RF Receiver Module Guide: Types, Applications & How It Works
Introduction to RF Receiver Modules
Receiving and decoding radio signals, an RF (Radio Frequency) receiver module is an electronic device that communicates over the air via a radio signal. The modules play a crucial role in wireless communicating networks, and they are operative throughout distinct activities such as remote controls, Internet of Things gadgets, and telemetry tools. Be its hobby electronics, embedded design requires the ability to receive wireless data, RF receiver modules cost and easy to integrate.
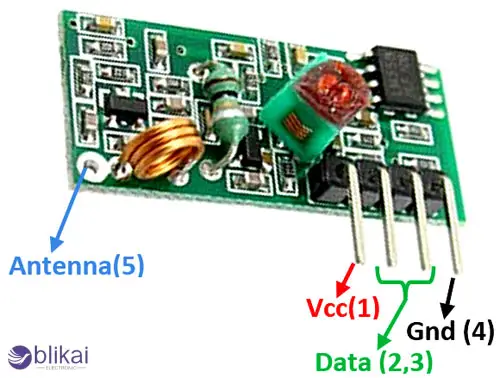
How RF Receiver Modules Work
RF receiver modules are used to receive electromagnetic waves that are broadcast by an RF transmitter. Generally, the module will also have an antenna to pick up the radio wave, an amplifier to improve weak inputs, a demodulator to recover the original information contained in the modulated wave and a decoder to bring it out in usable digital form. They are modules operating at differing frequencies like 315 MHz, 433 MHz, 868 MHz and 2.4 GHz.
There are two main types of signal reception:
- Analog Reception: Suitable for audio and broadcast systems
- Digital Reception: Ideal for data transmission in wireless control systems
Types of RF Receiver Modules
Superheterodyne RF Receiver
This type applies a frequency mixer to an IF of fixed frequency, which enhances selectivity and sensitivity of the received signal. These receivers are the most suitable in long-range applications and where there might be interference with the signals.
Superregenerative RF Receiver
These are simpler and less expensive modules that use regenerative feedback to detect signals. They consume less power but are more prone to interference and have shorter range compared to superheterodyne receivers.
ASK, FSK, and OOK Receiver Modules
ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying): Easy to implement, good for low-data-rate applications
FSK (Frequency Shift Keying): More robust against noise, better for high-reliability systems
OOK (On-Off Keying): A form of ASK with simple encoding, ideal for remote controls
433 MHz and 2.4 GHz Receiver Modules
433 MHz: Widely used in short-range devices like remote keys and wireless alarms
2.4 GHz: Supports higher data rates, used in Bluetooth and Wi-Fi systems, but is more affected by obstacles and interference
Key Features to Consider When Choosing an RF Receiver
The following specifications should be taken into consideration when choosing an RF receiver module:
- Operating Frequency: Must match the transmitter’s frequency (e.g., 433 MHz)
- Sensitivity: Determines how weak a signal it can receive
- Data Rate: Affects how quickly information is received
- Range: Depending on antenna design, power, and frequency
- Supply Voltage and Current: Must match your system requirements
- Modulation Type: Must be compatible with the transmitter
- Interference Resistance: Better shielding and filtering provide stable performance
Applications of RF Receiver Modules
RF receivers are used in a wide variety of electronic systems:
Remote Controls and Keyless Entry Systems
Safe RF Applications The remote control of such devices as garage doors, electric gates, ceiling fans, and lights uses RF receivers in this manner. They form a core part of keyless entry systems in automotive electronics, where a user can unlock or start vehicles without using any wires. These systems are usually 315 MHz or 433 MHz ASK or OOK modulated receiver modules using a robust and low-cost wireless connection, which can range between short and medium distances.
Wireless Security and Alarm Systems
RF communication is of great importance in home and commercial security systems. The wireless PIR (passive infrared) sensor, the magnetic door/ window sensor and panic buttons can be used with receiver modules. The sensors will transmit a signal to the central alarm panel through an RF transmitter when motion or a breach is detected, after which the signal will be received and processed by the RF receiver module. These systems provide easy installation, and there is little wiring.
Smart Home and Automation Devices
Smart home technology utilizes RF receivers to not only control and monitor other equipment, such as lights, smart plugs, blinds, garage doors, thermostats, and many more. With RF modules, the systems can be used without being dependent on the Wi-Fi or even the internet, and this is advantageous when it comes to standalone systems or when the Wi-Fi is unreliable. Smart switches that use RF are able to communicate with a central hub or controller in order to automatically control the operation by time, motion or user input.
