What is a Transceiver ?All You Need to Know
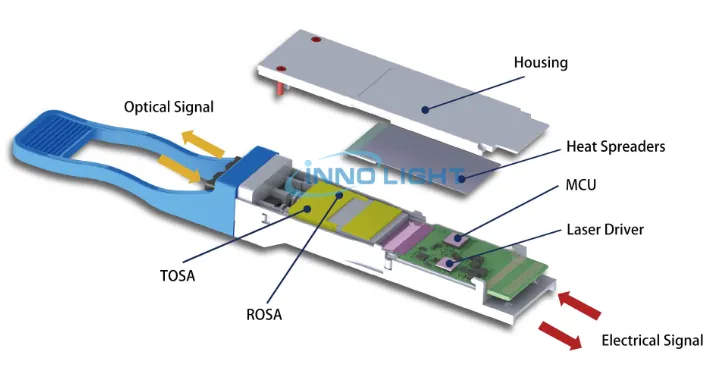
A transceiver embodies a dual-functionality unit housing both a transmitter and a receiver within a singular package. While predominantly associated with wireless communication apparatus, the term extends to encompass transmitter/receiver devices within cable or optical fiber systems.
The primary function of this electronic apparatus is to both transmit and receive diverse signals.
Within local area networks, the transceiver constitutes an integral component of the network interface card. It facilitates the transmission of signals across the network wire while simultaneously detecting electrical signals coursing through the wire. Nevertheless, certain network configurations necessitate an external transceiver.
In wireless communication gadgets such as smartphones and cordless telephones, the transceiver is seamlessly integrated into the mobile device.
What sets apart a transmitter from a transceiver?
A transmitter stands as an individual electronic element responsible for producing a radio frequency (RF) current or radio waves. These waves serve as the medium for transferring data, such as audio, video, and more, within communication systems.
Conversely, a transceiver possesses the capability to both transmit and receive digital signals.
How does a radio transceiver operate?
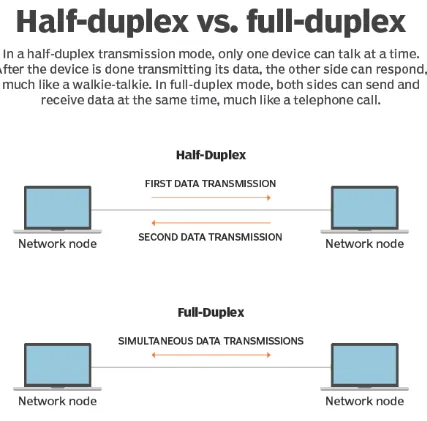
In radio communications, the transceiver can function in either half-duplex or full-duplex mode:
Half-duplex transceivers. These devices have the capability to either transmit or receive signals, but not both simultaneously. This limitation arises because both the transmitter and receiver are linked to the same antenna via an electronic switch. This operational mode is commonly found in ham radios, walkie-talkies, and similar single-frequency devices.
Full-duplex transceivers. In this configuration, the radio transmitter and receiver operate concurrently, enabling transmission and reception to occur on distinct radio frequencies. This mode is prevalent in handheld and mobile two-way radios.
What function do transceivers serve in a wireless communication network?
The role of a transceiver varies depending on its classification. Various types of transceivers are utilized in wireless communication systems:
RF transceivers are integrated into baseband modems and routers to facilitate both analog (over the wire) and digital transmission. They are also instrumental in satellite communications networks.
Optical transceivers harness fiber optic transceiver technology to convert electronic signals into light signals, enabling high-speed transmission.
Ethernet transceivers establish connections between electronic devices within Ethernet circuitry, also known as media access units.
Wireless transceivers amalgamate technologies from Ethernet and RF transponders to enhance Wi-Fi transmission speed.
Delve into the distinctions among macrocell, small cell, and femtocell base stations, or transceivers, in the context of 5G cellular wireless communications in the video provided below.
What Are the Various Types of Transceivers?
Transceivers can be categorized into four primary groups: RF (radio frequency), fiber optic, ethernet, and wireless. Below, we'll explore each category and delve into their specific applications.
RF Transceivers
RF Transceivers enable the transmission of voice or video data without the need for wiring. They find utility in digital transmissions, baseboard modems, and over-the-wire routers. These transceivers accomplish this by converting intermediate frequencies (IF) into radio frequencies (RF). While commonly associated with radios, they are also employed in the transmission and reception of television signals.
