Understanding Thermal Fuse: Function, Applications, and Safety Tips
What is a Thermal Fuse?
A thermal fuse is a safety device intended to prevent overheating of electrical appliances and circuits. It is a non-resettable, single-use switch that interrupts the flow of current when the temperature exceeds its recommended level. This constructed but essential component acts as a safeguard against fire hazards and damage to equipment due to overheating.

Key components and mechanism
The main components of a thermal fuse include:
- Temperature-sensitive material (often a metal alloy)
- Conductive leads
- Insulating body
When the temperature rises over a specific limit, the heat-sensitive material melts, thus breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity.
Difference between thermal fuses and other types of fuses
Different from other types of electrical current limiters, thermal fuses take a cue from temperature. In contrast, circuit breakers or fuses are tripped with electrical overload, and thermal fuses work as one-time series switches. They open the circuit when heat fills the electrical appliance; therefore it doesn't react with current sways in contrast with the sloppy hots. This they do to ensure safety, especially when overheating is the primary concern. Thermal fuses also jumbled that they're not resettable and need replacement after activation; thus, they push sort of a supplied factor before the equipment can take the test of other usages.
The Function of Thermal Fuses
Temperature-sensitive cut-off mechanism
Thermal fuses are designed with a unique temperature-sensitive mechanism that quickly responds to extreme heat. This mechanism commonly comprises a fusible alloy or a spring-loaded contact maintained in place by heat-sensitive materials. After the temperature reaches a specific limit, the fusible alloy melts or the heat-sensitive material softens, so finishing the performance of the fuse to open the circuit.
One-time use nature
Unlike circuit breakers or resettable fuses, thermal fuses are single-use devices. Once they activate and break the circuit, they cannot be reset or reused. This one-time use nature ensures that the device remains in a safe state until a professional can inspect and replace the fuse, addressing the underlying cause of the overheating issue.
Protection against overheating
The most crucial role thermal fuses play is the preservation of equipment or retention of the electrical systems from cases of severe overheating. The thermal fuses act in the cut-off positions, cutting off electrical flows to prevent component damage, fire hazards, and injuries to users, provided only the safe maximum temperature is exceeded. Applied in general protective devices, this term may range from household types of machines to industrial machines.
Preventing electrical fires
Thermal fuses are the last board toward electrical fires. Such auxiliary safety mechanisms fuse into thermal engines merely to function in the event the earlier safety mechanisms on the device fail or when such a device misfires. Once installed, these special fuses cut off the electric circuit depending on the temperature so that it does not go to unsafe levels, resulting in a chance of developing a combustive fire around that particular device. Temperature safety devices have been specifically designed for use in devices where heat generation or high power cost is regarded.
How Does a Thermal Fuse Work?
1. Normal operation: The fuse allows current to flow through the device.
2. Temperature increase: The fuse monitors the heat as the device heats up.
3. Threshold reached: When temperatures exceed the fuse's rating, the internal component will melt.
4. Circuit interruption: The melted material will break the electrical connection and stop current flow.
5. Device shutdown: The appliance or equipment turns off, preventing further heating.
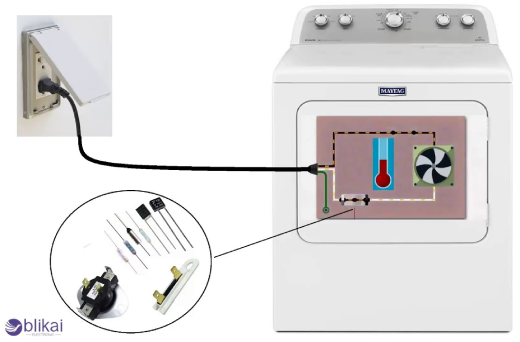
Applications of Thermal Fuses
Household appliances
While they may be small parts, they are crucial in providing a safety guard for appliances against possible risks that may arise due to overheating of home appliances such as hair dryers, coffee makers, and irons. One such example is that of the hair dryer, which is fitted with a thermal fuse to cut it off from the supply line in cases of increased internal temperature that could lead to a fire.
Industrial machinery
The use of thermal fuses within an industrial area becomes a necessity to protect central installations and equipment. These would include thermal fuses located within motors, pumps, and conveyors, where overheating might end in disaster in terms of failures. Their very function is the interruption of power to the machinery before it attains dangerous and fatal temperature settings, thus avoiding expensive damage and hazards in the workplace.
