RG213 vs LMR400:Which is Your Best Choice
Both RG213 and LMR400 are types of coaxial cables widely used across various applications. While LMR400 and RG213 share many similarities, there are key differences that set them apart. These distinctions can significantly influence the choice of cable for specific electrical requirements. This article will delve into the detailed comparison of LMR400 versus RG213, elucidating the disparities between the two.
What is LMR400?
LMR400, manufactured by Times Microwave, is engineered to offer flexibility, minimal loss, shielding against RF interference, and durability. Its design allows for the tightest bend radius among cables of similar dimensions and performance while boasting the lowest loss compared to its counterparts. With an exceptional RF protection rating of 90%, it is well-suited for environments with high levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI). This versatile cable is suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. Utilize Times Microwave's LMR400 cable to establish connections for devices requiring low-loss rerouted wiring, such as WLL, GPS, LMR, WLAN, WISP, WiMax, SCADA, and mobile antennas. The LMR-400 serves as a direct replacement for RG-8 cables.
Overview of RG213
The RG213 coaxial cable, designated RG213/U, is a flexible cable offered by Pasternack. This 50 Ohm coaxial cable features a PE dielectric material. Encased in a PVC jacket with a thickness of 0.405, the RG213 coaxial cable comprises a single shield. With a maximum frequency rating of one GHz, this cable exhibits a 9 dB attenuation at 1 GHz and can handle a maximum power of 190 watts.
Pasternack's RG213 coaxial cables contribute to a vast inventory of over 40,000 RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave components. Worldwide same-day shipping services are available for RG213 cables and other RF components. Additionally, RF cable assemblies crafted from RG213 or other coaxial cables can be swiftly assembled and dispatched on the same day.
LMR400 VS RG213 Features
LMR400 Features:
- Sold per foot
- Cable Type: LMR-400
- Impedance: 50 ohm
- Center Conductor: Bare Copper Covered Aluminum (BCCAI)
- Jacket: Polyethylene (PE)
- Outer Diameter: 0.405 inch
- Suitable for indoor and outdoor use
- Drop-in replacement for RG-8
- Attenuation @ 900 MHz/100 ft: 3.9 dB/100ft
- Attenuation @ 2.4 GHz/100 ft: 6.65 dB/100ft
- Versatile applications, including WLL, GPS, LMR, WLAN, WISP, WiMax, SCADA, Mobile Antennas, requiring easily routed, low-loss RF cable
- Maximum Continuous Length: 1000 FT
RG213 Features:
- Impedance: 50 ohm
- Capacitance: 98 pF/M
- Center Conductor: Strand Bare Copper Wire
- Shield Coverage: 96%
- Minimum Bend Radius: 42mm
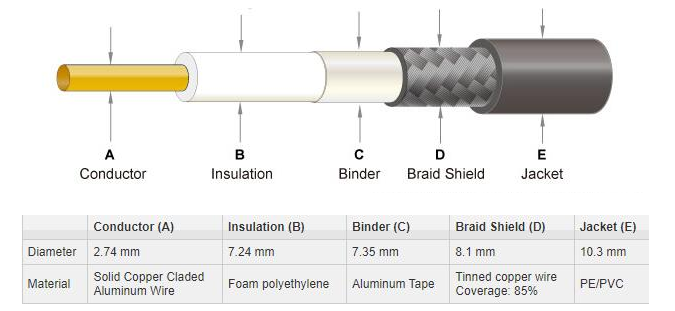
LMR400 VS RG213 Coaxial Cable Structure Illustration
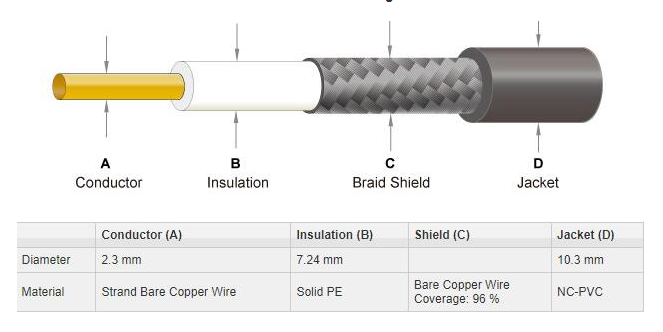
RG213 Structure Figure
LMR400 VS RG213 Frequency
| Frequency | RG213 Loss (Attenuation dB/100ft) | LMR400 Loss (Attenuation dB/100ft) |
| 100 MHz | 2.2 | 1.2 |
| 400 MHz | 4.8 | 2.5 |
| 1000 MHz | 8.2 | 4.1 |
LMR400 VS RG213 Electrical Features
| LMR400 | RG213 | |
| Min. Temperature Rating | -40°C | -40°C |
| Max. Temperature Rating | 75°C | 85°C |
| Max. Voltage | 5,000 | 2,500 |
| Impedance (ohms) | 50 | 50 |
| Capacitance (pF/ft) | 32.2 | 23.9 |
| Max. Freq. (GHz) | 11 | 6 |
LMR400 VS RG213 Specifications
| Generic Name | RG213 | LMR-400 |
| Flex Type | Flexible | Flexible |
| Impedance | 50 Ohm | 50 Ohm |
| Dielectric Type | PE | PE (F) |
| Velocity of Propagation | 66% | 85% |
| Jacket Diameter | 0.405 in | 0.405 in |
| Jacket Material | PVC | PE |
| No. of Shields | 1 | 2 |
| Attenuation at 1 Ghz. | 9 dB | 4.25 dB |
| Power, Max at 1 Ghz. | 190 Watts | 90 dB |
| Frequency, Max | 1 GHz | 6 GHz |
| Max Operating Temperature | 70 deg C | 85 deg C |
| Center Conductor Type | Stranded | Solid |
| Inner Conductor, Number of Strands | 7 | 1 |
| Minimum Bend Radius, Repeated | 1.6 in | 1 in |
| Coax Type | Coax | Coax |
Conclusion of LMR400 VS RG213 Specifications
