What Is a Power Inverter? Function & Applications
What Is a Power Inverter?
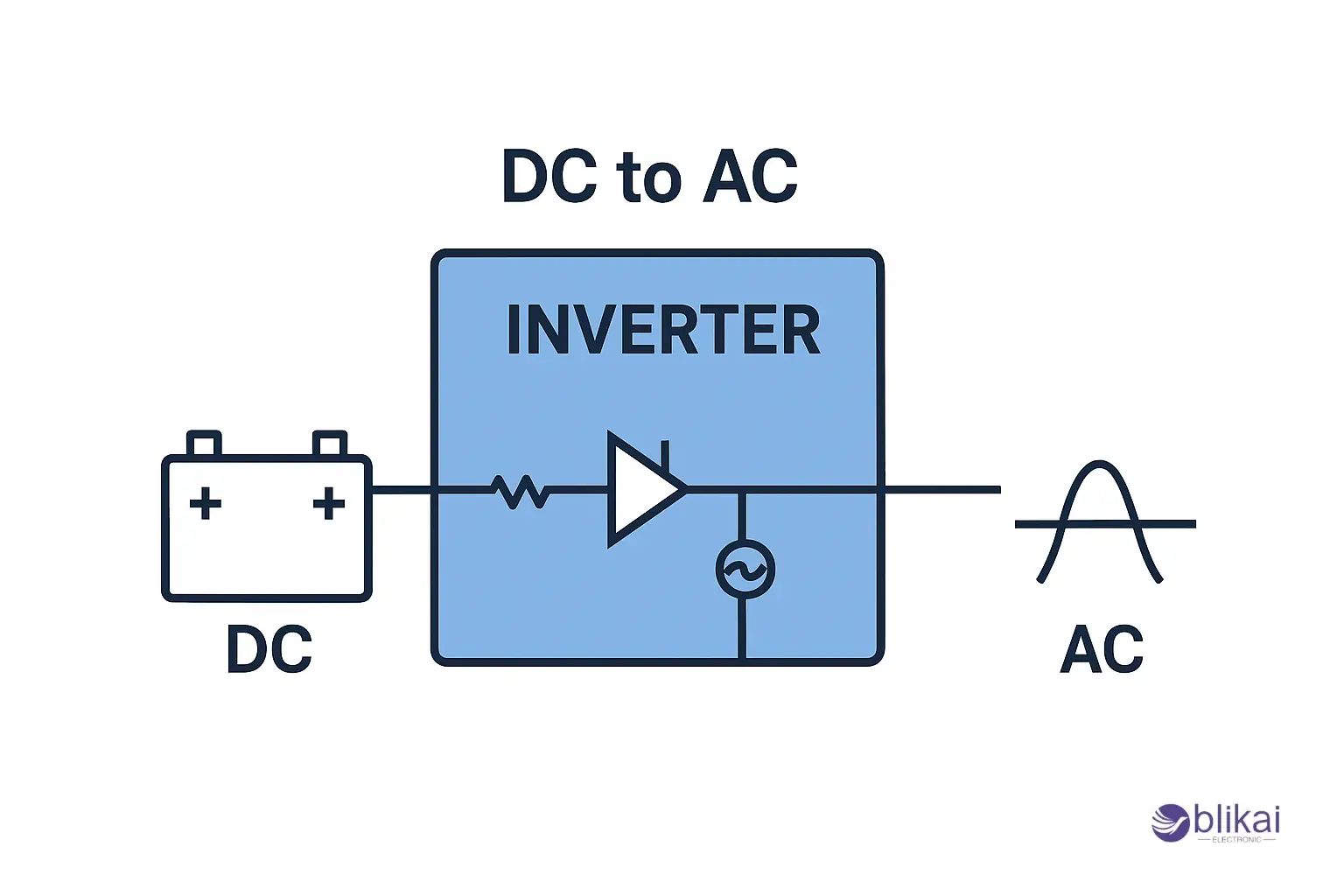
The power inverter is an electronic appliance that changes direct current (DC) into other types of current (AC), which is the form of electricity used by most home and industrial appliances. The power inverters are a good and effective source of power as they convert stored DC power to useful AC power. They give it the capability to have devices operated safely and efficiently, and resist the alteration of important electronics due to changes in voltage or frequency.
How Does a Power Inverter Work?