Automotive systems
With modern cars, thermal fuses play a large part in protecting the various electrical components of the assembly. From the engine cooling system to air conditioning units, tearing the fuse ensures the part is operated within the designated temperature range. It becomes more critical in the aspect of defense against battery issues, not to mention sensitive electronic control unit protection.
Electronics and gadgets
Thermal fuses are a significant source of protection for consumer electronics and gadgets. The thermal fuse can cover against damage caused by heat buildup in particulars similar to laptops, smartphones, and gaming consoles. This is of utmost significance in the case of lithium-ion batteries, given the implicit safety pitfalls posed by thermal raw.
HVAC equipment
On HVAC systems, thermal fuses are employed to shut down the system when the temperatures reach a dangerous level. Such fuses are installed in furnaces, air-conditioning equipment, and heat pumps in order to get protection against overheating and fire. Thermal fuses break off power whenever the temperature surpasses a specific safe limit to enhance HVAC machines' safety and efficacy.
Advantages of Using Thermal Fuses
1. Simple and reliable protection against overheating
2. Cost-effective safety solution
3. Compact size allows for easy integration into devices
4. No need for external power or control circuits
5. Helps comply with safety regulations and standards
Selecting the Right Thermal Fuse
Temperature ratings
When it comes to choosing the thermal fuse, temperature rating is one essential factor to be considered. The fuse will operate when it reaches the temperature that blows, cutting off the circuit. Choose a thermal fuse that has a temperature rating above the normal operating temperature of your appliance, if possible, but below the temperature that is likely to cause damage.
Current and voltage considerations
It becomes essential that all current and voltage ratings of a thermal fuse interrupting the circuit meet or exceed the basic requirements of the application. A lower current or voltage may result in premature failure or ineffective protection against failure. This evaluation must include consideration of maximum current and voltage levels that might be expected at the operating conditions and some maximum surge conditions.
Size and form factor
Physical size is always an essential part of choosing a thermal fuse for proper mounting and compatibility with any device. While selecting a fuse, it is always good to remember the type of space available and the mounting arrangements in your device. Miniature fuses may need to be installed in some applications, while others may mount larger sizes. Ensure the fuse can be safely installed and not interfere with the functioning of other components.
Response time
The response time will inform how quickly the thermal fuse will react to a fault where there is overheating. As a rule of thumb, the quicker the response time, the better the protection, while being more prone to nuisance tripping. Consider in your choice of a fuse with an appropriate response time the characteristics of your application and the potential consequences of overheating.
Safety Tips for Using Thermal Fuses
- Proper installation guidelines
- Follow manufacturer instructions carefully
- Ensure adequate placement near heat sources
- Use appropriate mounting methods
- Avoid mechanical stress on the fuse
How to identify a faulty thermal fuse
Signs of a faulty thermal fuse include:
- The device is not turning on
- Intermittent operation
- Burning smell from the appliance
Tips for preventing overheating in devices
- Keep devices clean and free from dust
- Ensure proper ventilation
- Avoid blocking air vents
- Use appliances as intended, and don't overload them
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
- Common issues with thermal fuses
- False tripping due to improper installation
- Failure to trip when needed
- Degradation over time due to repeated heat exposure
Steps to test and replace a thermal fuse
1. Disconnect the device from power
2. Locate the thermal fuse
3. Use a multimeter to check for continuity
4. If there is no continuity, replace the fuse with an identical model
5. Reassemble the device and test for proper operation
Maintenance best practices to ensure longevity and reliability
- Regularly clean devices to prevent dust accumulation
- Inspect for signs of wear or damage
- Replace thermal fuses preventively in critical applications
- Keep devices in well-ventilated areas
Related Articles
How Does a Fuse Work? [Full Guide]
Is a Fuse a Resistor? [Everything Explained]
Circuit Board Repair: Guide for Beginners
Types of Circuit Breakers: Overview and Applications
Discrete Circuit vs Integrated Circuits: What's the Differences?
Best FHP100N07 Replacement MOSFETs for High-Performance Circuits
Microprocessor vs Integrated Circuit:Which One Is Better
What is an Integrated Circuit (IC)? Working, and Types (Guide)
Applications of Circuit Protection: Everything Explained
Isolator vs Circuit Breaker: What's the Differences?
What Is Circuit Protection And Why Is It Important? (Guide)
LM386 Audio Amplifier Circuit: Features, Applications and Datasheet