Industrial Automation and Telemetry
RF receiver modules are used in an industrial setting where the modules are utilized to receive and control wireless data acquisition. RF transmitters on sensors can be used to monitor temperature, humidity, pressure, or the state of a machine and transmit the data wirelessly to the central monitoring point. The RF modules are also used in latent control of assembled equipment such as water pumps, valves and generators, particularly in remote or dangerous locations where wire communication will not be feasible when used on telemetry systems.
Internet of Things (IoT) Applications
IoT operates under a wireless connection where devices are interconnected. Smart agriculture (e.g., soil moisture sensors), asset tracking, logistics, smart meters (utilities), and environmental monitoring make use of an RF receiver module. 433 MHz or 868 MHz are modules that operate at low power, with long-range communication of sensor nodes. RF receivers are combined with low-power MCUs to capture and interpret the sensor information that may be transmitted to the cloud or local gateway.
Wireless Audio and Video Transmission
Audio and video transmission systems, RF receivers may also be the audio and video in wireless microphones and baby monitors, wireless surveillance cameras and remote AV senders. Audio or video signals being high bandwidth may involve the application of higher frequency modules, such as 2.4 GHz. The source sends the signal to the receiver, who relays it to a speaker, recording device or monitor without the use of cables.
Toys and Consumer Gadgets
Remote-controlled (RC) toys like cars, drones, and helicopters use RF receiver modules in perceiving instructions sent through the handheld gadget. These are receivers that convert the signal from the RF to control motors and servos. In other wearable technology, such as fitness trackers or smartwatches, the RF modules may also be used to synchronize data wirelessly with a smartphone or computer.
Example Circuits and Module Integration
Integrating an RF receiver module is relatively straightforward. Here's what a basic setup includes:
Circuit Diagram: The data output of the RF receiver goes to one of the input pins of a microcontroller (e.g., to one of the digital pins of an Arduino).
Microcontroller Programming: The signal heard, decoded data: Simple code listens to the signal and decodes the received data.
Power Supply: Usually 3.3V or 5V, depending on the module
Antenna: A straight wire or helical coil to give the greatest range
Tips:
- Avoid placing the antenna near metal or ground planes
- Keep RF modules away from power supply noise sources
Troubleshooting and Best Practices
When using RF receiver modules, problems like limited range or missed signals may occur. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Check Frequency Match: Ensure your transmitter and receiver operate on the same frequency and modulation.
- Inspect Antenna Setup: A poorly placed or missing antenna drastically reduces range.
- Minimize Interference: Keep RF modules away from motors, relays, or switching regulators.
- Improve Grounding: A solid ground connection improves signal stability.
- Use Decoupling Capacitors: These help reduce noise in power supply lines.
Conclusion
The RF receiver modules are cheap and yet potent devices that allow us to incorporate any and every electronic project with them wirelessly. They can be applied to anything, including low-level applications like simple remote controls and high-level applications such as IoT systems, and that is why they are a splendid selection when it comes to the use and application to hobbyists and professionals. This comprehension of various fronts, working principles and application requirements will help you make the correct decision regarding which RF receiver module to choose in order to have a successful system with quality wireless functionality.
FAQs
Can I use any RF receiver with any transmitter?
Not always. The frequency, modulation type and data rate have to be the same between the transmitter and the receiver.
What is the maximum range of a typical RF receiver module?
Distance ranges vary between a few meters (in case of simple 433 MHz modules) to several kilometers (in case of long-range modules with LoRa or superheterodyne radio with external antenna).
What’s the difference between 433 MHz and 2.4 GHz RF modules?
The 433 MHz modules will have a better ability to penetrate obstacles and distance at slower data rates, whereas the 2.4 GHz ones will be more suitable for transference of data close packed, like video or Wi-Fi.
Some images are sourced online. Please contact us for removal if any copyright concerns arise.
How to Dispose of Capacitors?
Polyester vs Polypropylene Capacitors: Explained
Air Conditioner Capacitor Basics: What You Need to Know
Exploring Electronic Components - Their Varieties, Roles, and Future Directions
ESP32 vs ESP8266: Which One Should You Choose?
Difference Between Serial and Parallel Communication
What are Audio Transformers for?
Multimeter Not Working: But How to Fix it?
Semaphore in Embedded System
Different Types of Mixers