In the realm of high-end radio frequency antennas, the comparison between LMR400 and RG213 coaxial cables presents two formidable options. Despite their similar dimensions, these cables exhibit distinct constructional variances. A pivotal discrepancy lies in the composition: RG213 features a stranded bare copper center conductor, offering a cost-effective alternative, while LMR400 boasts a solid bare copper-wrapped aluminum conductor, enhancing durability and performance. Moreover, the outer jackets diverge; RG213 utilizes a PVC jacket, whereas LMR400 employs a PE jacket. These jacket materials carry intriguing implications.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) finds widespread use in domestic applications such as pipes, garden hoses, and raincoats, owing to its versatility. Conversely, polyethylene (PE) is prized for its resilience and is employed in diverse products, including bulletproof vests. Consequently, LMR400, with its polyethylene outer jacket, holds an advantage in terms of cable protection. Another notable disparity lies in the shielding conductor: RG213 features a single bare copper braid shield, whereas LMR400 integrates two shields—one aluminum braid and one braided tinned copper. Once again, LMR400 emerges as the superior choice.
LMR400 VS RG213 Applications
LMR400 Applications
- Wireless communication systems
- Drop-in replacement for RG8/9913 air-dielectric type cable
- Short antenna
- Feeder runs
- Easily-routed, low-loss RF cable
- RG213 Applications
- Telecommunications
- Radio communications
- Broadcast
- Computer applications
- Conclusion of LMR400 VS RG213
The RG213 shield comprises a single bare copper braid, whereas the LMR400 shield consists of an aluminum braid and a braided tinned copper braid. These cables primarily differ in terms of maximum voltage rating, capacitance, and maximum frequency within their electrical specifications.
Signal loss stems from various sources, but in this context, the conductors play a significant role in attenuation differences. A larger conductor results in lower attenuation. Due to LMR400's larger conductor compared to RG213, RG213 experiences higher signal loss.
RG213 coaxial cable finds application in diverse military and commercial sectors, including radio communications, high-performance electrical and data transmission, broadcast, and computer applications. It serves well in scenarios requiring low signal loss and high operating voltages, and it can be utilized as an antenna feed cable when necessary. Moreover, it exhibits reliability in heat-sensitive environments, boasting a maximum temperature rating of 75°Celsius. The military counterpart of RG213 is the M17/74-RG213.
Designed as a drop-in replacement for RG8/9913 air-dielectric type cable and suitable for short antennas and feeder runs in wireless communication systems, LMR400 also meets the demands of applications necessitating low-loss, easily routed RF connections.
Manufacturer of LMR400
Times Microwave Systems is renowned as a leader in the innovation and production of coaxial transmission lines. Their portfolio includes a diverse range of RF and microwave transmission line solutions tailored for military, aerospace, wireless communications, and industrial applications. Their engineering expertise and extensive manufacturing capabilities are highly respected in the industry. With production facilities in the United States and China, they are capable of serving specialized applications with stringent performance requirements as well as high-volume commercial applications across frequencies from a few kHz to 110 GHz. Since 2009, Times Microwave Systems has been backed by the resources of Amphenol, a global leader in the production of electrical, electronic, and fiber-optic connectors, along with connection systems and specialized coaxial cables.
How to Charge Capacitor Without Resistor?
Variable Capacitors: A Complete Guide
2N3904 vs 2N2222:What You Need to know
Semaphore in Embedded System
What does Comparator Do?
How does the Oscilloscope's X-Y Display Work ?
Transformer Core Faults: Hazards, Causes, Types, Testing, and Remediation
Intelligent Sensors: Definition, Configurations, and Utilizations
Comparing FPGA vs Microcontroller: Optimal for Your Needs?
PC817 Optocoupler: Working & Its Applications [2024 Updated]