The Basic Conversion Process: DC to AC
A power inverter starts its operation by changing the direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). Batteries, solar panels or other energy storage systems become the source of the DC power and a stable supply of current in one direction is naturally generated. By contrast, the vast majority of domestic and industrial equipment operates using AC power, which is a periodic alternating power source, usually at 50 or 60 Hz, depending on the area. Electronic circuits are used in the inverter to rapidly switch the DC voltage on and off to make an AC waveform. This is referred to as inversion. Transistors or MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effects Transistors) are usually used to regulate the flow of electricity in order to facilitate easy conversion of DC to AC.
Generation of the AC Waveform
The second process will be in the generation of the actual AC waveform. Inverters have two predominant types of waveforms, which include the pure sine and modified sine waveforms.
- Pure Sine Wave inverters produce a smooth, clean AC signal that is close to the power produced on the electric grid. This waveform is also suitable for sensitive electronics such as computers, medical equipment and audio systems, as it provides stable and high-quality power.
- The Sine Wave inverters, however, are modified to generate a step-like waveform, which is not as smooth. Even though such a type of waveform is tolerable to most of the common appliances, such as lights, fans and refrigerators, it may result in the inconvenience of other appliances that are expected to be powered by uniform voltage and frequency, as it may result in increased inefficiencies and even damage in the long term.
Voltage Regulation and Frequency Control
The vital point concerning the work of an inverter is the possibility of its regulation of both the voltage and the frequency of the AC output. The inverters are usually equipped with voltage regulation to match the output voltage with the needs of the load that is connected to them. An example of this is in the case of an illustration of a 12 V DC to 120 V AC inverter, the device will ensure that the output power is at the right frequency, either 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on the location.
What Are the Types of Power Inverters?
Pure Sine Wave Inverters
The pure sine wave inverters are stated to be of the best quality inverters as they have a clean and smooth waveform that is much closer to the AC power that the electrical grid uses. This has made pure sine wave inverters the most appropriate to energize sensitive electronic devices, such as computers, medical devices and high-end music players. The waveform is smooth to ensure the integrity and efficiency of equipment, which is dependent on constant power, avoiding problems like electrical noise, overheating and long-term damage. Pure sine wave inverters are costlier than their counterparts, but offer the best performance and safety of high-tech appliances and electronics and are thus a better choice for users who require reliable and efficient power.
Modified Sine Wave Inverters
Another less expensive alternative to the pure sine wave inverters is the modified sine wave inverters. They produce a stepped waveform that is close to an AC waveform; however, not as smooth as a pure sine wave. Although they are suitable in most of the appliances at home, such as lights, fans and fridges, they may cause problems when connecting them to sensitive electronics or even those with motors that need a constant supply of current.
Hybrid Inverters
A hybrid inverter is a solar inverter and a battery charger in one, and therefore is another natural element of a solar energy system with storage. Hybrid inverters are multifunctional in converting DC power supplied by solar panels into AC power that is utilized in the house; besides that, the hybrids control the storage and distribution of energy in batteries. This is what makes them suitable for users who wish to save the surplus energy produced throughout the day to be used during the night or in the case of a power failure. The higher functionality of hybrid inverters compared to pure sine wave and modified sine wave inverters has frequently made them costly, although hybrid inverters are necessary in off-grid systems or in solar installations where storage of energy is required.
Square Wave Inverters
The least efficient and least expensive kind of power inverter is called a square wave inverter, which is also the least efficient and produces the poorest quality output. The resultant of these inverters is a square-like waveform, which is highly unlike the continuous AC waveforms that pure or modified sine wave inverters offer. Although simple devices like small motors and small devices can be powered using the square wave inverters, they cannot be applied to devices that have a motor that needs a more stable power connection.
Off-Grid Inverters
Off-grid inverters are designed to operate in off-grid power plants, i.e., in remote locations or locations not served by the main electrical grid. These inverters convert DC power to AC power to be used in homes or businesses by converting the DC power from batteries or solar panels. The off-grid inverters can be primarily used together with battery banks and can also perform battery charging and DC-AC conversion. A high number of off-grid inverters are hybrid inverters and can thus store and use solar energy efficiently, and thus are a very good option to use in a renewable energy application.
What Are the Applications of Power Inverters?
Solar Power Systems
The DC produced by the solar panels in a solar system is then converted to AC with the help of inverters, which homes and businesses can use. This shall enable domestic appliances such as light, refrigerators and computers to run using solar energy.
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Systems
UPS systems that have power inverters will ensure the continued use of certain important gadgets like computers and servers in case of power breakdowns. The DC power stored in batteries is transformed to AC through the inverter that is employed to supply power whenever the grid is out.
Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Hybrid Vehicles
The power inverters in electric automobiles (EVs) and hybrids receive the DC power of the battery and transform it into power (AC power) and supply it to the electric motor. Inverters are also used in hybrid cars to handle energy between the battery and the gasoline engine, which enhances fuel economy and car performance, particularly in the case of energy transition.
Remote and Off-Grid Power Systems
Power inverters are needed in off-grid power systems because they change DC produced in the solar panels or battery storage into AC, which can be used in everyday activities.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Power Inverters
Advantages
- AC Power Anywhere: A power inverter enables you to have access to AC-powered devices even in cases when only DC sources such as batteries are accessible, and it is very handy to live off-the-grid, on a road trip, on a camping trip, or even during a crisis.
- Supports Renewable Energy Systems: Inverters enable solar and wind energy to be accessible through conversion of DC power to stable AC power, enabling homeowners to cut on energy bills, enhance efficiency and also make renewable energy systems more reliable.
- Backup Powers in Case of Failure: Power inverters, when used together with batteries, will offer reliable reserve power to commonly needed items like lights, communication gadgets, medical equipment, and computers during unforeseen outages of the grid.
- Shields Sensitive Electronics: Quality pure sine wave inverters provide stable high high-quality AC output, which preserves sensitive electronics against voltage variations, electrical noise and distortion of waveforms, which otherwise reduce the life of related devices.
Disadvantages
- Power Loss During Conversion: Power inverters are not one hundred percent efficient; there is a loss of power during the DC to AC conversion process, and so the total system may end up using more power than predicted.
- Greater Expenditure on Pure Sine Wave Models: Pure sine wave inverters, which are also recommended in cases of sensitive electronics, are much more expensive than modified sine wave units and do not represent a financial option in low-end applications.
- Stable Battery Source: An inverter needs a stable DC source of power. When the battery bank is weak or small, the inverter will not be able to provide continuous performance and this is particularly in the case of high-load appliances.
- Possible Interference With Some Equipment: Modified sine wave inverter can hum or lead to lower efficiency or even breakage of equipment using motors, compressors or audio equipment, reducing its compatibility with pure sine wave units.
How to Use a Power Inverter
- Attach the inverter to a suitable DC power supply. Ensure the DC source has been connected to a compatible DC source, e.g., battery or solar panel, with the same voltage and capacity.
- Consume good and well-rated cables and fix all connections firmly to avoid overheating and also electrical problems.
- The first thing you need to do is turn on the inverter before you can insert your AC devices, so that the power does not spike.
- Test the inverter wattage capacity to ensure that the total load is not more than the inverter capacity.
- Put the inverter where there is free air circulation in order to avoid overheating the inverter.
- To ensure that the voltage of the battery is not excessively low to cause deep discharge and damage the battery, measure the voltage regularly.
- It should never be forgotten to turn off the inverter and disconnect it from the power source after its use in order to preserve the battery life and prevent unnecessary power wastage.
Conclusion
The power inverter is a necessary tool that enables the transformation of DC electricity from batteries or renewable sources to provide useful AC power to serve a large variety of residential, commercial, and industrial applications. By ensuring the reliability and safety of worked devices, inverters give them dependable electricity, either in the form of delicate electronics or heavy-duty power gear.
FAQ
Is it possible to power a power converter for all appliances in the home?
Most appliances, and more sensitive electronics, like medical equipment or high-end audio, have pure sine wave inverter compatibility to be able to use safely and without damage.
What is the correct selection of the inverter to use in solar power?
Take into account your overall AC load, battery type, and waveform needs. Pure sine wave inverters are suitable for sensitive electronics, and modified sine wave inverters can be suitable for basic appliances.
Can a power inverter be powered during a power outage?
Backup AC will be provided by a power inverter, which will be in a position to store a battery or even a solar store; therefore, in case the grid underperforms, the critical devices can still be used.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.
Electromagnetic Shielding for Electronics: Top Materials & Component Guide
LR14 Battery Guide: Applications, Specs, Lifespan & Troubleshooting
How an Electromagnetic Field Detector Works in Electronics
What is Battery Monitor & How to Use It
SMD Capacitor: Types, Characteristics & Applications
48V Battery: Power, Efficiency & Applications
Passive Infrared Detector: Working Principle, Types & Applications
21700 Battery: Power, Performance & Applications
5V Battery: Functions, Types & Common Applications
UB1250 Battery: Specifications, Lifespan & Replacement Guide