Fiber-Optic Transceivers
For those seeking rapid data transmission speeds, fiber-optic transceivers offer an ideal solution. Leveraging the same technology that renders fiber optics swift in their data transmission, these transceivers convert data into light signals. This enables data to travel at the speed of light, with electronic components facilitating signal decoding or encoding as necessary. It's imperative to conduct thorough testing of fiber-optic cables prior to installation.
Ethernet Transceivers
Ethernet transceivers facilitate signal transmission and reception between computers and various electronic devices. Sometimes referred to as media access devices, these products adhere to the stringent standards outlined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Ethernet transceivers serve as the primary physical component of ethernet cables, granting network access, detecting potential collisions, encapsulating digital data, and managing the Ethernet interface.
Wireless Transceivers
A wireless transceiver combines the functionalities of RF and ethernet transceivers. Comprising two main components, the physical layer incorporates a baseband processor and an RF front-end component, while the media access control section integrates the ethernet component. This arrangement enables the transceiver to evade collisions, optimize data flow, and establish connections with wireless links in the vicinity, resulting in noticeable enhancements in transmission speeds.
How to Select and Configure a Transceiver
At this juncture, you likely possess a clearer understanding of the type of transceiver your organization necessitates. However, if uncertainties persist, there's no cause for concern. Simply enlist the assistance of a seasoned professional well-versed in transceiver technology.
Professionals can guide you in devising an optimal telecoms system tailored to your unique requirements by recommending the most suitable transceiver. Moreover, they can aid in seamlessly integrating it into your existing infrastructure.
Choose a technology firm with a wealth of experience in utilizing and configuring transceivers. This ensures that you derive maximum benefit from their expertise.
The Significance of Transceivers
Transceivers undeniably constitute a pivotal element in radio communication operations. Despite society's shift away from traditional radio, transceivers retain their significance in the realm of digital communication.
This indispensable technology facilitates the transmission and reception of the data integral to our daily routines. Nonetheless, given the multitude of transceivers available today, it's imperative to comprehend how this technology functions and the diverse types that remain relevant. This knowledge ensures that you select the appropriate transceiver tailored to your specific needs.
WHAT DISTINGUISHES A TRANSMITTER FROM A TRANSCEIVER?
Despite their apparent similarity, transmitters and transceivers serve distinct functions. Transmitters generate radio frequencies or waves, facilitating the communication of audio and video signals.
However, transmitters solely emit information outward; they lack the capability to receive data. In contrast, transceivers possess the dual capability of both receiving and transmitting information, offering balanced functionality.
WHAT ARE THE UTILITIES OF TRANSCEIVERS?
Transceivers boast a multitude of applications, reflecting the diverse array of transceiver types available. Their specific function is contingent upon their classification. For instance:
RF transceivers: Employed in baseband modems for over-the-wire (analog) data transmissions. They may also find usage in satellite communication networks.
Ethernet transceivers: Employed to interconnect numerous electronic devices within an ethernet circuit.
Optical transceivers: Harness fiber optic technology to convert electronic signals into light signals, facilitating high-speed data transmission.
Wireless transceivers: Resulting from the fusion of ethernet and RF transponders, enhancing the transmission speed of Wi-Fi signals.
The ultimate purpose of your transceiver hinges largely upon its underlying technology, necessitating thorough research prior to procurement.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What Are the Applications of Transceivers?
Transceivers serve a vital function in enabling two-way communication within wireless systems, effortlessly transmitting and receiving audio signals. Tailored to specific uses, transceivers are available in a range of types, encompassing fiber-optic, Ethernet, RF, and wireless variants.
What are Wireless Sensor Networks : All Explained
Networking Solution: Everything You Need to Know
What Is Network Interface Card: Applications and Functions
Network Layer In OSI Model (Fully Explained)
What Is CBB61 Capacitor - Function and Applications
ATMega328P Microcontroller: A Powerful Microcontroller
2N3904 vs 2N2222:What You Need to know
How Does a Single Phase Motor Work?
How To Charge Lead Acid Battery: [Explained]
Regulated vs Unregulated Power Supply: What's the difference?










