes by selectively applying brakes to specific wheels, aiding in vehicle stability and reducing the risk of skidding or spinning out of control.
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
ADAS technologies use steering angle sensors to monitor the driver’s intended steering inputs and compare them with the vehicle’s actual movement. For example, if the vehicle begins to drift from its lane without signaling, the lane-keeping assist system uses steering angle information to determine corrective action, gently guiding the vehicle back into the correct lane. Additionally, if the sensor data indicates that the driver is steering towards a detected vehicle in the blind spot, the system alerts the driver. This alert may be visual, such as flashing lights in the side-view mirror, or audible.
Autonomous Driving
Steering angle sensors are crucial for the advancement of autonomous driving. In the future, as self-driving cars navigate roads safely without human intervention, they rely heavily on precise and continuous steering angle data. This data helps autonomous vehicles accurately plan routes, stay within lanes, and navigate consistently, contributing to a safer and more efficient transportation system.
Applications/Uses
The applications or uses of the steering angle sensor include the following:
- The steering angle sensor (SAS) measures the position angle and rate of steering wheel rotation.
- It determines the driver's intended steering direction to align the steering wheel with the vehicle's wheels.
- This sensor is a crucial component of a vehicle's safety system, transmitting data on steering wheel angle, turning speed, and other essential parameters to the vehicle's computer system.
- It monitors steering inputs by detecting the position and rotational speed of the steering wheel.
- The sensor provides critical information about the condition of the steering system to the vehicle.
- Steering angle sensors are integral to various ADAS functions, ranging from blind-spot detection to autonomous driving.
- It plays a vital role in the ECS (Electronic Stability Control) of the vehicle.
This overview highlights the steering angle sensor, its function, and its diverse applications. Installed in the vehicle's steering column, it measures the steering wheel's position angle and rotation speed, providing validation and redundancy through multiple sensors.
Here's a question for you: What are the different sensors used in automobiles?
Related Articles
What is Optical Sensor ? Overview and Applications
What are Wireless Sensor Networks : All Explained










